3.5.4 Combinatorial Chemistry Technique Used to Mitigate Oxygen Inhibition for Low Energy UV-A Cure Resulting in Tack-Free Surfaces
As can be seen from above that oxygen inhibition is an issue that needs to be reconciled if one is going to cure UV nail gels. As was shown in Table 3.1the increase of PI concentration can help override oxygen inhibition. However, Arceneaux does not mention the most efficient type of PI that should be used to obtain the maximum efficiency of the PI as well as overriding the oxygen inhibition issue [6]. Besides the PI issue, the types and variety of oligomers and monomers used in the formulations can have a dramatic effect on cure. Such a complex problem was essentially solved by researchers in the UV cure automotive refinish industry where the same issue was faced in developing a UV cure product using only UV-A light sources and formulations that could override the oxygen inhibition issues.
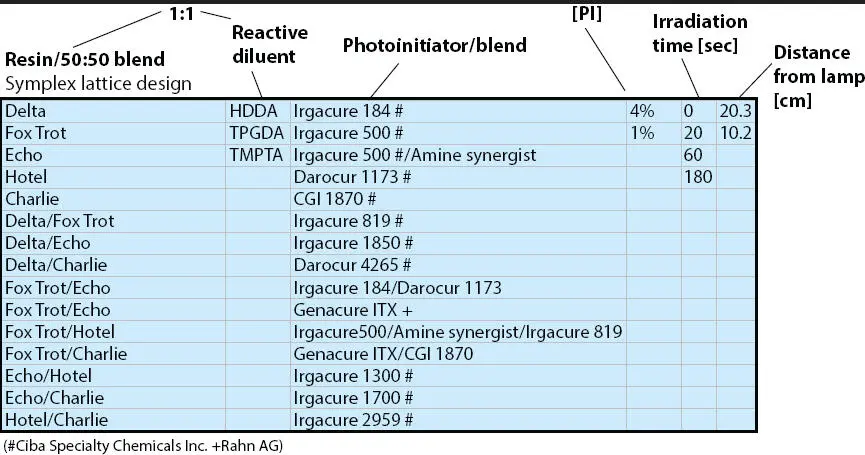
As can be seen in Table 3.2a screening was done using 6 independent factors, namely UV curable resins, reactive diluents, PI, PI levels, irradiation time, and distance from the lamp. In this evaluation the so-called Edisonian method meets the combinatorial world of chemistry. In this analysis, over 15,000 coatings were evaluated looking for the sweet spot and synergistic effects between these 6 independent factors.
It is obvious from Figure 3.12that the only way to obtain the full surface cure (and the minimization of oxygen inhibition) of a UV-A system is to run massive amounts of tests to see if a combination or synergistic effect can be found. Figure 3.12x-axis shows the PI and PI combinations that were evaluated. Also in Figure 3.12the y-axis shows the oligomers and oligomer combinations that were evaluated. In this test protocol the R2/R5 (oligomer) along with IRGACURE ®819 showed a synergistic effect. Even though the test resins were evaluated in the past, the fact they cured as well as they did without surface tack (i.e. surface inhibition by oxygen) was a surprise. All of this testing was done on clear coatings followed by evaluation of pigment systems. The pigmented systems were evaluated at a P/B (Pigment to Binder ratio) = 0.8, ≤75 µm dry, 2 minutes under a 250 W UV-A lamp and 25 cm distance. The resultant primers had no surface tack and required no surface solvent wipe before the traditional sanding step.
Table 3.2 Factors and levels covered in the search for formulations exhibiting tack-free surfaces (due to oxygen inhibition) when UV cured using a low intensity 250 W UV-A lamp. The screening was done using the following 6 independent factors: UV curable resins, reactive diluents, PIs, PI levels, irradiation time and distance from lamp.
The development work also revealed in these papers [7, 8] that showed the development of a one-component (1K; komponente; Ger.) UV-A curable clear coat. Issues that these papers raised regarding developing this 1K UV-A curable clear coat are: 1) lack of flexibility in polymers based on radical polymerization, 2) keep the unreacted double bonds very low(≤10%) due to post-cure issues, 3) formulation and coating color due to visible light PI, and 4) primer, base coat and clear coat compatibility [7, 8].
Curing a UV nail gel with low wattage GA-FL or LED UV certainly needs more in-depth laboratory work as shown by these researchers [7, 8].
3.6 How to Formulate a UV-A Cure Nail Gel
With the obvious issues stated in section 5 the formulator needs to be cognizant of the following questions,
1 a. Which oligomers should one use to give the best performance during cure with the least amount of oxygen inhibition?
2 b. Which monomers should one use to give the best performance with the minimum amount of oxygen inhibition?
3 c. Which PIs should one use to utilize the wavelength emitted by the GA-FL and LED light sources?
4 d. From an industrial hygiene (IH) standpoint which are the safest acrylate monomers that should be evaluated in developing a nail gel UV-A cured system?
As was shown earlier in Figure 3.12the type of oligomer used will have a strong impact on cure and performance. Targeting oligomers that respond best to low wattage GA-FL and LED units should be the formulation chemists top priority.
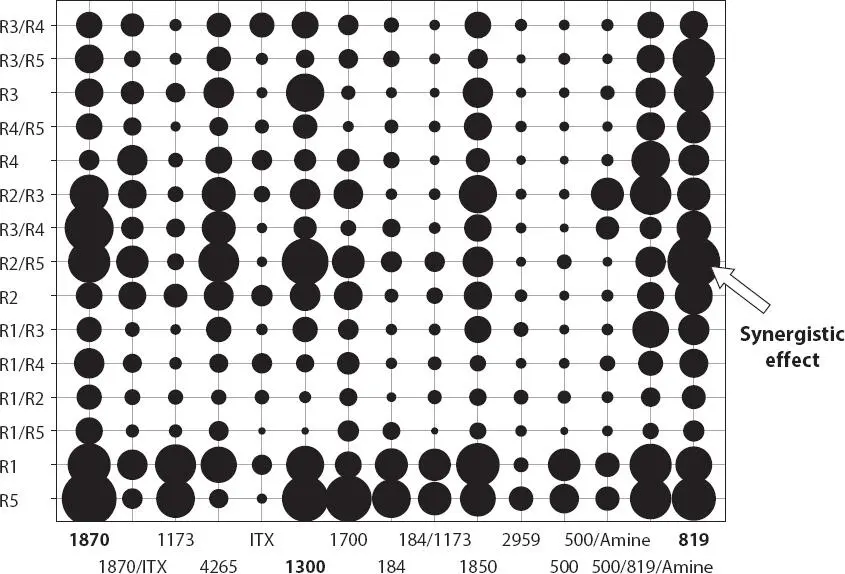
Figure 3.12 High throughput primary screening results based on the evaluation of over 25,000 coatings followed by a statistical analysis. The x-axis shows the PI and PI combinations that were evaluated. The y-axis shows the oligomers and oligomer combinations that were evaluated. Shown is the average predicted surface cure for all resin-photoinitiator combinations after curing using a 250 W UV-A light source. The average is taken over all other parameters screened in this experiment. Thus, each circle represents an average of 48 values (3 reactive diluents, 2 photoinitiator concentrations, 4 irradiation times and 2 lamp distances). The bigger the circle the better the surface cure.
3.6.1 Formulating with (Meth) Acrylate Monomers
Selection of the acrylate monomer needs to be carefully considered. As can be seen in Figure 3.13a multitude of acrylated monomers are available to the formulator.
It was found [9] that compared to acrylates, methacrylates are much less sensitive to oxygen inhibition. Model compound systems were evaluated to determine the effect of ether groups on polymerization inhibition. They found that the reduction of oxygen inhibition occurs by a series of chain transfer/oxygen scavenging reactions [9].
3.6.2 Formulating with the Proper Photoinitiator
The ability to cure the coating with low intensity UV-A light sources requires PIs that operate within the wavelength of the GA-FL and LED units available in the cosmetic marketplace. As was shown in Figure 3.6and Figure 3.7the selection criteria for pigmented UV-A formulations require that the PIs used operate at 380 nm and above.
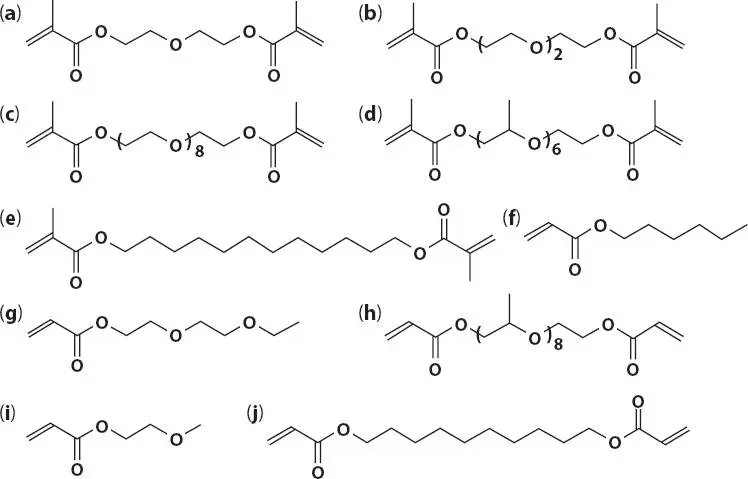
Figure 3.13 Chemical structures of methacrylates and acrylates that could be considered in UV nail gel technology. The following structures are: (a) DEGDMA (Di (Ethylene Glycol) Dimethacrylate), (b) TEGDMA (Tri (Ethylene Glycol) Dimethacrylate), (c) PEGDMA (Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Dimethyacrylate), (d) PPGDMA (Poly(Propylene Glycol) Dimethacrylate, (e) DDDMA (1,12-Dodecane Dimethacrylate), (f) HA (Hexylacrylate) (g) DEGEEA (Diethylene Glycol Ethylether Acrylate), (h) PPGDA (Poly (Propylene Glycol) Diacrylate), (i) EGMEA (Ethylene Glycol Methylether Acrylate) and (j) DDA (1,10-Decane Diacrylate).
As one can see in Figure 3.14the best choice for both nail gel UV-A cure light units (GA-FL and LED) is the bis-acylphosphine oxide (BAPO) PI. The BAPO PI cleaves to give a two-photon photo-bleachable free radicals once exposed to either the UV-A GA-FL or LED unit. This PI has wide wavelength overlap and will function at 365 nm, 380 nm and 390 nm. The photobleaching enhances the optical penetration and results in lower delta E (lower yellowing of the cured coatings) values. In addition to this performance shown in Figure 3.6and Figure 3.7the BAPO also helps in the curing of pigmented coatings as shown in Figure 3.15. Since BAPO PI activates at 365 nm, 380 nm and 390 nm colored pigmented coatings will through-cure since the pigments absorbance is below these wavelengths.
Читать дальше















