www.e‐lfh.org.uk
www.esge.com/elearning
www.asge.org/home/education‐meetings/products/endoscopic‐learning‐library
www.ueg.eu/education/online‐courses
www.espghan.org/education/e‐learning
Part Two Diagnostic Pediatric Endoscopy
10 Indications for gastrointestinal endoscopy in childhood
Dalia Belsha, Jerome Viala, George Gershman, and Mike Thomson
 KEY POINTS
KEY POINTS
Diagnostic and therapeutic endoscopy are as available now for children as they were in previous years for adults.
Ideally, a pediatric practitioner would perform these although in adolescents, adult GI practititoners are sometimes involved.
Updated diagnostic and management guidelines for common disorders including celiac disease (CD), gastroesophageal reflux (GER), eosinophilic esophagitis (EE), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) illustrate the central role for endoscopy in pediatric practice.
It is also recognized that therapeutic endoscopic approaches are widely available now and further broaden the referral spectrum – these include treatment of GI bleeding, gastrostomy insertion, dilation of strictures, polypectomy, and many others.
The advent of newer technologies allows the examination of hitherto inaccessible areas of the GI tract such as the mid‐small bowel by wireless capsule videoendoscopy and enteroscopy.
Endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) for diagnostics and therapy has evolved markedly over the last 20 or so years and is now usually undertaken by pediatric endoscopists. Updated diagnostic and management guidelines for common disorders including celiac disease (CD), gastroesophageal reflux (GER), eosinophilic esophagitis (EE) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) illustrate the central role for endoscopy. It is also recognized that therapeutic endoscopic approaches are widely available now and further broaden the referral spectrum – these include treatment of GIT bleeding, gastrostomy insertion, dilation of strictures, polypectomy, and many others. Lastly, the advent of newer technologies allows the examination of hitherto inaccessible areas of the GIT such as the mid‐small bowel by wireless capsule videoendoscopy and enteroscopy. This chapter is more symptom focused as the place of endoscopy in various pathologies is covered in the relevant chapters later on.
Changing indications for pediatric endoscopy over the last 25 years may have also influenced other disease detection rates such as that of IBD. In prospective studies, pediatric IBD incidence rates are higher than had been reported previously, which might reflect a real increase but also may have been affected by acquisition bias secondary to wider availability of, and improvement in the quality of, endoscopic assessment
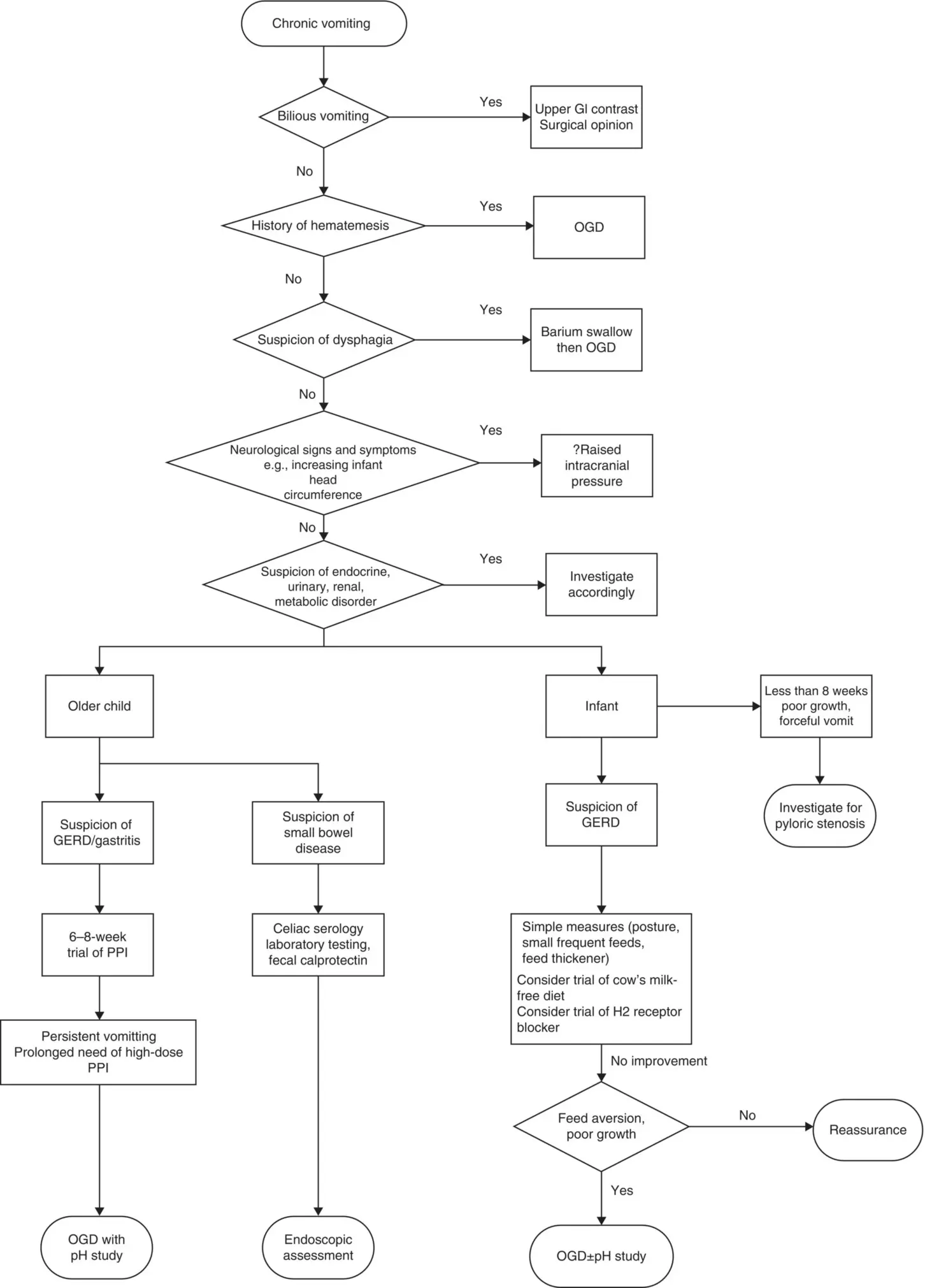
Figure 10.1Suggested diagnostic algorithm of chronic vomiting. PPI, proton pump inhibitor.
Source: BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health.
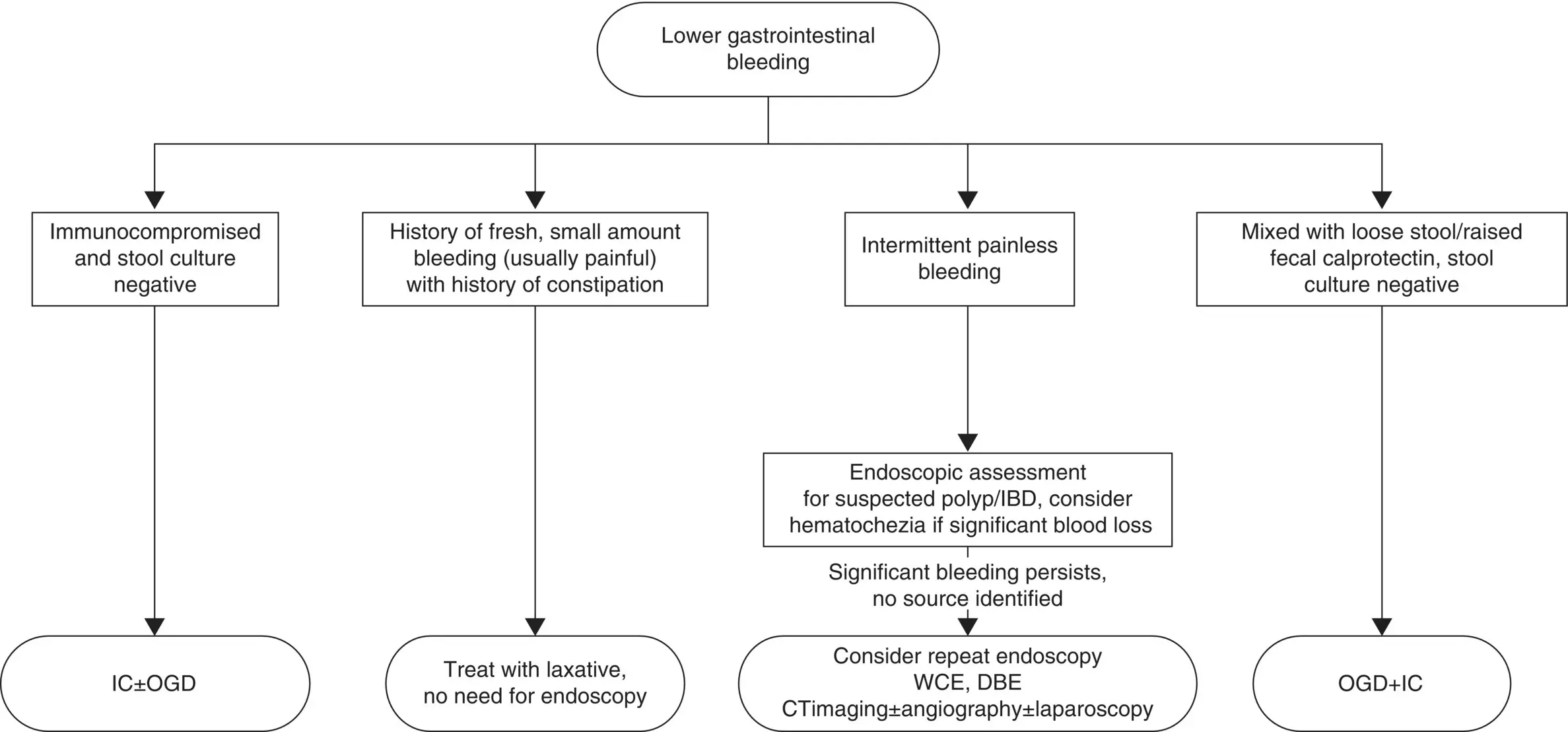
Figure 10.2Suggested diagnostic algorithm of lower gastrointestinal bleeding.
Source: BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health.
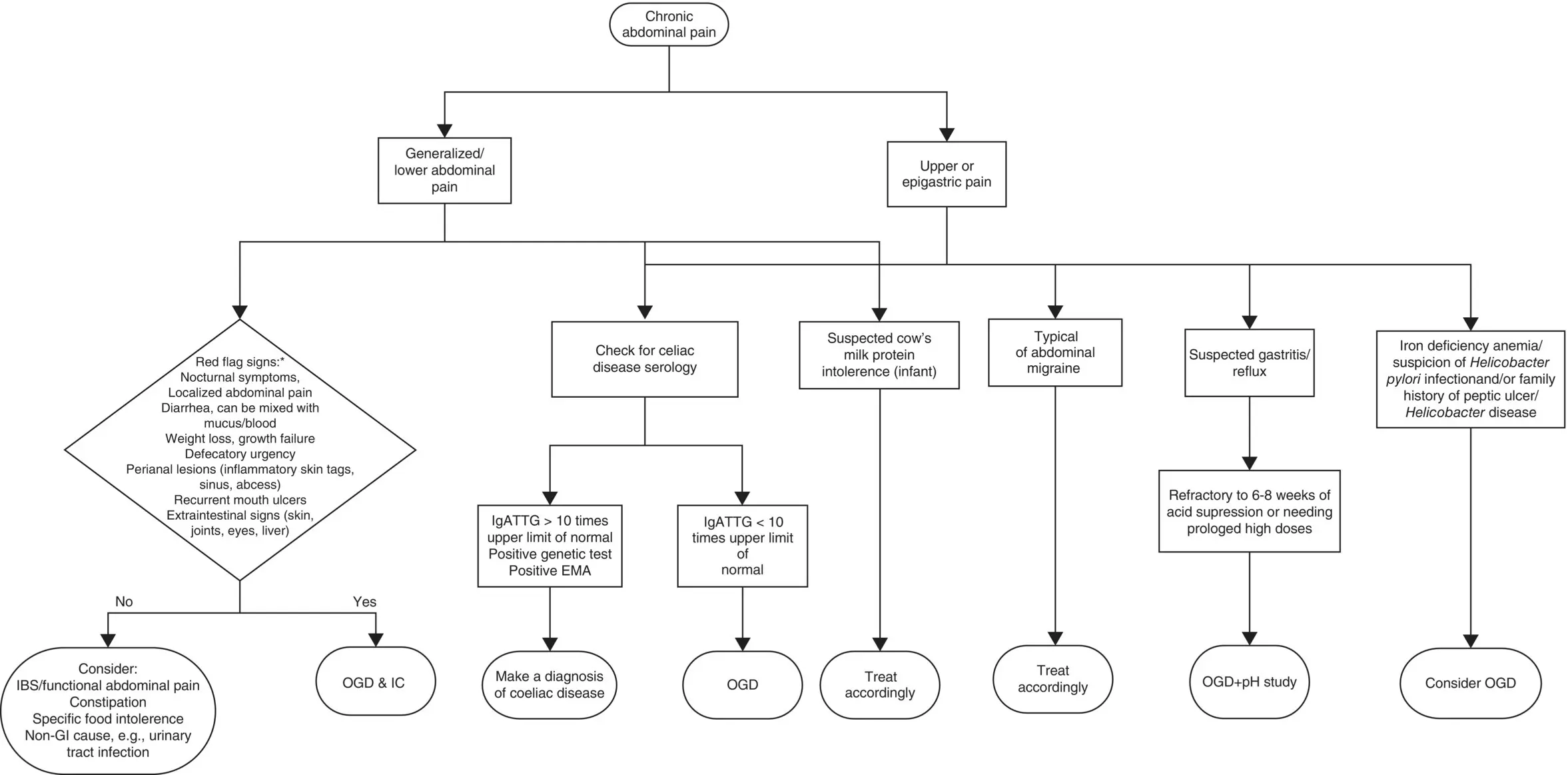
Figure 10.3Suggested diagnostic algorithm for chronic abdominal pain.
Source: BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health.
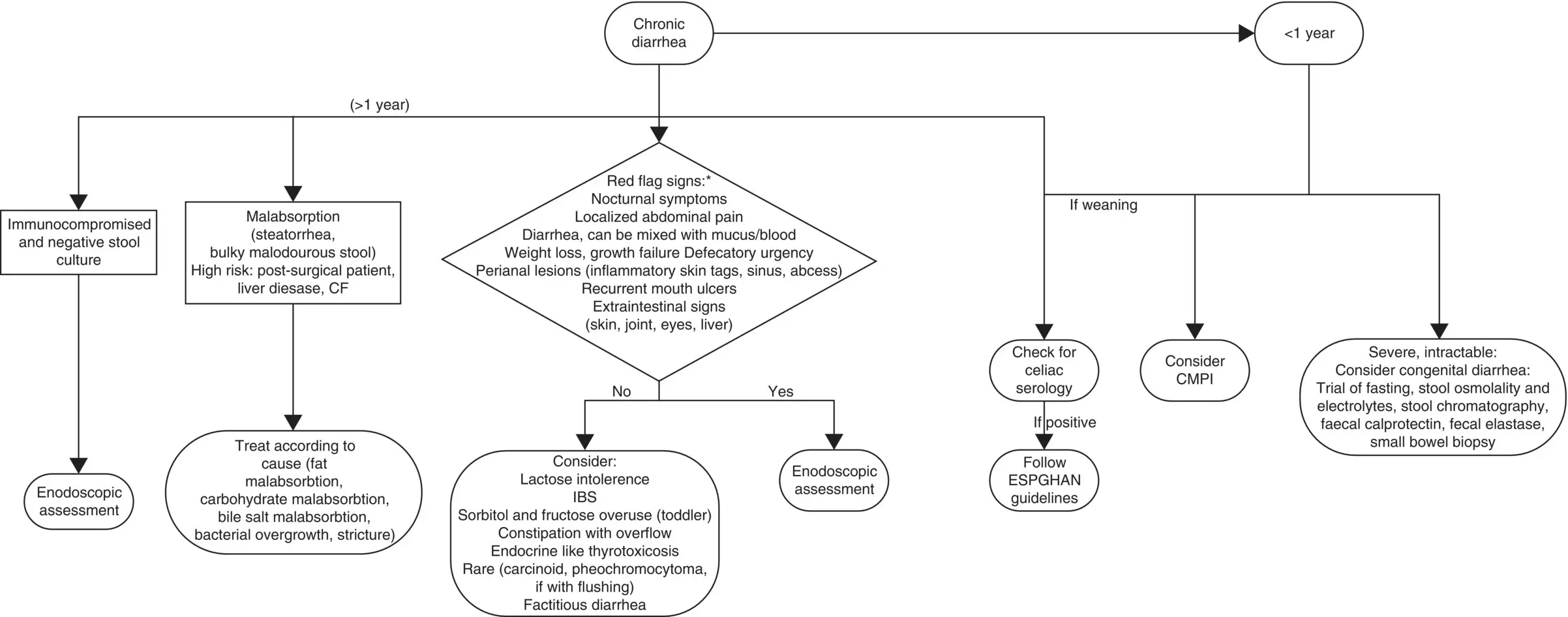
Figure 10.4Suggested diagnostic algorithm of chronic diarrhea.
Source: BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health.
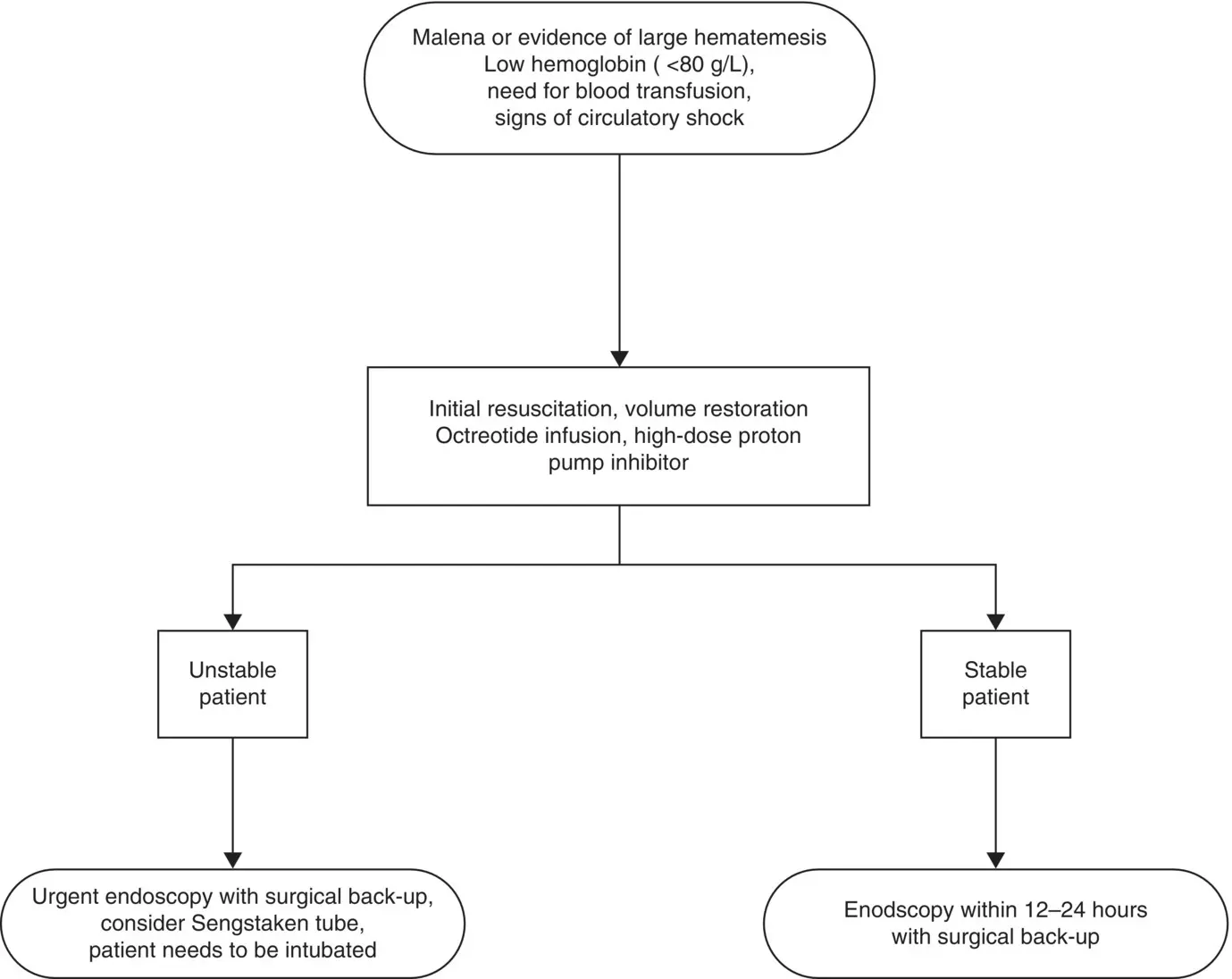
Figure 10.5Suggested initial management of upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
Source: BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health.
Table 10.1 Therapeutic indications for EGD
| Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) insertion |
| Changing PEG tube to button/balloon gastrostomy |
| Naso‐jejunal (NJ) or gastro‐jejunal (GJ) tube placement |
| Foreign body removal |
| Food bolus impaction removal |
| Dilation of esophageal strictures ± topical application of antifibrotic mitomycin C |
| Esophageal stent placement – usually reserved for the palliative situation |
| Dilation of achalasia |
| Closure of esophageal fistulae with tissue glue and endo‐clips |
| Upper GI polypectomy |
| Upper GI nonvariceal bleeding therapy |
| Esophageal varices banding (emergency or as prophylactic) |
| Injection of gastric fundal varices with histoacryl glue |
| Division of duodenal web/diaphragm/stenosis |
| Delivery of wireless video capsule |
| Laparoscopy‐assisted percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy (LAPEJ) |
| Endoscopic fundoplication |
| Endomucosal resection of sessile lesion (EMR) |
| Transgastric drainage of pancreatic pseudocyst |
| Endoultrasound‐guided celiac plexus neurolysis |
| Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) – stent placement both biliary and pancreatic |
| ERCP – sphincterotomy and removal of biliary stones |
Table 10.2 Indications for therapeutic colonoscopy in children
| Polypectomy |
| Dilation of ileocolonic stenosis |
| Treatment of hemorrhagic lesions |
| Foreign body removal |
| Reduction of sigmoid volvulus (rare and usually not successful) |
| Stenting of strictures |
| Sigmoidostomy |
| Cecostomy |
On the other hand and despite an increase in the number of GI endoscopies over recent years, diagnostic yield with abnormal histology results in overall endoscopic procedures remains constant at 62–76%. This suggests that the increase in number of pediatric endoscopies performed is due to increased demand rather than a lower threshold for the procedures.
In addition to IBD and EE, diagnosis of CD is increasing with increased awareness of the disease.
It is important to bear in mind that, in appropriately trained and experienced hands, endoscopy is very safe, it can be associated rarely with morbidity and it is not cheap compared to other less invasive diagnostic routes and hence a pragmatic approach is required in children.
Читать дальше

 KEY POINTS
KEY POINTS