 The opposite of the top-down approach is the bottom-up approach. In a bottom-up approach environment, the IT staff makes security decisions directly without input from senior management. The bottom-up approach is rarely used in organizations and is considered problematic in the IT industry.
The opposite of the top-down approach is the bottom-up approach. In a bottom-up approach environment, the IT staff makes security decisions directly without input from senior management. The bottom-up approach is rarely used in organizations and is considered problematic in the IT industry.
Security management is a responsibility of upper management, not of the IT staff, and is considered an issue of business operations rather than IT administration. The team or department responsible for security within an organization should be autonomous. The information security (InfoSec) team should be led by a designated chief information security officer (CISO) who reports directly to senior management, such as the chief information officer (CIO), the chief executive officer (CEO), or the board of directors. Placing the autonomy of the CISO and the CISO's team outside the typical hierarchical structure in an organization can improve security management across the entire organization. It also helps avoid cross-department and internal political issues. The term chief security officer (CSO) is sometimes used as an alternative to CISO, but in many organizations the CSO position is a subposition under the CISO that focuses on physical security. Another potential term for the CISO is information security officer (ISO) , but this also can be used as a subposition under the CISO.
 The chief information officer (CIO) focuses on ensuring information is used effectively to accomplish business objectives. The chief technical officer (CTO) focuses on ensuring that equipment and software work properly to support the business functions.
The chief information officer (CIO) focuses on ensuring information is used effectively to accomplish business objectives. The chief technical officer (CTO) focuses on ensuring that equipment and software work properly to support the business functions.
Elements of security management planning include defining security roles; prescribing how security will be managed, who will be responsible for security, and how security will be tested for effectiveness; developing security policies; performing risk analysis; and requiring security education for employees. These efforts are guided through the development of management plans.
The best security plan is useless without one key factor: approval by senior management . Without senior management's approval of and commitment to the security policy, the policy will not succeed. It is the responsibility of the policy development team to educate senior management sufficiently so managers understand the risks, liabilities, and exposures that remain even after security measures prescribed in the policy are deployed. Developing and implementing a security policy is evidence of due diligence and due care on the part of senior management. If a company does not practice due diligence and due care, managers can be held liable for negligence and held accountable for both asset and financial losses.
A security management planning team should develop three types of plans, as shown in Figure 1.3:
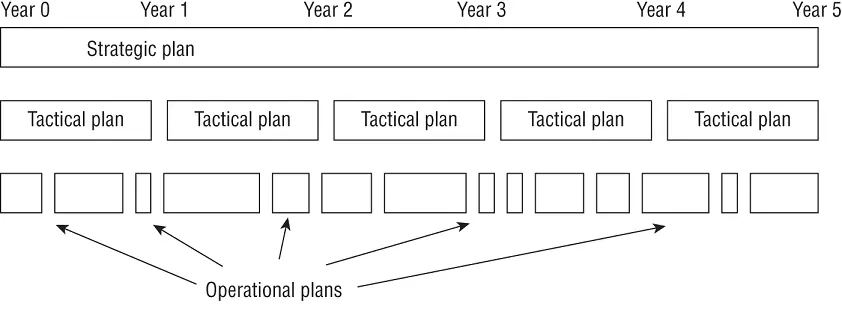
FIGURE 1.3Strategic, tactical, and operational plan timeline comparison
Strategic Plan A strategic plan is a long-term plan that is fairly stable. It defines the organization's security purpose. It defines the security function and aligns it to the goals, mission, and objectives of the organization. It's useful for about five years, if it is maintained and updated annually. The strategic plan also serves as the planning horizon. Long-term goals and visions for the future are discussed in a strategic plan. A strategic plan should include a risk assessment.
Tactical Plan The tactical plan is a midterm plan developed to provide more details on accomplishing the goals set forth in the strategic plan, or can be crafted ad hoc based on unpredicted events. A tactical plan is typically useful for about a year and often prescribes and schedules the tasks necessary to accomplish organizational goals. Some examples of tactical plans are project plans, acquisition plans, hiring plans, budget plans, maintenance plans, support plans, and system development plans.
Operational Plan An operational plan is a short-term, highly detailed plan based on the strategic and tactical plans. It is valid or useful only for a short time. Operational plans must be updated often (such as monthly or quarterly) to retain compliance with tactical plans. Operational plans spell out how to accomplish the various goals of the organization. They include resource allotments, budgetary requirements, staffing assignments, scheduling, and step-by-step or implementation procedures. Operational plans include details on how the implementation processes are in compliance with the organization's security policy. Examples of operational plans are training plans, system deployment plans, and product design plans.
Security is a continuous process. Thus, the activity of security management planning may have a definitive initiation point, but its tasks and work are never fully accomplished or complete. Effective security plans focus attention on specific and achievable objectives, anticipate change and potential problems, and serve as a basis for decision making for the entire organization. Security documentation should be concrete, well defined, and clearly stated. For a security plan to be effective, it must be developed, maintained, and actually used.
Security governance should address every aspect of an organization, including the organizational processes of acquisitions, divestitures, and governance committees. Acquisitions and mergers place an organization at an increased level of risk. Such risks include inappropriate information disclosure, data loss, downtime, or failure to achieve sufficient return on investment (ROI). In addition to all the typical business and financial aspects of mergers and acquisitions, a healthy dose of security oversight and increased scrutiny is often essential to reduce the likelihood of losses during such a period of transformation.
Similarly, a divestiture or any form of asset or employee reduction is another time period of increased risk and thus increased need for focused security governance. Assets need to be sanitized to prevent data leakage. Storage media should be removed and destroyed, because media sanitization techniques do not guarantee against data remnant recovery. Employees released from duty need to be debriefed. This process is often called an exit interview. This process usually involves reviewing any nondisclosure agreements as well as any other binding contracts or agreements that will continue after employment has ceased.
When acquisitions and mergers are made without security considerations, the risks inherent in those obtained products remain throughout their deployment life span. Minimizing inherent threats in acquired elements will reduce security management costs and likely reduce security violations.
It is important to evaluate the risks associated with hardware, software, and services. Products and solutions that have resilient integrated security are often more expensive than those that fail to have a security foundation. However, this additional initial expense is often a much more cost-effective expenditure than addressing security deficiencies over the life of a poorly designed product. Thus, when considering the cost of a merger/acquisition, it is important to consider the total cost of ownership over the life of the product's deployment rather than just initial purchase and implementation.
Читать дальше

 The opposite of the top-down approach is the bottom-up approach. In a bottom-up approach environment, the IT staff makes security decisions directly without input from senior management. The bottom-up approach is rarely used in organizations and is considered problematic in the IT industry.
The opposite of the top-down approach is the bottom-up approach. In a bottom-up approach environment, the IT staff makes security decisions directly without input from senior management. The bottom-up approach is rarely used in organizations and is considered problematic in the IT industry. The chief information officer (CIO) focuses on ensuring information is used effectively to accomplish business objectives. The chief technical officer (CTO) focuses on ensuring that equipment and software work properly to support the business functions.
The chief information officer (CIO) focuses on ensuring information is used effectively to accomplish business objectives. The chief technical officer (CTO) focuses on ensuring that equipment and software work properly to support the business functions.











