Figure 1.7 Expressive tasks. Meaning of expressive tasks.
1.5 Assumptions of this monograph
At this point, two primary assumptions related to the work presented in this monograph are highlighted.
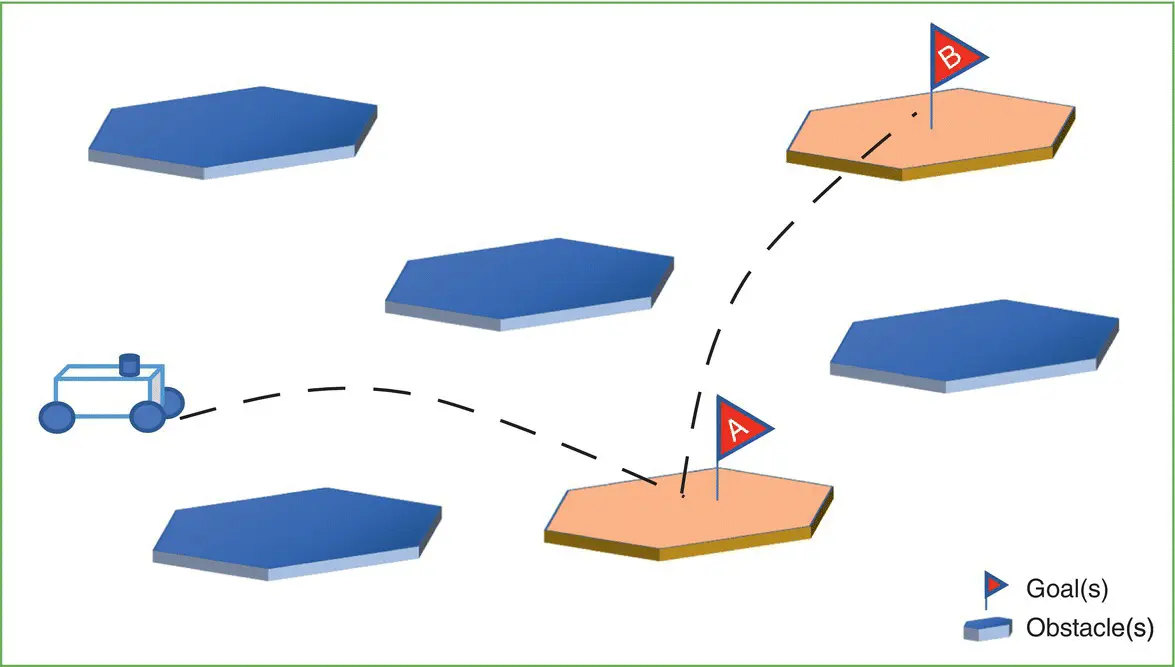
The first assumption is that the mobile robots are considered as omnidirectional points 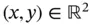 , where the domain of operation is a continuous Cartesian plane (2D plane). In this sense, the path planning problem can now be stated as moving the robot from its initial position
, where the domain of operation is a continuous Cartesian plane (2D plane). In this sense, the path planning problem can now be stated as moving the robot from its initial position 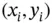 to another position
to another position 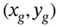 (or list of high‐level goals) while avoiding obstacles or while driving over the free space.
(or list of high‐level goals) while avoiding obstacles or while driving over the free space.
The second assumption is that the robot evolves in a known and static 2D environment cluttered with convex polygonal obstacles. This means that the robot should move from one position to another while remaining within  , where
, where  is an obstacle‐free space for the map where the robot is going to move.
is an obstacle‐free space for the map where the robot is going to move.
1.6 Outline of this monograph
This book is composed of seven chapters. This current chapter serves as an introduction and gives an historical perspective of two important topics: path planning and motion control in the field of mobile robotics.
Chapter 2presents a Matlab‐based interactive software tool, called Robot Motion Toolbox (RMTool) [82, 165]. With RMTool, the interested reader can test various theoretical concepts introduced throughout this monograph. The software tool offers the user the advantage of instantly seeing the motion planning results in a Graphical User Interface. Therefore, there is no need for previous knowledge in Matlab or in programming the methods and algorithms tackled in this book. However, the available functions can also be used outside RMTool for implementing new algorithms. The chapter includes illustrative examples demonstrating the benefits of the proposed simulator, and at the same time it informally introduces some planning strategies that are to be detailed in the subsequent chapters.
Chapter 3focuses on cell decompositions, which will be further used for automatically planning mobile robots. The chapter discusses the algorithms for performing four types of decompositions for bidimensional environments [76, 114]. Details on the available Matlab implementation are also given, the mentioned functions being part of RMTool. The chapter includes different qualitative and quantitative comparisons regarding the relative performance of the four cell decompositions.
Chapter 4defines the discrete event system models that are to be used for abstracting the motion of a single robot or of a team of identical robots in a given environment. Two types of models are constructed by using cell decompositions, namely transition systems and Petri nets. The chapter presents some high‐level specifications that can be used for imposing desired robot behaviors. Based on the constructed models and on specifications, the following chapters will present automatic methods for planning the robotic motion.
Chapter 5focuses on planning based on transition system models. First, algorithms are presented for classical planning of a robot toward a target position, while several methods are investigated for optimizing the intermediate points through which the robot passes [85, 124, 207]. Then, automatic planning methods based on Linear Temporal Logic requirements are presented for a single robot [111] and for a team of robots that has to fulfill a global mission [54, 118]. For e resulting robot trajectories, the chapter includes a collision avoidance strategy using initial time delays [210].
Chapter 6presents planning methods for a team of identical robots based on Petri net models. The targeted requirement can be expressed through Boolean‐based specifications [147, 148, 206] or through Linear Temporal Logic formulas [119, 120], while the methods include integer optimizations. The chapter also presents two specific problems, a sequencing one, where a linear programming optimization suffices to obtain a solution [116], and a task accomplishment one, which needs to gather more robots in the same place [117, 164]. Collision and deadlock avoidance by means of resource allocation techniques are also discussed [123].
Finally, Chapter 7presents the conclusions of this monograph, as well as a brief discussion about some possible future works in the field of path planning in mobile robotics.
1 1Motion planning in a broad sense involves the generation of inputs to a nonlinear dynamical system that drives it from an initial state to a specified goal state [135]. In this sense, path planning can be considered as a subfield within motion planning.
2 2Non‐holonomic systems are, roughly speaking, mechanical systems with constraints on their velocity that are not derivable from position constraints [17].
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.


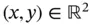 , where the domain of operation is a continuous Cartesian plane (2D plane). In this sense, the path planning problem can now be stated as moving the robot from its initial position
, where the domain of operation is a continuous Cartesian plane (2D plane). In this sense, the path planning problem can now be stated as moving the robot from its initial position 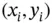 to another position
to another position 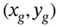 (or list of high‐level goals) while avoiding obstacles or while driving over the free space.
(or list of high‐level goals) while avoiding obstacles or while driving over the free space. , where
, where  is an obstacle‐free space for the map where the robot is going to move.
is an obstacle‐free space for the map where the robot is going to move.