The scheduler makes its decisions at each slot. The duration of the TTI slot depends on the spacing between SCS (SubCarrier Spacing). While the scheduler decision is 1 ms in 4G, it is variable from 1 ms, 500 μs or 250 μs for 5G on the FR1 (Frequency Range 1) band, and can go down to 125 μs or 62.5 μs for the FR2 band.
Transmission on the downlink direction can be pre-empted for critical communication (low latency). The NG-RAN node informs the mobiles by transmitting the INT-RNTI identifier over the PDCCH control channel.
Semi-persistent scheduling allows us to periodically allocate radio resources for a mobile. The periodicity of the messages is transmitted over the RRC layer and the resource allocation is transmitted to the mobile via the CS-RNTI identifier.
1.4.2. Support for quality of service on radio link
The QoS (Quality Of Service) control consists of implementing the maximum quality of service applicable to a data flow.
Like the 4G mobile network, only the core network is aware of the service requirements: QoS management is under the control of the core network (AMF). The NG-RAN has no knowledge of the service to be managed. Thus, when establishing a PDU session, the AMF entity establishes QoS rules between the radio node and one or more UPF entities.
The PDU session carries IP flows with one or more different qualities of service for all flows. Each flow is associated with a QFI flow profile identifier. The flow profile corresponds to a QoS indicator (5QI: 5G QoS Identifier) and an allocation and retention priority (ARP). The QFI flag is unique within a PDU session. The flag is either configured during the PDU session establishment procedure or during the PDU session modification procedure.
The value of a QFI is configured by the AMF during the procedure of session establishment; the AMF querying the unified UDR database to know the user’s authorized QoS. For the establishment of dedicated services, the SMF chooses the QoS characteristics (5QI/ARP) according to the values stored at the SMF or by querying the PCF entity. The 5QI/ARP combination defined by the PCF link in a PDU session is a QoS flow binding.
The 5QI indicator is a parameter standardized by the 3GPP standard, allowing us to define:
1 – the type of resource (Guaranteed Bit Rate or not): GBR or non-GBR;
2 – priority;
3 – the maximum transmission delay within the 5GS mobile network;
4 – the residual error rate.
5 The standardization of the 5QI value makes it possible to indicate how the flow is processed on each element of the user’s plan, in order that processing is consistent between the entities of the 5G core network and of the NG-RAN access.
The 5QI indicator is identical to the QCI (QoS Class Identifier) indicator for the 4G network for non-critical services (indicator from 1 to 80). New QCI values (81–85) have been defined in the case of URLLC services to guarantee speed and critical delay (delay critical GBR).
Table 1.2. 5G QoS characteristics
| 5QI |
Type |
Priority |
Packet Delay Budget |
PLER |
Services |
| 1 |
GBR |
2 |
100 ms |
10 −2 |
Conversational Voice |
| 2 |
4 |
150 ms |
10 −3 |
Conversational Video (Live Streaming) |
| 3 |
3 |
50 ms |
10 −3 |
Real Time Gaming, V2X messages |
| 4 |
5 |
300 ms |
10 −6 |
Non-Conversational Video (Buffered Streaming) |
| 65 |
0.7 |
75 ms |
10 −2 |
Mission Critical user plane Push To Talk voice (e.g. MC-PTT) |
| 66 |
2 |
100 ms |
10 −2 |
Non-Mission-Critical user plane Push To Talk voice |
| 75 |
2.5 |
50 ms |
10 −2 |
V2X messages |
| 5 |
Non-GBR |
1 |
100 ms |
10 −6 |
IMS Signaling |
| 6 |
6 |
300 ms |
10 −6 |
Video (Buffered Streaming) TCP-Based (e.g. www, email, chat, ftp, p2p, etc.) |
| 7 |
7 |
100 ms |
10 −3 |
Voice, Video (Live Streaming), Interactive Gaming |
| 8 |
8 |
300 ms |
10 −6 |
Video (Buffered Streaming) TCP-Based (e.g. www, email, chat, ftp, p2p, etc.) |
| 9 |
9 |
300 ms |
10 −6 |
Video (Buffered Streaming) TCP-Based (e.g. www, email, chat, ftp, p2p, etc.). Typically used as default bearer |
| 69 |
0.5 |
60 ms |
10 −6 |
Mission Critical delay sensitive signaling (e.g. MC-PTT signaling) |
| 70 |
5.5 |
200 ms |
10 −6 |
Mission Critical Data (e.g. example services are the same as QCI 6/8/9) |
| 79 |
6.5 |
50 ms |
10 −2 |
V2X messages |
| 80 |
6.8 |
10 ms |
10–6 |
Low latency eMBB applications (TCP/UDP-based); Augmented Reality |
| 82 |
Delay Critical GBR |
1.9 |
10 ms |
10 −4 |
Discrete Automation (small packets) |
| 83 |
2.2 |
10 ms |
10 −4 |
Discrete Automation (big packets) |
| 84 |
2.4 |
30 ms |
10 −5 |
Intelligent Transport Systems |
| 85 |
2.1 |
5 ms |
10 −5 |
Electricity Distribution-high voltage |
The ARP parameter allows the NG-RAN node to choose whether the bearer establishment request should be made or rejected in the event of congestion.
The QFI value is coded on 6 bits. The 5QI value is set between 1 and 85. For any 5QI value less than or equal to 64, the QFI indicator and 5QI can be the same.
When the mobile is in the RRC_CONNECTED state, the management of QoS rules is delegated to the 5G-NR radio interface.
A user’s plane traffic in a PDU session with the same QFI flag is handled with the same traffic routing rules (e.g. sequencing rules, admission level).
The role of the radio node is to configure one or more radio data bearers (RAB: Radio Access Bearer) and to perform a mapping between the QFI and the bearer(s) from a TFT flow filtering template (Traffic Flow Template).
For uplink, there are two ways to control the mapping between the radio bearers and the QoS of IP flows:
1 – reflective QoS for which the mobile replicates QoS rules received in downlink (configuration of the TFT flow policy rules);
2 – explicit configuration for which the uplink QoS configuration is defined by configuring the radio bearer.
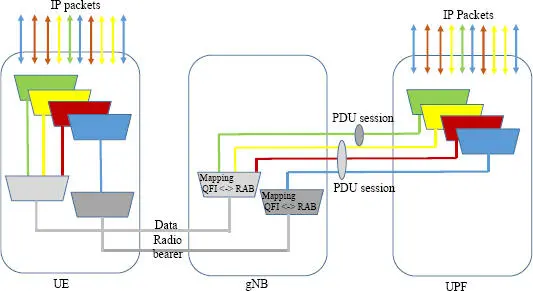
Figure 1.10. QFI management in the user’s plane
1.5. Security architecture
The security architecture implemented on the 5G mobile is based on:
1 – mutual authentication between the 5GC core network and mobile (UICC);
2 – ciphering and integrity of NAS signaling messages exchanged between the mobile and the AMF;
3 – AS security through the 5G-NR radio interface between the mobile and the NG-RAN node. Security concerns the integrity control and encryption of RRC messages and IP packets. Integrity on IP packets is optional.
Data integrity:
1 – ensures that the data have not been altered by a third party between transmission and reception;
2 – verifies the transmitting source;
3 – ensures that a message already received is not reused.
Читать дальше













