To estimate expected returns, we start by assuming that markets are fairly priced; therefore, expected returns represent fair compensation for the degree of risk each asset class contributes to a broadly diversified market portfolio. These returns are called equilibrium returns, and we estimate them by first calculating the beta of each asset class with respect to a broad market portfolio. This calculation implicitly reflects the historical standard deviations and correlations of the assets. Next, we estimate the expected return for the market portfolio and the risk-free return. We calculate the equilibrium return of each asset class as the risk-free return plus the product of its beta and the excess return of the market portfolio. Moreover, we can easily adjust the expected return of each asset class to accord with our views about departures from fair value. Suppose we estimate the market's expected return to equal 7.5% and the risk-free return to equal 3.5%. Given these estimates, together with estimates of beta based on monthly returns from January 1976 through December 2015, we derive the equilibrium returns shown in Table 2.1.
TABLE 2.1Expected Returns
| Asset Classes |
Equilibrium Returns (%) |
Views (%) |
Confidence (%) |
Expected Returns (%) |
| US Equities |
8.8 |
|
|
8.8 |
| Foreign Developed Market Equities |
9.5 |
|
|
9.5 |
| Emerging Market Equities |
11.4 |
|
|
11.4 |
| Treasury Bonds |
4.1 |
|
|
4.1 |
| US Corporate Bonds |
4.9 |
|
|
4.9 |
| Commodities |
5.4 |
7.0 |
50.0 |
6.2 |
| Cash Equivalents |
3.5 |
|
|
3.5 |
Assumes 3.5% risk-free return and 4.0% market risk premium.
This approach is straightforward to implement in practice, even with more nuanced assumptions. The current risk-free return is readily observable. There are a variety of methods for estimating the expected return of a diversified market portfolio. For example, we might adjust the historical risk premium to accord with current risk levels and add this adjusted risk premium to the current risk-free return. We may expect some asset classes to produce returns that differ from those that would occur if markets were in equilibrium and perfectly integrated, especially if they are not typically arbitraged against other asset classes. Suppose we expect commodities to return 7.0% and we assign as much confidence to this view as we do to the equilibrium return. We can blend the equilibrium estimate with our view to derive expected return. The final column of Table 2.1shows the expected returns for each of the asset classes in our analysis.
Estimating Standard Deviations and Correlations
We also need to estimate the standard deviations of the asset classes as well as the correlations between each pair of asset classes. We estimate these values, shown in Table 2.2, from the monthly returns for the period beginning in January 1976 and ending in December 2015.
TABLE 2.2Standard Deviations and Correlations
|
Asset Classes |
Standard Deviations (%) |
Correlations |
| a |
b |
c |
d |
e |
f |
| a |
US Equities |
16.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| b |
Foreign Developed Market Equities |
18.6 |
0.66 |
|
|
|
|
|
| c |
Emerging Market Equities |
26.6 |
0.63 |
0.68 |
|
|
|
|
| d |
Treasury Bonds |
5.7 |
0.10 |
0.03 |
−0.02 |
|
|
|
| e |
US Corporate Bonds |
7.3 |
0.31 |
0.24 |
0.22 |
0.86 |
|
|
| f |
Commodities |
20.6 |
0.16 |
0.29 |
0.27 |
−0.07 |
0.02 |
|
| g |
Cash Equivalents |
1.1 |
0.02 |
0.02 |
0.03 |
0.18 |
0.09 |
0.06 |
With this information, we use optimization to combine asset classes efficiently, so that for a given level of expected return the efficiently combined asset classes offer the lowest level of risk, measured as the standard deviation. A continuum of these portfolios plotted in dimensions of expected return and standard deviation is called the efficient frontier, as we discussed earlier.
There are a variety of methods for identifying portfolios that reside along the efficient frontier. We next describe two methods and illustrate them with a hypothetical portfolio that consists of just two asset classes: stocks and bonds.
To begin, we define a portfolio's expected return and risk.
As noted earlier, the expected return of a portfolio is simply the weighted average of the assets' expected returns. Equation 2.1shows expected return for a portfolio consisting of only stocks and bonds:
(2.1) 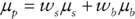
In Equation 2.1, 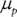 equals the portfolio's expected return,
equals the portfolio's expected return, 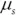 equals the expected return of stocks,
equals the expected return of stocks, 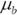 equals the expected return of bonds,
equals the expected return of bonds, 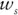 equals the percentage of the portfolio allocated to stocks, and
equals the percentage of the portfolio allocated to stocks, and 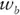 equals the percentage allocated to bonds.
equals the percentage allocated to bonds.
As noted earlier, portfolio risk is a little trickier. It is defined as volatility, and it is measured by the standard deviation or variance (the standard deviation squared) around the portfolio's expected return. To compute a portfolio's variance, we must consider not only the variance of the asset class returns, but also the extent to which they covary. The variance of a portfolio of stocks and bonds is computed as follows:
(2.2) 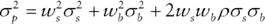
Here 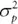 equals portfolio variance,
equals portfolio variance, 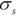 equals the standard deviation of stocks,
equals the standard deviation of stocks, 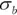 equals the standard deviation of bonds, and
equals the standard deviation of bonds, and 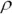 equals the correlation between stocks and bonds.
equals the correlation between stocks and bonds.
Our objective is to minimize portfolio risk subject to two constraints. Our first constraint is that the weighted average of the stock and bond returns must equal the expected return for the portfolio. We are also faced with a second constraint: we must allocate our entire portfolio to some combination of stocks and bonds. Therefore, the fraction we allocate to stocks plus the fraction we allocate to bonds must equal 1.
Читать дальше

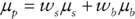
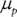 equals the portfolio's expected return,
equals the portfolio's expected return, 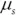 equals the expected return of stocks,
equals the expected return of stocks, 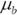 equals the expected return of bonds,
equals the expected return of bonds, 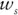 equals the percentage of the portfolio allocated to stocks, and
equals the percentage of the portfolio allocated to stocks, and 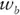 equals the percentage allocated to bonds.
equals the percentage allocated to bonds.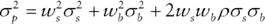
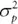 equals portfolio variance,
equals portfolio variance, 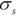 equals the standard deviation of stocks,
equals the standard deviation of stocks, 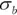 equals the standard deviation of bonds, and
equals the standard deviation of bonds, and 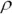 equals the correlation between stocks and bonds.
equals the correlation between stocks and bonds.










