α Angle, pressure ratio in constant‐volume combustion, angular acceleration β Angle, volume ratio in constant‐pressure combustion γ Ratio of specific heats, V‐angle (engine crank) Δ Symbol for difference δ Expansion ratio in an engine cylinder ε Compression ratio (volume ratio) ε Heat‐exchanger effectiveness η Efficiency θ Angle, crank angle 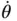 Angular velocity
Angular velocity 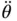 Angular acceleration κ Compressibility λ Relative air‐fuel ratio μ Dynamic viscosity, coefficient of molecular change ν Kinematic viscosityΠNon‐dimensional group ρ Density, volume ratio during heat rejection at constant volume (generalized air‐standard cycle) σ Stress, rounding‐off coefficient in piston engine cycles τ Ratio of crank radius to connecting rod length φ Flow coefficient, crank angle (Wiebe function), equivalence ratio ϕ Angle (Wiebe function), heat utilization coefficient ψ Loading coefficient, coefficient of molar change ω Angular velocity, degree of cooling
Angular acceleration κ Compressibility λ Relative air‐fuel ratio μ Dynamic viscosity, coefficient of molecular change ν Kinematic viscosityΠNon‐dimensional group ρ Density, volume ratio during heat rejection at constant volume (generalized air‐standard cycle) σ Stress, rounding‐off coefficient in piston engine cycles τ Ratio of crank radius to connecting rod length φ Flow coefficient, crank angle (Wiebe function), equivalence ratio ϕ Angle (Wiebe function), heat utilization coefficient ψ Loading coefficient, coefficient of molar change ω Angular velocity, degree of cooling
aAir, actual, total volumebBrakeCCarbon mass fraction in liquid or solid fuelcCompressor, clearance (volume), crankcomCompressor (volume ratio)cpCrank pincrCriticalctCompressor turbinecwCrank webeexitfFuel, frictional, formationgGas, gravimetricHHydrogen mass fraction in liquid or solid fuelhHigheriInlet, intake, indicated, species, inertialLiquid, lowermMean N Nitrogen mole fraction in gaseous fuelnNozzleOMass fraction of oxygen in liquid or solid fuelPProduct of combustionpPiston, propulsivepcCompressor polytropic efficiencyppPiston pinptTurbine polytropic efficiency, power turbineRReactants (air plus fuel)rRod (connecting rod)SSulfur mass fraction in liquid or solid fuelsIsentropic, stoichiometric, swept (volume)tTurbine, total (stagnation) conditionwWhirl (velocity)
g GravimetricReference state (pressure) v Volumetric
A/FAir‐fuel ratioAFTAdiabatic flame temperatureBDCBottom dead centrecaCrank angleCICompression ignitionF/AFuel‐air ratiobmepBrake mean effective pressureGTGas turbinebsfcBrake specific fuel consumptionimepIndicated mean effective pressureICEInternal combustion engineisfcIndicated specific fuel consumptionmepMean effective pressureNINatural‐induction (engine)ReReynolds numberrpmRevolutions per minuteSISpark ignitionTDCTop dead centreTETTurbine entry temperature
About the Companion Website
The companion website for this book is at
www.wiley.com/go/JamilGhojel_Fundamentals of Heat Engines 
The website includes:
Solution manual for instructors
PPTs
Scan this QR code to visit the companion website.

Part I
Fundamentals of Engineering Science
Introduction I: Role of Engineering Science
For the last 200 years or so, humans have been living in the epoch of power in which the heat engine has been the dominant device for converting heat to work and power. The development of the heat engine was for most of that time slow and chaotic and carried out mainly by poorly qualified practitioners who had no knowledge of basic theories of energy and energy conversion to mechanical work. In the field of engineering mechanics, drawings of early steam engines depict various, at times strange, inefficient mechanisms to convert steam power to mechanical power, such as the walking beam and sun and planet gear systems. The piston‐crank mechanism was first used in a steam engine in 1802 by Oliver Evans (Sandfort 1964) despite a design being proposed as early as 1589 for converting the rotary motion of an animal‐driven machine to reciprocating motion in a pump. The first internal combustion engine (ICE) to be made available commercially was Lenoir's gas engine in 1860. This engine was also the first to employ a piston‐crank mechanism to convert reciprocating motion of the piston to rotary motion, which has become, despite its shortcomings, a fixed feature and highly efficient mechanism in modern reciprocating engines. However, engine designers were never fully satisfied with this mechanism due to the need to balance numerous parasitic forces generated during operation and were constantly looking for alternative ways of obtaining direct rotary motion. This is said to have been one of the stimuli to develop steam and gas turbines in which a fluid, flowing through blades, causes the shaft to rotate, thus eliminating the need for a crankshaft. The results are smoother operation, lower levels of vibration, and low‐cost support structures. All of these developments occurred over a very long period of time with advances in the science of engineering mechanics (more specifically, engineering dynamics), together with other engineering science branches such as fluid mechanics and thermodynamics.
Examples of the principles of fluid mechanics of relevance to the topics of Parts I and II in the book include the momentum equation used to calculate thrust in aircraft gas turbine engines, Bernoulli's equation to calculate flow in the induction manifold of piston engines, and dimensional analysis to determine the characteristics of turbomachinery for gas turbines.
The great scientific breakthroughs in the development of heat‐engine theory came with the development of the science of thermodynamics, starting with the pioneering work of Nicolas Sadi Carnot (1796–1832) and followed by the monumental contributions of Rudolf Clausius (1822–1888) and William Thomson (Lord Kelvin, 1824–1907). Ever since, knowledge of thermodynamics has become essential to improving existing heat engine designs and developing new types of engine processes for superior economy and reduced emissions. At the same time, the heat engine, particularly the reciprocating ICE, has become an ideal tool for teaching mechanical and automotive engineering, as it features, in addition to thermodynamics, fundamental principles of engineering mechanics and fluid mechanics as discussed earlier.
A chapter on thermochemistry (Chapter 2) is included in Part I, dealing with fuel properties and the chemistry of combustion reactions and the effect of control of the combustion temperature through control of air‐fuel ratios in order to preserve the mechanical integrity of engine components. Extensive numerical data on gas properties and adiabatic flame temperature calculations are included, which can be used for preliminary design‐point calculations of practical piston and gas turbine engine cycles.
1 Review of Basic Principles
1.1 Engineering Mechanics
Mechanics deals with the response of bodies to the action of forces in general, and dynamics is a branch of mechanics that studies bodies in motion. The principles of dynamics can be used, for example, to solve practical problems in aerospace, mechanical, and automotive engineering. These principles are basic to the analysis and design of land, sea, and air transportation vehicles and machinery of all types (pumps, compressors, and reciprocating and gas‐turbine internal combustion engines). A review of some principles relevant to heat engines is presented here.
Читать дальше

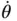 Angular velocity
Angular velocity 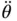 Angular acceleration κ Compressibility λ Relative air‐fuel ratio μ Dynamic viscosity, coefficient of molecular change ν Kinematic viscosityΠNon‐dimensional group ρ Density, volume ratio during heat rejection at constant volume (generalized air‐standard cycle) σ Stress, rounding‐off coefficient in piston engine cycles τ Ratio of crank radius to connecting rod length φ Flow coefficient, crank angle (Wiebe function), equivalence ratio ϕ Angle (Wiebe function), heat utilization coefficient ψ Loading coefficient, coefficient of molar change ω Angular velocity, degree of cooling
Angular acceleration κ Compressibility λ Relative air‐fuel ratio μ Dynamic viscosity, coefficient of molecular change ν Kinematic viscosityΠNon‐dimensional group ρ Density, volume ratio during heat rejection at constant volume (generalized air‐standard cycle) σ Stress, rounding‐off coefficient in piston engine cycles τ Ratio of crank radius to connecting rod length φ Flow coefficient, crank angle (Wiebe function), equivalence ratio ϕ Angle (Wiebe function), heat utilization coefficient ψ Loading coefficient, coefficient of molar change ω Angular velocity, degree of cooling










