Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Based on the given case study on the need for a genetic and molecular level of differentiation among the patient population, it is essential for the healthcare professionals to titer the doses of the drugs for individual patients using the following technologies for safe and effective therapy [19].
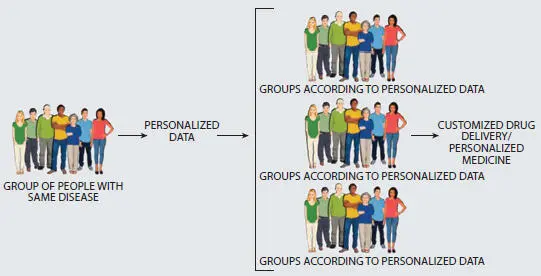
Figure 3.1 Basic personalized drug delivery approach.
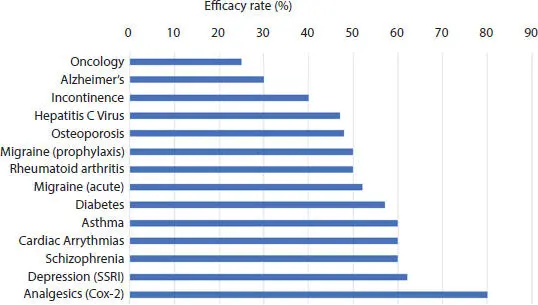
Figure 3.2 Response rates of patients to a major drug for a selected group of therapeutic areas.
The primary objective of a personalized and customized drug delivery system is to analyze the clinical pharmacogenetics of each and every individual to distinguish the responders and nonresponders in the patient population for a particular drug and also the differences in risks of adverse drug reactions among the same population with the same drug [20]. This information provides the best choice of drug for a particular individual or a group of patients for better therapy with lesser adverse drug reactions and maximum likeliness of efficacy. It is essential to test a patient to identify whether the individual is responsive or nonresponsive to the particular agent or a class of therapeutic agents. Similarly, it paves an opportunity to understand whether the individual is prone to adverse effects and its degree of risk/benefits [21].
A patient may or may not show therapeutic response to a particular drug or even its adverse effects. There exist many reasons such as drug–drug interactions, drug causing hypersensitive reactions, allergic reactions, wrong dosing, and medicament fault. On the other hand, the patient’s genetic susceptibility to pathogen remains ambiguous for the drugs’ inappropriate response. Various genes are shown to associate to a specific drug molecule showing no response or fluctuations in the therapeutic effects, and some may also lead to ADRs (adverse drug reactions) [22]. For example, 5-lipoxygenease (ALOX-5) directly influences the production of leukotrienes, helps in treating asthma; clinically it is proved that patients with gene expression of inactive alleles of 5-lipogenase are not responsive to ALOX-5 inhibitor. Likely drug metabolizing enzyme CYP2D6 having two non-expressive alleles cannot perform its functional metabolism of codeine to morphine and no activity of analgesia is showcased [23].
In 2017, Arellano et al . conducted a study on multiple ADRs associated with genetic polymorphism. CYP2D6 is a polymorphic isozyme having more than 100 allelic variants; it is suspected to have a higher degree of risk causing ADR in individuals using the commonly prescribed therapeutic agents such as analgesics, beta adrenergic antagonists, anti-arrhythmic, antipsychotics, antidepressants, and cough suppressants that are metabolized to an extent of 25% by CYP2D6 due to a higher dose of drug accumulation in systemic circulation. Likewise, the lack of this enzyme leads to poor effect of drug response in prodrugs like tramadol [24].
The study of the genetic relations associated with ADRs is more important; therefore, recognizing the pathophysiologic mechanism of the drug reactions helps to identify safer drugs and biomarkers in the future for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of patients developing ADRs. Studies associated with genetics in relation to ADR are quite challenging due to their heterogeneity in clinical demonstrations and broad range of therapeutic agents causing ADRs [25]. From the above-discussed examples and the needs of the patients for better therapy, the transformation of pharmacogenomics and pharmacogenetics in the field of advancing medicines must be enhanced by creating a patient genetic database, providing the healthcare professionals with detailed information about the predisposition of the therapy for a particular disease and drug [26]. The nongenomic factors acculturate a significant and better composition of data to increase the exactness of the patient therapy, which includes clinical and environmental factors. The advancing field of pharmacogenomics is now highly attractive and is now newly encouraged by the poly-omics tech. A gathered determination is necessary for the healthcare professionals to equip the implications of pharmacogenomic technique essentially and fundamental research in the area of clinical healthcare community, commercial enterprises, and regulatory bodies [27].
3.3 Customized Nanotools and Their Benefits
The applications of gene therapy in approaching the target disease by genetic material engineered modification or substitution at the site of gene expression in the target cells are vectored by the nanotools [28]. The advances in nanoparticles as an emerging technique are a promising tool for clinical therapy utilizing their nature of shape, size, surface, biological deportment, and properties. Gene-based therapy is showcased as an emerging advanced significant strategy for the treatment of many diseases associating the specific gene responsible for the following diseases: tumors, neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune disease, hypercholesterolemia, hemophilia, many microbial caused diseases, etc. The strategy involves introducing a gene into a particular target pathogen tissue causing modification or substitution at the endogenous gene expression by employing nanoparticle dosage form as a vehicle for delivery, preventing and curing the progression of that disease. The major challenges of this particular delivery of genomic material to the target site by equipping nanotech are the encapsulation efficacy of the genomic material in the nanodosage form, degradation in systemic circulation, endocytosis and endosomal escape by the target tissues, efficacy of the delivery system, pharmacological toxicity, and nanoparticle stability [29]. To bypass these many hinders, there are researchers forecasting many different types of nanocarriers for genetic material delivery such as lipoid-based nanoformulations, polymeric nanoparticles, and inorganic nanovehicles [30]. In 2016, Farris et al . developed and formulated a clinical nanocarrier for delivering a gene. A multinucleotide vaccine synthesizes a protein antigen in the area neighboring the antigen presenting cell leading to immunological responses. The key components (DNA) of the formulated vaccine delivery system can economically produce and has better storage and handling property than the components present in the other major peptide-based vaccines [31].
Various types of nanoformulations ( Table 3.1) as carriers opting the advantage of their morphology, function, and composition are mentioned below:
Table 3.1 An overview of the nanotools.
| Customized nanotools | Size range (nm) | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liposomes | 50 to 100 | A spherical vesicle containing minimum of one lipid bilayer encapsulating the aqueous core contain the drug molecules serve as a carrier. | Increase the efficacy and therapeutic index of the drugReduce toxicityFlexibility to couple to the target specific ligandsBiocompatible, biodegradable, non-immunogenic for both systemic and nonsystemic administration | Low solubilityLesser half-lifeLipids undergo reactions like oxidation and hydrolysis to a specific extentLeakage and fusion of the vesiclesEconomically high in costLess stable |
| Solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN) | 50 to 1000 | Globular structure vesicles encapsulated by monolayers of phospholipids containing dissolved or dispersed drug in the core media. | Control and/or target drug release and enhance bioavailabilityExcellent biocompatibilityHigh and enhanced drug contentEasy to scale up and sterilizeBetter control over release kinetics of encapsulated compoundsLiable drugsChemical protection of labile incorporated compoundsCan be subjected to commercial sterilization procedures. | Particle growthUnpredictable gelation tendencyUnexpected dynamics of polymeric transitions. |
| Nanocarbon tubes | 20 to 1000 | They are cylindrical molecules consisting of multilayers of rolled-up sheets of carbon atoms. | High bioavailability because of its high specific surface area and nanosize range.Multiple conjugation sites for the drug molecule. | Lack of solubility in aqueous media |
| Polymer-based nanoparticles | 10 to 1000 | Colloidal particles comprising drugs encapsulated or impinged by polymeric substance. | Increase the stability of volatile drug substance Biodegradable, biocompatible, and non-immunogenic Site-specific targeted drug delivery Reduce the adverse drug reactions | Toxic monomer aggregation Polymeric degradation On degradation, they yield toxic residual material |
| Polymer-based micelles | 10 to 100 | Self-assembled nanoscopic core shell formed by amphiphilic copolymer, containing hydrophobic drugs surrounded by micelles and hydrophilic bioactive materials. | Serves the advantage of controlled drug release NontoxicHigher physical stability Greater cargo capacity of drugs | Poor drug loading efficiency.Poor in vivo stability Poor cellular interaction with malignant tissues |
| Dendrimers | < 10 | Branched molecules that consist of a core and spherical 3D morphology. | Low toxic and antigenic.Biodegradable and metabolized.Can increase the half-life of the moiety.Good tissue permeability.Aids sustained and controlled drug release. | Limited storage condition.Time consuming.High material and equipment cost.Low retention.More complex in nature. |
| Metallic nanoparticles | < 100 | They are nanosized metals that are synthesized and modified to bind along with ligands, antibodies, drugs, etc. | Optical properties like photo absorption, light scattering, modified SERS (surface enhanced Raman scattering) and fluorescenceEnhance the resolutions of the imaging techniques such as MRI, tracking stem cells, and cellular molecules. | They are concerned with the issues of high toxicity.Their shape, size, surface chemistry, targeting ligands, elasticity, and composition largely influence their toxic profile.High in material and production cost. |
| Quantum dots | 2 to 10 | They are smaller nano range tiny nanoparticles and have good optical and electronic properties that vary from larger particles due to their intrinsic quantum mechanics. | They are better than fluorophore dyes that are 20 times brighter.Variations in the wavelength ranging from 400 to 4000 nm range.They are economically cost effective and also amenable to high-speed printing techniques. | Highly toxic and require stable polymer shell.The shells can alter the optical property.Hard to control the particle size of the nano structures.DegradationOverall conversion yield is poor. |
| Nanodiamonds | ~5 | Medically used diamonds of size range lesser than 5 nm containing three main components: the core, surface, and the overall shape. | They can be used in the drug delivery in their original form whereas there is no need to apply the oxidation modification process due to their good aqueous solubility nature, without any acidic media treatment.Reduces adverse effects.High affinity towards proteins and antibodies forming stable conjugates | Chances of genotoxicity occurrence due to the introduction of various chemical groups into the nanodiamonds.Difficulties in evaluation due to being smaller in size; special techniques such as radionuclide tracer are to be adopted.The process is quite complicated during the complexation of nanodiamonds with the active drug molecules covalently.Economically high in cost. |
3.3.1 Liposomes
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Nanopharmaceutical Advanced Delivery Systems» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












