1 ...6 7 8 10 11 12 ...17 Naturally such a bonanza of new sites has prompted some revisionism. The uniformity of Harappan culture, necessarily dented by local adaptations to the desert, upland and maritime extremities of such a vast area, is no longer taken for granted. Theories based upon it about the existence of a strong central authority, a pervasive administration and a heavily regulated and stratified society have also suffered. The easy assumptions made on the basis of a few partially and imperfectly excavated sites are dubbed ‘old platitudes’ as a new generation of scholars and field workers gingerly sifts the incontrovertible from the fanciful.
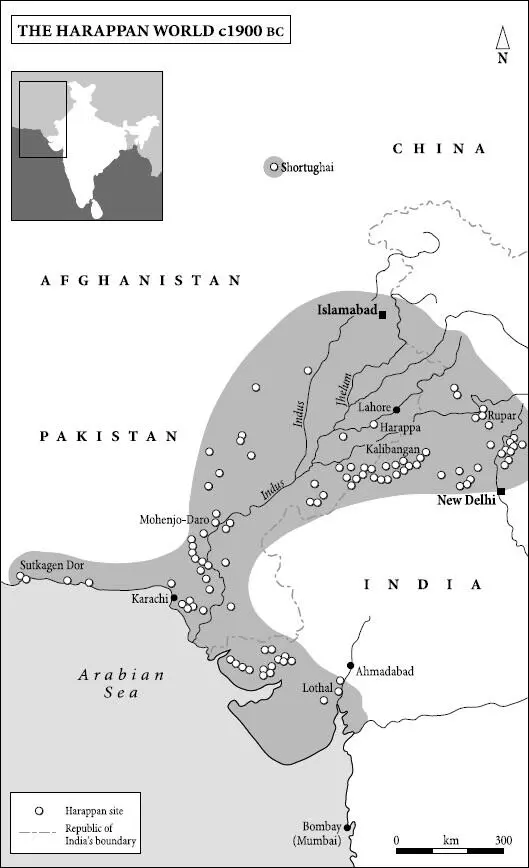
One mystery has certainly been solved. Pioneers like Marshall were puzzled how such a sophisticated culture could have sprung up from nowhere. Unaware of any other Bronze Age cultures in the region, not impressed by the Indian characteristics of Harappan architecture and artefacts, and wrongly assuming dates of about 3500–3000 BC, they duly looked to the west for an explanation, and suggested that the Indus valley civilisation must be a colony or offshoot of Mesopotamian or even Mycenaean civilisation. This idea is now quite untenable. At numerous sites to the west of the Indus in Baluchistan and Afghanistan, as well as in the Indus valley itself, sufficient pre-Harappan and Early Harappan settlements have been found to establish a local progression from hunter-gatherer to urban dweller by way of all the various stages of pastoralism, agricultural settlement, technological advance and cultural refinement. No such consensus exists about the Late Harappan and post-Harappan periods, but it is now possible to assign most Chalcolithic (Bronze/Stone) Age sites in the region to one of these categories and to give approximate dates for each.
Designated by their find sites and principally distinguished by their pottery styles, the pre-Harappan peoples of C3000 BC had already progressed to building houses and tilling the land. They had some knowledge of metals and had access, through trading links, to other precious materials and manufactures. Some time around 2600 BC – the dating varies from site to site – the appearance of typically Harappan styles in pottery and tools announces the Early Harappan phase. Brick-built houses assume a regular design with a courtyard and rooms off it. Figurines anticipate later Harappan styles. Towards the end of the millennium, say 2300 BC, this Early Harappan style gives way to the Mature Harappan phase, in which appears the full inventory of Harappan artefacts – standardised bricks and pots; regular streets above a network of well-made sewerage ducts; typical terracottas; a notable production of decorative artefacts including beads, faïence and shell work; more copper and bronze hardware; and a plenitude of the mysterious seals (as well as the impressions made by them) whereon that enigmatic script features prominently. In some cases, to produce the typical grid layout of streets, sites were apparently cleared and then rebuilt. Other sites were briefly deserted before being rebuilt. Still others suggest a continuance of non-Harappan or pre-Harappan styles, particularly in ceramics, side by side with the Mature Harappan. It is thus far from clear what relationships – of tribute, migration, conquest, intermarriage or cultural attraction – underlay the transition to greater standardisation.
Even worse inconsistency characterises the Late Harappan phase. Around 1900 BC Mohenjo-daro was gradually abandoned, possibly because of those floods and the associated salination of the soil. Kalibangan, an important town in Rajasthan, suffered a similar fate, but probably from desertification and the drying-up of the Ghaggar river. Elsewhere there is evidence of declining authority and of population decrease, possibly as a result of migration from the central settlements. Yet in some peripheral areas like Gujarat, Haryana and the Panjab, the decline is less marked and there may even have been an increase in activity and population.
Dispersal or dilution are evident from the prevalence of non-Harappan pottery styles, impoverishment and disruption from the gradual disuse of the script and from the disappearance of the more fanciful manifestations of Harappan culture, including that obsessive standardisation. On the other hand, craft skills and agricultural expertise survived. The spinning and weaving of cotton, for instance, in which the Harappans seem to have been the world’s pioneers, must have been gradually disseminated throughout India, since by the mid-first millennium BC it was commonplace. The finer textiles were by then an important item of trade and would remain so ever after, enticing to India Roman, Arab and eventually European merchants.
A similar case might be made for the ox-drawn wagon, which was as much a cliché of the Harappan world as it is of the Indian subcontinent today. Again, the Harappans may have been the first in the world to use wheeled transport. Numerous toy carts in terracotta and bronze testify to their pride in this technological breakthrough, and the generous street widths of their cities were presumably dictated by the consequent traffic.
Provisioning cities the size of Mohenjo-daro, with its estimated thirty to fifty thousand inhabitants, necessitated not only effective transport, both by river and road, but also a reliable rural surplus, a large labour force, and some means of crop storage. It has been conjectured that the largest structures at Mohenjo-daro, Harappa, Kalibangan and possibly Lothal may have been granaries, although their internal arrangements, consisting of carefully aligned brick plinths, await a satisfactory explanation.
The only public building whose function is beyond dispute is the great bath at Mohenjo-daro. The size of a modest municipal swimming pool, carefully sealed with bitumen, and with steps down at each end, it was clearly designed to hold water and to be used for bathing. Quite probably the ablutions, or immersion, were of some ritual significance. The bath forms the inner sanctum of an elaborate building, although there is no clear evidence that, as with later temple tanks, it was a place of worship. In fact, we have no idea what part religion played in the lives of the Harappan people. No site has certainly been identified as a temple, and most suppositions about sacrificial fires, cult objects and deities rest on doubtful retrospective reference from the Hindu practices of many centuries later. Such inferences may be as futile as, say, looking to Islamic astronomy for an explanation of the orientation of the pyramids. In short, ‘these theories are all fanciful and do not bear scrutiny.’ 6
A much-cited example, depicted on some of the Harappan seals, is that of a big-nosed gentleman wearing a horned head-dress who sits in the lotus position with an erect penis, an air of abstraction and an audience of animals. He may indeed be an early manifestation of Lord Shiva as Pashupati, ‘Lord of the Beasts’. But myth, as has been noted, is subject to frequent revision. The chances of a deity remaining closely associated with the same specific powers – in this case, fertility, asceticism and familiarity with the animal kingdom – for all of two thousand years must raise serious doubts, especially since, during the interval, there is little evidence for the currency of this myth. Rudra, a Vedic deity later identified with Shiva, is indeed referred to as pasupati because of his association with cattle; but asceticism and meditation were not Rudra’s specialities, nor is he usually credited with an empathy for animals other than kine. More plausibly, it has been suggested that the Harappan figure’s heavily horned headgear bespeaks a bull cult, to which numerous other representations of bulls lend substance.
Читать дальше













