ED physicians can manage many of the complications from GI diversions such as small parastomal hernias, uncomplicated prolapses, and dermatitis. Cases of early postoperative complications and any concern of ischemia require immediate surgical consultation.
1 1 Bafford, A.C. and Irani, J.L. (2013). Management and complications of stomas. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 93: 145–166.
2 2 Fine, J.A., Cronan, K.M., and Posner, J.C. (2010). Approach to the care of the technology‐assisted child. In: Textbook of Pediatric Emergency Medicine, 6e (eds. G.R. Fleisher and S. Ludwig), 1510–1513. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins.
3 3 Landman RG. Routine care of patients with an ileostomy or colostomy and management of ostomy complications (ed. Weiser M). UpToDate, 2016.
4 4 Martin, S.T. and Vogel, J.D. (2012). Intestinal stomas. Indications, management, and complications. Adv. Surg. 46: 19–49.
5 5 Shabbir, J. and Britton, D.C. (2010). Stoma complications: a literature overview. Colorectal Dis. 12: 958–964.
3 Management of the Bariatric Surgery Patient in the Emergency Department
Megan Lavoie1,2 and Joy Collins1,3
1 Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA
2 Division of Emergency Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, USA
3 Division of General and Thoracic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Obesity, defined as BMI > 35 kg/m 2, is becoming increasingly prevalent in the US and globally. According to the most recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) data, in the US, >35% of adults in the US are obese and close to 20% of children meet the definition of obesity or severe obesity (BMI > 40 kg/m 2). Obesity brings with it significant physical and psychosocial comorbidities that carry a large health burden: type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and orthopedic complications, among others, have been seen in severely obese adolescents as well as in adults. Medical and psychological management alone is often not adequate to achieve significant, sustainable weight loss. Surgical weight loss techniques are increasingly being offered to severely obese patients experiencing comorbid conditions. According to the American Society of Metabolism and Bariatric Surgeries, in 2015, over 195 000 bariatric surgeries were performed in the US in adults or adolescents. Over 50% of patients had the gastric sleeve procedure, and approximately 25% underwent the Roux‐en‐y‐gastric bypass (RYGB). The adjustable gastric band is another surgical option for severe obesity in adults but has not been approved for use in adolescents under 18 years of age.
RYGB, laparoscopic adjustable gastric band (LAGB), and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) are the most commonly performed weight loss surgeries ( Figures 3.1– 3.3). Gastric band and sleeve gastrectomy are restrictive procedures (meaning that they cause limitation to food intake), while the RYGB has been described as a procedure whose effects are related to a combination of gastric restriction and intestinal malabsorption. Despite these classifications, it has become clear that all weight loss procedures have metabolic effects, which may contribute more significantly to postoperative weight loss than can be explained simply by gastric restriction and intestinal malabsorption alone.
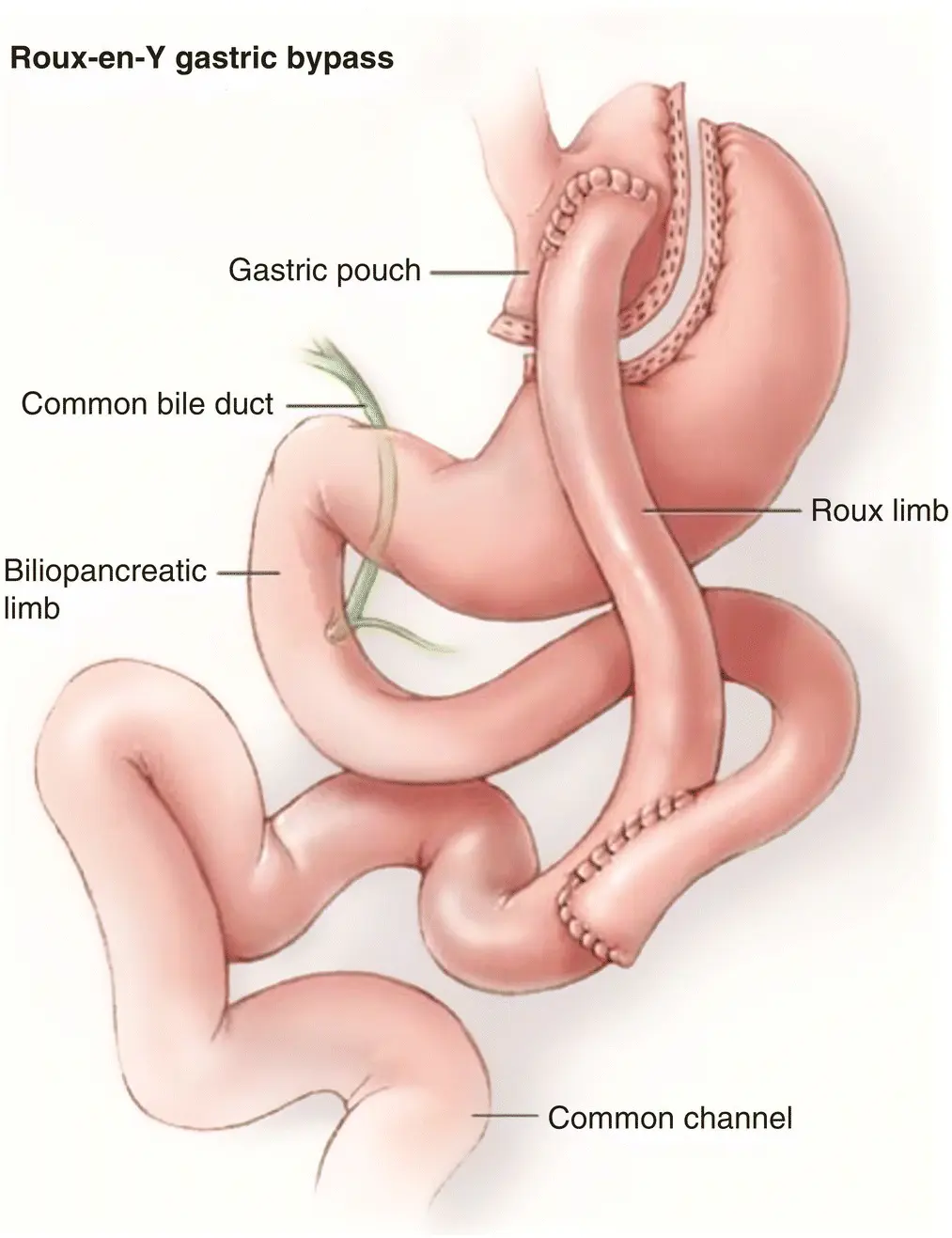
Figure 3.1 Pencil drawing of RYGB.
Source: Penn Medicine
In the RYGB, a small stomach pouch is created and the jejunum is divided. The distal limb of the jejunum is then connected directly to the small gastric pouch, bypassing the rest of the stomach and the proximal intestine. The small bowel is then placed in continuity with itself more distally, thereby providing a route for biliopancreatic secretions to mix with food. The small size of the stomach limits the capacity of food intake, while calorie and fat absorption is limited as the majority of the stomach and duodenum are bypassed.
The LAGB is a laparoscopic procedure where an inflatable silicone band is placed around the upper part of the stomach, creating a tiny new stomach pouch that limits the capacity to take in large amounts of food. The band position results in a small stomach outlet that leads to slowing of upper gastric emptying and increases the sensation of satiety. The band is able to be inflated and deflated by injecting a needle through the skin into a port connected to the band to adjust the size of the opening from the gastric pouch. Gastric banding has the benefit of being relatively reversible and minimally invasive, as it requires no cutting or stapling of the stomach or bowel ( Figure 3.4).
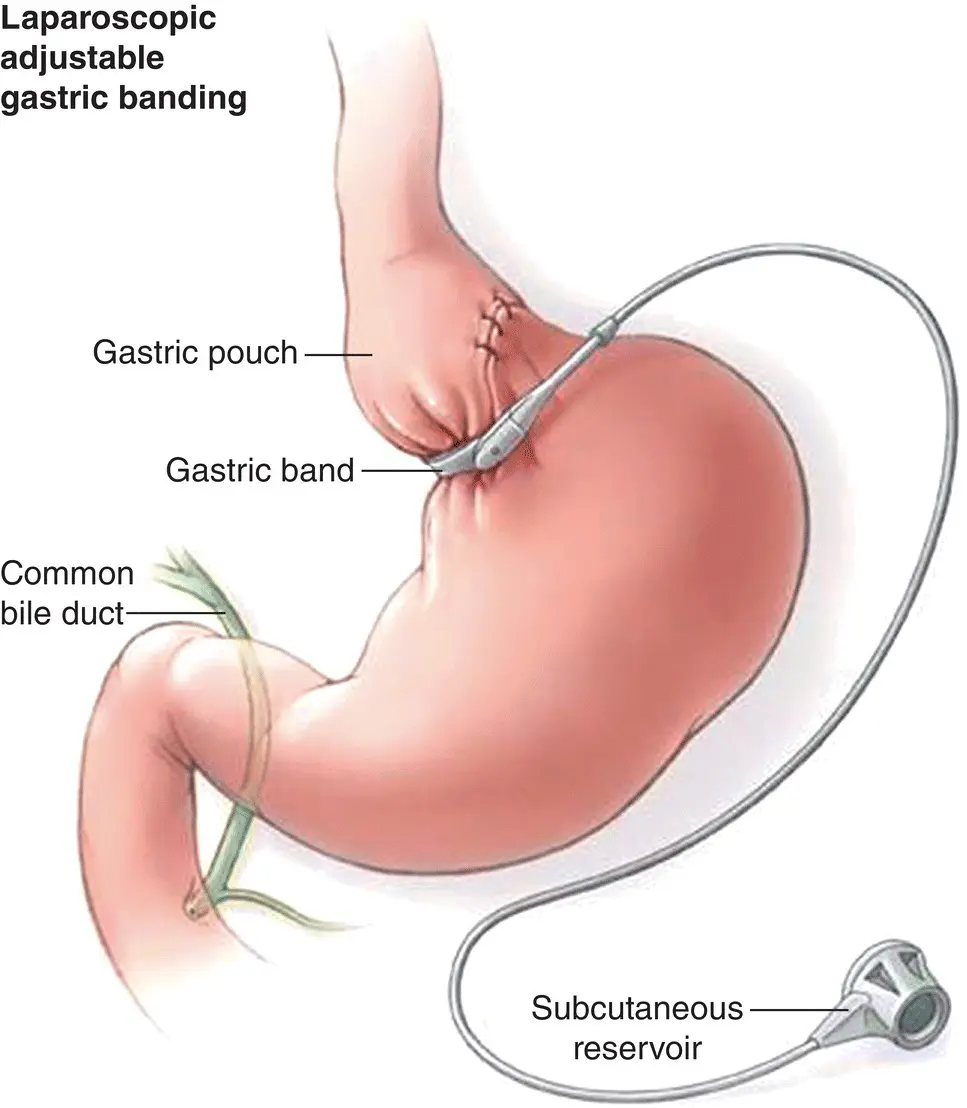
Figure 3.2Pencil drawing of LAGB.
Source: Swedish Health Services
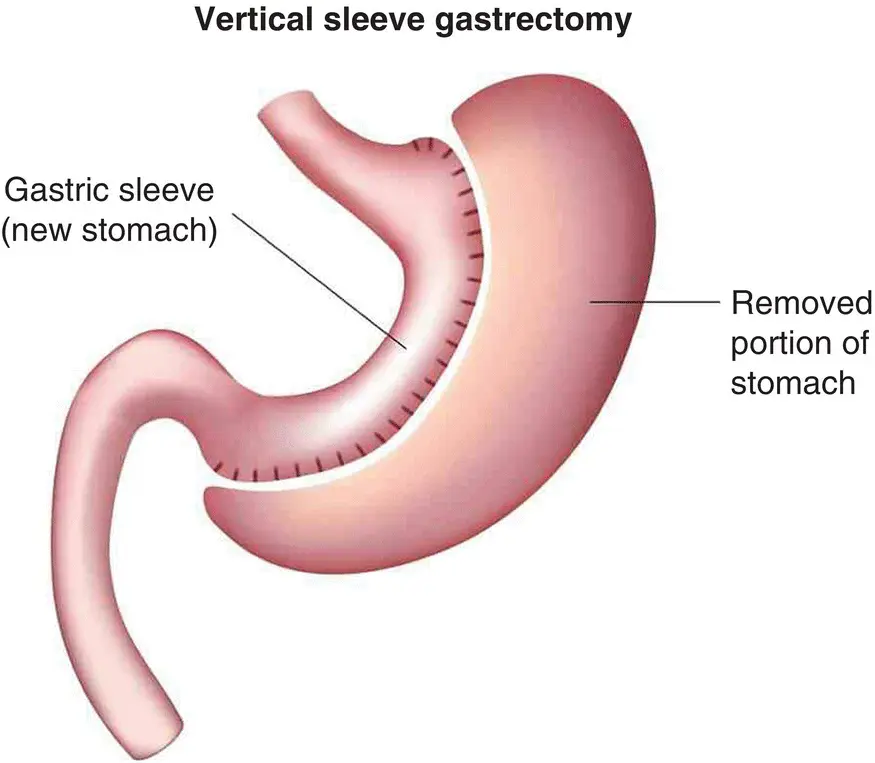
Figure 3.3 Pencil drawing of LSG.
Source: UNC Medical Center
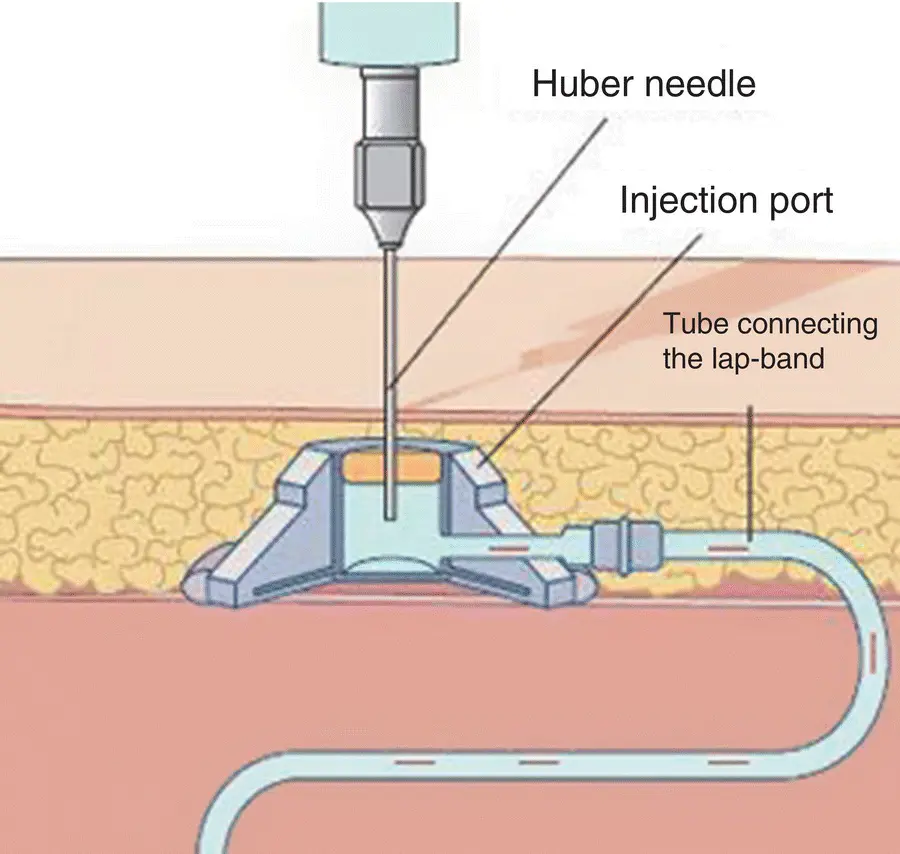
Figure 3.4 Pencil drawing of how to deflate port on LAGB.
Source: Reproduced from Hamdan et al. (2011)
The LSG is performed by removing 75–80% of the stomach and leaving a long gastric tube or sleeve of the stomach, thereby restricting intake. This procedure was initially part of a staged approach to more complex weight ‐loss procedures but has been shown to offer significant weight loss and improvement of comorbid conditions such that it is currently offered as a stand‐alone procedure.
Bariatric surgery is available to patients with severe obesity who have a low probability of successful weight loss with nonoperative measures, and who demonstrate motivation to continue medical treatment and lifestyle changes after surgery. In adults, criteria for bariatric surgery include those with a BMI > 40 or those with a BMI > 35 with comorbid diseases. As the risks of bariatric surgery in adolescents are not yet completely understood, adolescents are typically offered bariatric surgery primarily if they have comorbidities. Adolescents with severe comorbidities such as type 2 DM, moderate to severe sleep apnea, or pseudotumor may be considered surgical candidates with a BMI as low as 35. Adolescents with mild comorbidities and a BMI of 40 or greater are also potential candidates for weight loss surgery. While degree of obesity and weight‐related medical problems are the most basic determinants of potential candidacy, adolescent patients should undergo a thorough workup to rule out medically reversible causes of obesity or contraindications to surgery. The workup typically involves evaluation by a multidisciplinary team, including a pediatric/adolescent medical weight loss specialist, a bariatric surgeon (or pediatric surgeon with expertise in performing bariatric procedures), a dietician, a mental health professional with experience in evaluating bariatric patients, an exercise specialist, and others. In addition, most patients undergo an intensive medical weight management program throughout the evaluation period prior to proceeding to weight loss surgery.
Читать дальше
















