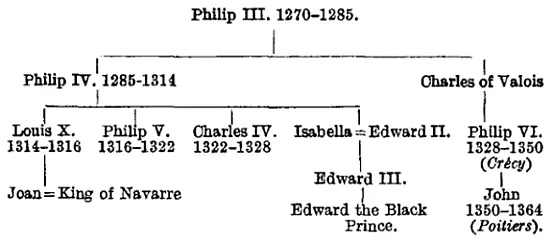
Charles IV. had been the son of King Philip IV., and Philip of Valois was the son of Charles of Valois, Philip IV.’s brother. Philip of Valois was therefore the eldest in unbroken male descent of the house.
It might be claimed (and it was claimed by Edward III.) that the daughters of elder brothers and their issue should count before the sons of younger brothers. Now there were two female heiresses or their issue present as against Philip of Valois. Charles IV., the king just dead, had a sister Isabella, and Isabella was the mother of Edward III. of England.
But an elder brother to Charles IV., namely, Louis X., had himself left a daughter, who was now the Queen of Navarre.
If this principle that the daughter or the issue of the daughter of an elder brother should count before the male issue of a younger brother had been granted in its entirety, Edward would have had no claim, because this elder brother of Charles IV., Louis X., had had issue—that daughter, Joan, the wife of the King of Navarre. So Edward qualified this first general principle, that one could inherit through women, by another principle, to wit, that, though the claim to the throne should proceed through the daughters of elder brothers rather than through the sons of younger ones, yet the throne could itself only actually be held by a male!
By this tortuous combination Edward III. advanced his claim. His mother had been the grand-daughter of Philip III. of France, and he was a male. Her father was the elder brother of Philip of Valois’ father, so he claimed before Philip of Valois.
The whole scheme is apparent from the following table:—
But, I repeat, we must not take Edward’s political claim too seriously. His real object was not so much to establish himself upon the throne of France and to create a great French-speaking united monarchy of French and British under the single rule of the Plantagenets, as to try a great adventure and to see what would come of it.
It was this that gave to Edward’s wars the character not of campaigns with a fixed object, but Great Raids, the very successes of which were unexpected and only half fruitful. It was this, again, which made him so uncertain and vacillating as to how he should use those successes when they came; which made him suggest now this, now that basis for peace after each victory, but never to insist very particularly, however surprising and thorough his work in the field, upon the French throne.
It was this, again, which gave to the actual results of his battles haphazard consequences, as it were, the most notable and permanent of which was the English hold upon Calais. And it was this which always left so huge a disproportion between the object he in theory desired to obtain and the forces with which he set out to attain it. To sum up, we shall only understand the victory of Crécy and the succeeding twin victory of Poitiers ten years later, if we conceive of the whole business as something of a tournament rather than a true political or even dynastic struggle.
Further, we must always remember that the leaders upon both sides came of one society, were of one speech and of one manner, often closely related in blood. We must remember that it was no desertion for a French lord to serve the King of England, and that even brothers would be found (as were the two Harcourts) honourably attached, according to the ideas of the time, to opposing forces.
Beneath this social aspect of the wars there was, of course, the growing national sentiment of the French and of the English. Most of the men who fought against Edward at Crécy, especially of the obscure men, thought of Paris as the only possible seat of authority, and of the Valois as their only possible king. All the Archers at Crécy, and many of the squires there—and a good half even of the forces at Poitiers—were English-speaking, and had no experience of life save that confined to this island, up to the moment when they set out for the Great Raids upon the Continent.
As the Hundred Years’ War proceeded, as it approached its second phase in which Henry V. was actually successful in obtaining the Crown of France, or rather the reversion of it, the national feeling was growing rapidly upon either side, and by the time of Joan of Arc’s campaign and of the subsequent loss of Normandy by the Plantagenets, everyone outside the small governing class of either country had come to think of the business as a national one upon either side. But with Crécy it was not so, and we must approach the military problems of Crécy with the political provision in mind that the whole affair of that battle and of its immediate successors was a feudal occupation—one had almost said pastime—engaged within the circle of that widespread French-speaking nobility, common to and intermarried between Gaul and Britain, which, for three hundred years, ruled society from the Grampians to the Mediterranean.
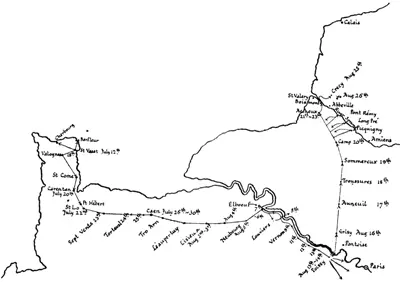
Table of Contents
The Campaign of Crécy took place within a district of France contained by an east and west base 200 miles in length and an eastern border north and south 160 miles in length, and sketched in the map opposite.
The rectangular parallelogram so formed is nearly equally divided between land and sea, the south-eastern half being a portion of Northern France, and the north-western half the English Channel. The land half is thus roughly triangular, having Paris at its extreme south-eastern corner, Calais at its extreme north-eastern, the neighbourhood of Avranches with St. Malo Bay at its south-western corner. It includes part of the provinces of Normandy, the Ile de France, Picardy and Artois, and part, or all, of the modern departments of the Manche, Orne, Calvados, Eure, Seine-et-Oise, Seine, Seine-Inférieure, Oise, Somme, and Pas-de-Calais.
It will be seen that this territory is nearly evenly divided by the River Seine, and the campaign of Crécy is also divided by that river in the sense that the English advance took place wholly to the west of it, and the English retreat wholly to the east of it.
The campaign, as a whole, resolves itself (up to and including the Battle of Crécy, which is the subject of this book, and excluding the continuation of the march after Crécy, and the capture of Calais) into an advance from the Channel coast to Paris, and a retreat from Paris to the Channel again, the two portions being divided by the crossing of the Seine at Poissy. The advance leaves the coast at the summit of that projection of Normandy called the Cotentin, and proceeds a little south of east towards Paris, the walls of which are reached by its outermost skirmishers, while the main army crosses the Seine at Poissy. The retreat is effected from Poissy northward to the victorious field of Crécy, and later from Crécy, on the same line, to the siege and capture of Calais.
The time occupied from the day of landing to the day of the Battle of Crécy inclusive, is but forty-six days, of which not quite two-thirds are taken up by advance, and rather more than a third by the retreat. The English troops landed on Wednesday, July 12th, 1346. They crossed the Seine at Poissy upon August 14th. They fought at Crécy upon Saturday, August 26th.
The total distance traversed by the main body in these two limbs of the campaign is instructive as showing the leisure of the first part, its advance, and the precipitancy of the second part, its retreat.
Читать дальше














