These general orders given—orders that betray no grasp of the nearness of the issue—Wellington went off to the Duchess of Richmond’s ball in what the impartial historian cannot doubt to be ignorance of the great stroke which Napoleon had so nearly brought off upon that very day, and would certainly attempt to bring off upon the next.
In the midst of the ball, or rather during the supper, definite news came in that the French army had crossed the river Sambre, and had even pushed its cavalry as far up the Brussels road as Quatre Bras.
The Duke does not seem to have appreciated even then what that should mean in the way of danger to the Prussians, and indeed of the breaking of the whole line. He left the dance at about two in the morning and went to bed.
He was not long left in repose. In the bright morning sunlight, four hours afterwards, he was roused by a visitor from the frontier, and we have it upon his evidence that the Duke at last understood what was before him, and said that the concentration of his forces must be at Quatre Bras.
In other words, Wellington knew or appreciated extremely tardily on that Friday morning about six that the blow was about to fall upon his Prussian allies to the south and east, and that it was the business of his army upon the west to come up rapidly in succour.
As will be seen in a moment, he failed; but it would be a very puerile judgment of this great man and superb defensive General to belittle his place in the history of war upon the basis of even such errors as these.
True, the error and the delay were prodigious and, in a fashion, comic; and had Napoleon delivered upon the Thursday afternoon, as he had intended, an attack which should have defeated the Prussians before him, Wellington’s error and delay would have paid a very heavy price.
As it was, Napoleon’s own delay in crossing the Sambre made Wellington’s mistake and tardiness bear no disastrous fruit. The Duke failed to succour the Prussians. His troops, scattered all over Western Belgium, did not come up in time to prevent the defeat of his allies at Ligny. But he held his own at Quatre Bras; and in the final battle, forty-eight hours later, the genius with which he handled his raw troops upon the ridge of Mont St. Jean wiped out and negatived all his strategical misconceptions of the previous days.
From this confusion, this partial delay and error upon Napoleon’s part, this ignorance upon Wellington’s of what was toward, both of which marked Thursday the 15th, we must turn to a detailed description of that morrow, Friday the 16th, which, though it is less remembered in history than the crowning day of Waterloo, was, in every military sense, the decisive day of the campaign.
We shall see that it was Napoleon’s failure upon that Friday completely to defeat, or rather to destroy, the Prussian force at Ligny—a failure largely due to Wellington’s neighbouring resistance at Quatre Bras—which determined the Emperor’s final defeat upon the Sunday at Waterloo.
Table of Contents
Friday the 16th of June
Quatre Bras and Ligny
We have seen what the 15th of June was in those four short days of which Waterloo was to be the climax. That Thursday was filled with an advance, rapid and unexpected, against the centre of the allied line, and therefore against that weak point where the two halves of the allied line joined, to wit, Charleroi and the country immediately to the north of that town and bridge.
We have further seen that while the unexpectedness of the blow was almost as thorough as Napoleon could have wished, the rapidity of its delivery, though considerable, had been less than he had anticipated. He had got by the evening of the day not much more than three-quarters of his forces across the river Sambre, and this passage, which was mapped out for completion before nightfall, straggled on through the whole morning of the morrow—a tardiness the effects of which we shall clearly see in the next few pages.
Napoleon’s intention, once the Sambre was crossed, was to divide his army into two bodies: one, on the left, was to be entrusted to Ney; one, on the right, to Grouchy. A reserve, which the Emperor would command in person, was to consist in the main of the Imperial Guard.
The left-hand body, under Ney, was to go straight north up the great Brussels road.
Napoleon rightly estimated that he had surprised the foe, though he exaggerated the extent of that surprise. He thought it possible that this body to the left, under Ney, might push on to Brussels itself, and in any case could easily deal with the small and unprepared forces which it might meet upon the way. Its function in any case, whether resistance proved slight or formidable, was to hold the forces of Wellington back from effecting a junction with Blucher and the Prussians.
Meanwhile, the right-hand body, under Grouchy, was to fall upon the extremity of the Prussian line and overwhelm it.
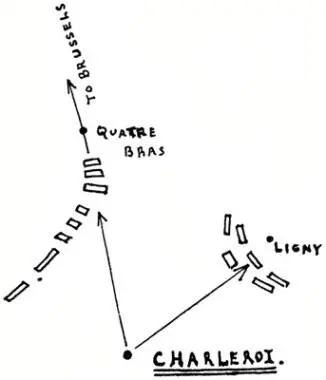
Such an action against the head of the long Prussian cordon could lead, as the Emperor thought, to but one of two results: either the great majority of the Prussian force, coming up to retrieve this first disaster, would be defeated in detail as it came; or, more probably, finding itself cut off from all aid on the part of Wellington’s forces to the west and its head crushed, the long Prussian line would roll up backwards upon its communications towards the east, whence it had come.
In either case the prime object of Napoleon’s sudden move would have been achieved; and, with the body upon the left, under Ney, pushing up the Brussels road, the body upon the right, under Grouchy, pushing back the head of the Prussian line eastward, the two halves of the Allies would be separated altogether, and could later be dealt with, each in turn. The capital disadvantage under which Napoleon suffered—the fact that he had little more than half as many men as his combined enemies—would be neutralised, because he would, after the separation of those enemies into two bodies, be free to deal with either at his choice. Their communications came from diametrically opposite directions, 5and, as the plan of each depended upon the co-operation of the other, their separation would leave them confused and without a scheme.
Napoleon in all this exaggerated the facility of the task before him; but before we go into that, it is essential that the reader should grasp a certain character in all military affairs, to misunderstand which is to misread the history of armies.
This characteristic is the necessary uncertainty under which every commander lies as to the disposition, the number, the order, and the information of his opponents.
It is a necessary characteristic in all warfare, because it is a prime duty in the conduct of war to conceal from your enemy your numbers, your dispositions, and the extent of your information. It is a duty which every commander will always fulfil to his best ability.
It is therefore a characteristic, be it noted, which no development of human science can conceivably destroy, for with every advance in our means of communicating information we advance also in our knowledge of the means whereby the new means of communication may be interrupted. An advantage over the enemy in the means one has of acquiring knowledge with regard to him must, of course, always be of supreme importance, and when those means are novel, one side or the other is often beforehand for some years with the new science of their use. When such is the case, science appears to uninstructed opinion to have changed this ancient and fixed characteristic which is in the very nature of war. But in fact there has been no such change. Under the most primitive conditions an advantage of this type was of supreme importance; under conditions the most scientific and refined it is an advantage that may still be neutralised if the enemy has learnt means of screening himself as excellent as our means of discovering him. Even the aeroplane, whose development in the modern French service has so vastly changed the character of information, and therefore of war, can never eliminate the factor of which I speak. A service possessed of a great superiority in this new arm will, of course, be the master of its foe; but when the use of the new arm is spread and equalised among all European forces so that two opposing forces are equally matched even in this new discovery, then the old element of move and countermove, feint, secrecy, and calculated confusion of an adversary, will reappear. 6
Читать дальше













