Franco Taroni - Statistics and the Evaluation of Evidence for Forensic Scientists
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Franco Taroni - Statistics and the Evaluation of Evidence for Forensic Scientists» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Statistics and the Evaluation of Evidence for Forensic Scientists
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Statistics and the Evaluation of Evidence for Forensic Scientists: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Statistics and the Evaluation of Evidence for Forensic Scientists»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
he leading resource in the statistical evaluation and interpretation of forensic evidence
The third edition of
is fully updated to provide the latest research and developments in the use of statistical techniques to evaluate and interpret evidence. Courts are increasingly aware of the importance of proper evidence assessment when there is an element of uncertainty. Because of the increasing availability of data, the role of statistical and probabilistic reasoning is gaining a higher profile in criminal cases. That’s why lawyers, forensic scientists, graduate students, and researchers will find this book an essential resource, one which explores how forensic evidence can be evaluated and interpreted statistically. It’s written as an accessible source of information for all those with an interest in the evaluation and interpretation of forensic scientific evidence.
Discusses the entire chain of reasoning–from evidence pre-assessment to court presentation; Includes material for the understanding of evidence interpretation for single and multiple trace evidence; Provides real examples and data for improved understanding. Since the first edition of this book was published in 1995, this respected series has remained a leading resource in the statistical evaluation of forensic evidence. It shares knowledge from authors in the fields of statistics and forensic science who are international experts in the area of evidence evaluation and interpretation. This book helps people to deal with uncertainty related to scientific evidence and propositions. It introduces a method of reasoning that shows how to update beliefs coherently and to act rationally. In this edition, readers can find new information on the topics of elicitation, subjective probabilities, decision analysis, and cognitive bias, all discussed in a Bayesian framework.

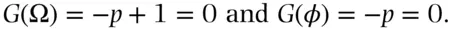
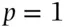 for
for 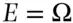 and
and 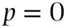 for
for 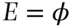 . Therefore if the subjective probability of
. Therefore if the subjective probability of 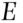 , that represents our degree of belief on
, that represents our degree of belief on  , is defined as an amount
, is defined as an amount 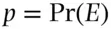 , which makes a personal bet on the event or proposition
, which makes a personal bet on the event or proposition 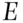 coherent, then the probability
coherent, then the probability 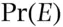 satisfies two conditions.
satisfies two conditions.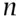 possible bets on events
possible bets on events  that partition
that partition  ; i.e.
; i.e.  are mutually exclusive and exhaustive (Scozzafava 1987, p. 686). Let
are mutually exclusive and exhaustive (Scozzafava 1987, p. 686). Let 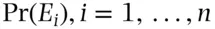 , be the amount paid for a coherent bet on
, be the amount paid for a coherent bet on  . These bets can be regarded as a single bet on
. These bets can be regarded as a single bet on 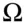 with amount
with amount  . Another condition may be specified from the requirement of coherence, namely
. Another condition may be specified from the requirement of coherence, namely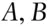 , and
, and 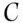 . A bookmaker offers probabilities of 1/4, 1/3, and 1/2, respectively, for these horses to win. Note that these probabilities add up to more than 1 and so violate condition 3. The corresponding odds are 3 to 1 against winning, 2 to 1 against winning and ‘evens’.
. A bookmaker offers probabilities of 1/4, 1/3, and 1/2, respectively, for these horses to win. Note that these probabilities add up to more than 1 and so violate condition 3. The corresponding odds are 3 to 1 against winning, 2 to 1 against winning and ‘evens’.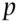 of occurring has odds
of occurring has odds 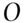 of happening where
of happening where 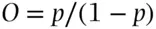 . Conversely, an event that has odds of
. Conversely, an event that has odds of 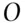 to 1 of happening has a probability of
to 1 of happening has a probability of 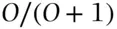 of happening and an event that has odds of
of happening and an event that has odds of 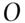 to 1 of not happening has a probability of
to 1 of not happening has a probability of 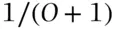 of happening. Odds of ‘evens’ correspond to
of happening. Odds of ‘evens’ correspond to 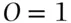 or
or 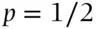 .
.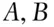 , or
, or 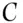 wins the race. The individual should therefore expect to break even on the outcome of the race; their winnings will equal their initial stake. Of course, it does not make sense to bet on the certain event as there should then be nothing to win or lose. This assumes the odds are fixed to satisfy condition 3. However, in this example, the odds do not satisfy condition 3 and the person will not break even. Suppose the following bets are placed: £3000 on
wins the race. The individual should therefore expect to break even on the outcome of the race; their winnings will equal their initial stake. Of course, it does not make sense to bet on the certain event as there should then be nothing to win or lose. This assumes the odds are fixed to satisfy condition 3. However, in this example, the odds do not satisfy condition 3 and the person will not break even. Suppose the following bets are placed: £3000 on 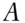 to win, £4000 on
to win, £4000 on 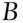 to win, and £6000 on
to win, and £6000 on 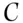 to win; i.e. £13 000 in total. If
to win; i.e. £13 000 in total. If 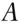 wins the bookmaker pays out £12 000, the original £3000 bet and another £9000 in accordance with the odds of 3 to 1 against. If
wins the bookmaker pays out £12 000, the original £3000 bet and another £9000 in accordance with the odds of 3 to 1 against. If 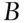 wins, the bookmaker also pays out £12 000, the original £4000 bet and another £8000 in accordance with the odds of 2 to 1 against. If
wins, the bookmaker also pays out £12 000, the original £4000 bet and another £8000 in accordance with the odds of 2 to 1 against. If 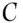 wins the bookmaker again pays out £12 000, the original £6000 bet and another £6000 in accordance with the odds of evens. Regardless of which horse has won the race, the individual has paid out £13 000 and receives £12 000 in winnings, thus incurring a loss of £1000. This situation is known as a Dutch book. The odds quoted did not satisfy condition 3. Conversely, if the set of odds determine probabilities that add up to less than 1, then the bookmaker will lose money. It would be incoherent for such odds to be set.
wins the bookmaker again pays out £12 000, the original £6000 bet and another £6000 in accordance with the odds of evens. Regardless of which horse has won the race, the individual has paid out £13 000 and receives £12 000 in winnings, thus incurring a loss of £1000. This situation is known as a Dutch book. The odds quoted did not satisfy condition 3. Conversely, if the set of odds determine probabilities that add up to less than 1, then the bookmaker will lose money. It would be incoherent for such odds to be set.










