1 Cover
2 Title Page Series Editor Robert Baptist
3 Copyright First published 2021 in Great Britain and the United States by ISTE Ltd and John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Apart from any fair dealing for the purposes of research or private study, or criticism or review, as permitted under the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988, this publication may only be reproduced, stored or transmitted, in any form or by any means, with the prior permission in writing of the publishers, or in the case of reprographic reproduction in accordance with the terms and licenses issued by the CLA. Enquiries concerning reproduction outside these terms should be sent to the publishers at the undermentioned address: ISTE Ltd 27-37 St George’s Road London SW19 4EU UK www.iste.co.uk John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 111 River Street Hoboken, NJ 07030 USA www.wiley.com © ISTE Ltd 2021 The rights of Thien-Phap Nguyen to be identified as the author of this work have been asserted by him in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988. Library of Congress Control Number: 2020948483 British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data A CIP record for this book is available from the British Library ISBN 978-1-78630-321-9
4 Introduction
5 1 Semiconductor Theory
1.1. Introduction
1.2. Review of the basic concepts of crystalline semiconductors
1.3. P–N junction
1.4. Impurities and defects
1.5. Metal/semiconductor contact
1.6. Semiconductors under non-equilibrium conditions
1.7. Space charge current
1.8. Hopping conduction
6 2 Materials
2.1. Introduction 2.2. Organic materials
2.3. Conjugated polymers
2.4. Energy bands
2.5. Small molecules
2.6. Design and engineering of organic materials
2.7. Hybrid materials or nanocomposites
2.8. Transparent and conductive materials
2.9. Materials for encapsulation
7 3 Optical Processes
3.1. Introduction 3.2. Interaction between light and molecules
3.3. Optical processes
3.4. Excitons
3.5. Experimental techniques
8 4 Electronic Processes
4.1. Introduction 4.2. Charge carrier injection process
4.3. Charge transport process
9 5 Interface Processes
5.1. Introduction 5.2. Formation of organic semiconductor/metal interfaces
5.3. Surface characterization techniques
5.4. Interface engineering
5.5. Conclusion
10 List of Acronyms
11 References
12 Index
13 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1. Generation and recombination process
Figure 1.2. Energy band diagram of a P–N junction. For a color version of this f...
Figure 1.3. Structural defects in semiconductors: a) vacancy; b) interstitial at...
Figure 1.4. Trapping and recombination mechanisms: a) capture of an electron; b)...
Figure 1.5. The pulse applied to the junction and the variation of the junction’...
Figure 1.6. Changes in the SCR of the junction during the trapping process: 1) b...
Figure 1.7. The process of light emission in SCs, with and without defects. For ...
Figure 1.8. The parameters in the energy band diagram for metals and SCs. For a ...
Figure 1.9. The parameters in the energy band diagram for metals and SCs. For a ...
Figure 1.10. Schottky barrier at a metal/SC interface with the Schottky effect
Figure 1.11. Electron transport in a contact between a metal and an N-type SC. F...
Figure 1.12. The change in the concentration of excess carriers as a function of...
Figure 1.13. Diffusion of excess carriers within the thickness of an SC lit on o...
Figure 1.14. Electronic conduction regime of the space-charge limited current. a...
2 Chapter 2Figure 2.1. Basic structure of an SC-based light-emitting diode: (a) inorganic S...Figure 2.2. Structures of polymers. For a color version of this figure, see www....Figure 2.3. Trans and cis configurations of polyacetylene Figure 2.4. Hybridization of the carbon atom and hybridization mechanism of sp2....Figure 2.5. Atomic orbitals π and π * of the π bond Figure 2.6. Structure of polyacetylene: a) chemical bonds between atoms; b) orbi...Figure 2.7. Structure of benzene: a) chemical bonds between atoms; b) orbitals o...Figure 2.8. Molecular structures of poly(phenylene) Figure 2.9. Different techniques for deposition of polymer films in a solution: ...Figure 2.10. Wave functions of atomic and molecular orbitals Figure 2.11. Energy levels of the isolated atom, the molecule formed by two atom...Figure 2.12. Representation of solitons: a) energy of a dimer consisting of two ...Figure 2.13. Formation of bipolarons by solitons. For a color version of this fi...Figure 2.14. Doping mechanisms for N-type and P-type organic SCs. For a color ve...Figure 2.15. Molecular structure of small molecules of benzene cycles Figure 2.16. Examples of polymers and small molecules and their use in electroni...Figure 2.17. Types of chain arrangement in poly(hexylthiophene) Figure 2.18. Preparation of composites by dispersion method: a) materials; b) di...Figure 2.19. Structure of a polyoctahedral silsesquioxane (POSS) Figure 2.20. Nanocomposites using a nanostructured substrate: (a) nanostructured...Figure 2.21. a) Nanowires; b) nanorods; c) nanorod arrays Figure 2.22. Hydrothermal fabrication of ZnO nanorods: a) buffer layer-covered s...Figure 2.23. Transparent and conductive electrodes: a) unordered array of metal ...Figure 2.24. Encapsulation of organic electronic devices: a) by a glass slide; b...
3 Chapter 3Figure 3.1. Potential energy of a diatomic molecule as a function of the inter-a...Figure 3.2. Diagram of the energy and electronic transitions in the process of a...Figure 3.3. Energy diagram and possible electronic transitions in a molecule acc...Figure 3.4. Overlap of the emission spectrum of the donor molecule D and the abs...Figure 3.5. Process of energy transfer between molecules: a) transfer by Förster...Figure 3.6. Excitons: a) Frenkel; b) charge transfer; c) Wannier–Mott. For a col...Figure 3.7. The steps of the exciton formation: a) initial electron–hole pair; b...Figure 3.8. Schematic representation of rate constants of photophysical processe...Figure 3.9. Transitions in the processes of: a) infrared absorption; B) Rayleigh...
4 Chapter 4Figure 4.1. Schematic representation of the movement of charge carriers in an or...Figure 4.2. Injection process of charge carriers in a simple diode structure. Fo...Figure 4.3. Energy band diagram of electronic devices: a) electron-only; b) hole...Figure 4.4. Energy band diagram of the electronic device with transport layers o...Figure 4.5. a) Intra-chain and inter-chain movements of electrons; b) energy dia...Figure 4.6. Density of states following the Gaussian disorder model (GDM). For a...Figure 4.7. a) Schematic setup for measuring time of flight; b) variation of non...Figure 4.8. a) CELIV measurement setup; b) applied voltage ramp and CELIV spectr...Figure 4.9. The conduction regimes limited by space charges in an SC: a) contain...Figure 4.10. Types of trap distributions: Gaussian and exponential Figure 4.11. Schematic representation of the effective capture cross-section: a)...Figure 4.12. Steps for measuring the thermally stimulated current Figure 4.13. The principle of fractional TSC current measurement: temperature cy...Figure 4.14. The principle of charge-based deep-level transient spectroscopy: a)...Figure 4.15. Variati on of capacitance C ( ω ) and its derivative 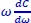 as a function o...Figure 4.16. Variation of
as a function o...Figure 4.16. Variation of 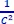 as a function of the direct voltage VDC . 1) trap-fre...
as a function of the direct voltage VDC . 1) trap-fre...
Читать дальше

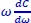 as a function o...Figure 4.16. Variation of
as a function o...Figure 4.16. Variation of 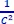 as a function of the direct voltage VDC . 1) trap-fre...
as a function of the direct voltage VDC . 1) trap-fre...










