This book is to present learning materials for students, instructors and engineers in various fields who wish to learn design, implementation and automatic tuning of PID control systems. The book begins with the basics in PID control systems (see Chapter 1), introducing the various PID control structures and the PID controller tuning rules. Chapter 2presents the necessary tools for closed-loop stability and performance analysis and explains the roles of sensitivity functions in relation to disturbance rejection, reference following and measurement noise attenuation. In Chapter 3, pole-assignment controller design methods are introduced for PID controllers and resonant controllers that will track a sinusoidal reference signal and reject a sinusoidal disturbance. Feedforward compensation is introduced in this chapter. Many analytical examples and two MATLAB tutorials are given in this chapter to show the details of the designs. Chapter 4discusses how a PID controller can be implemented in real-time with the topics of discretization, integrator windup problem, anti-windup mechanisms, and other implementation issues. A MATLAB real-time function is provided for PID controller implementation with anti-windup mechanism. Chapter 5examines the PID controller design and resonant controller design from a different angle to the previous chapters. It introduces the integral mode and resonant modes through disturbance estimation. With the disturbance observer based approaches, the implementations of these control systems naturally incorporate anti-windup mechanisms when the control signal reaches its limit. MATLAB real-time functions are provided for the implementation of the PID controller and resonant controller with anti-windup mechanisms. In Chapter 6, PID control of nonlinear systems is discussed, which includes the topics of linearization, case study of a ball and plate balancing system with experimental validation, gain scheduled PID control systems and gain scheduled disturbance observer based control systems. Chapter 7presents cascade PID control systems with the topics of cascade control system design, its roles in disturbance rejection and overcoming actuator's nonlinearities. Chapter 8considers PID controller design for complex systems using frequency response data, which includes the topics of PID controller design using gain and phase margins, PID controller design using two frequency points with a specification on the desired sensitivity function, and empirical rules derived for PID control of integrator with time delay systems that have a performance specification and corresponding gain and phase margin measurement. MATLAB functions are given for the computation of the PID controller parameters using two frequency response points. Chapter 9presents automatic tuning of PID controllers using relay feedback control. MATLAB real-time functions are created for relay feedback control and used for the Simulink simulations. The Fourier analysis and frequency sampling filter model are used, as two different methods, for the estimation of plant frequency response with the data generated from relay feedback control. The auto-tuners are created by linking the estimation to the PID controllers designed in the frequency domain as presented in Chapter 8. MATLAB functions are presented in a step-by-step manner for the estimation algorithms and for the auto-tuners. As case studies, Chapter 10applies the PID control system design and the auto-tuner to multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicles. This chapter is supported with experimental validations.
The book is self-contained with MATLAB/Simulink tutorials and supported with simulation and experimental results. Control system simulation and experimental implementation are emphasized in the book materials. The MATLAB real-time functions written for the use in Simulink simulations could be converted into C-codes for control system implementation with micro-controllers. For each section, there is a set of questions for us to reflect on. Some of them are easy and straightforward while others may require some thinking. At the end of each chapter, there is a set of problems for practicing the design and simulation of the control systems.
The book is suited for readers who have completed first three years engineering studies with some basic knowledge in block diagrams and Laplace transforms.
Liuping Wang
Melbourne, Australia
I wish to acknowledge the funding support from Mathworks Academic Support on the project entitled “PID Control Systems with Constraints: Design and Automatic Tuning using MATLAB/Simulink”. Particularly, I would like to thank Mr Bradley Horton from Mathworks for his help and support. I wish to thank Professors Shihua Li, Xisong Chen, Jun Yang and Dr Zhenhua Zhao in Southeast University, China, for interesting discussions on disturbance observer, during my visit to their university in 2014 and 2015. I wish to thank Dr Xi Chen and Dr Pakorn Poksawat previously at RMIT University Australia for their contributions on the automatic control of unmanned aerial vehicles.
For valuable comments towards improvement of this book, I wish to thank Professor Antonio Visioli at the University of Brescia, Italy, Dr John Tsing, who had worked in Measurex Corp. USA as a process control engineer and was an adjunct professor at San Jose State University, USA, Dr N. Leonard Segall of Sarnia, Ontario, Canada, Dr Chow Yin Lai, Dr Lasantha Meegahapola, Dr Arash Vahidnia, Dr Nuwantha Fernando, at RMIT University, Australia. I wish to thank Michelle Dunkley, Louis Vasanth Manoharan and Tessa Edmunds from Wiley and Sons Ltd for help and support during this book project, and Dipta Maitra for the book cover design.
I would like to thank my teaching team, Dr Robin Guan, Mr Long Tran Quang, Mr Junaid Saeed, Mr Luke McNabb and Mr Yifeng Sun, for their initiatives in teaching laboratory development. They have worked diligently to enhance students' learning experience in the subject of Advanced Control Systems at RMIT University, Australia.
List of Symbols and Acronyms
Symbols
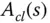 |
Closed-loop polynomial |
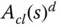 |
Desired closed-loop polynomial |
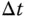 |
Sampling interval |
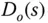 |
Laplace transform for output disturbance |
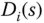 |
Laplace transform for input disturbance |
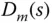 |
Laplace transform for measurement noise |
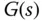 |
Transfer function model |
 |
Imaginary unit, 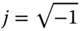 |
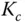 |
Proportional control gain |
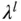 , , 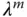 , , 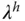 |
Scheduling parameters |
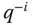 |
Backward shift operator, 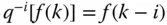 |
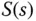 |
Sensitivity function |
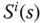 |
Input sensitivity function |
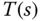 |
Complementary sensitivity function |
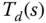 |
Desired complementary sensitivity function |
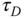 |
Derivative control gain |
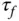 |
Derivative control filter time constant |
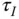 |
Integral control time constant |
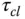 |
Closed-loop time constant |
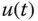 |
Control signal |
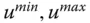 |
Minimum and maximum limits for 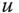 |
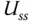 |
Steady-state value for a control signal |
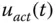 |
Actual control signal ( 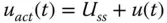 ) ) |
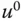 |
Operating condition of 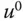 |
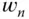 |
Bandwidth or natural frequency in PID controller design (rad/s) |
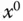 |
Operating condition of 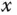 |
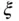 |
Damping coefficient in PID controller design |
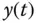 |
Output signal |
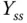 |
Steady-state value of the output signal |
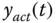 |
Actual output signal ( 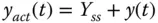 ) ) |
Acronyms
Читать дальше

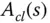
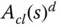
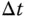
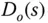
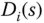
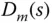
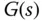
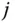
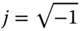
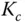
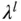 ,
, 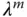 ,
, 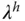
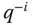
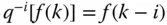
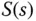
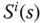
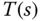
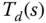
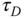
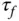
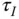
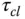
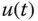
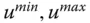
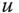
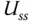
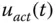
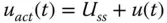 )
)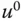
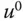
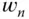
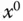
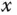
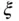
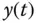
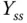
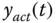
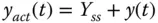 )
)










