Romeo Ortega - PID Passivity-Based Control of Nonlinear Systems with Applications
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Romeo Ortega - PID Passivity-Based Control of Nonlinear Systems with Applications» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:PID Passivity-Based Control of Nonlinear Systems with Applications
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
PID Passivity-Based Control of Nonlinear Systems with Applications: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «PID Passivity-Based Control of Nonlinear Systems with Applications»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
, expert researchers and authors Drs. Romeo Ortega, Jose Guadalupe Romero, Pablo Borja, and Alejandro Donaire deliver a comprehensive and detailed discussion of the most crucial and relevant concepts in the analysis and design of proportional-integral-derivative controllers using passivity techniques. The accomplished authors present a formal treatment of the recent research in the area and offer readers practical applications of the developed methods to physical systems, including electrical, mechanical, electromechanical, power electronics, and process control.
The book offers the material with minimal mathematical background, making it relevant to a wide audience. Familiarity with the theoretical tools reported in the control systems literature is not necessary to understand the concepts contained within. You’ll learn about a wide range of concepts, including disturbance rejection via PID control, PID control of mechanical systems, and Lyapunov stability of PID controllers.
Readers will also benefit from the inclusion of:
A thorough introduction to a class of physical systems described in the port-Hamiltonian form and a presentation of the systematic procedures to design PID-PBC for them An exploration of the applications to electrical, electromechanical, and process control systems of Lyapunov stability of PID controllers Practical discussions of the regulation and tracking of bilinear systems via PID control and their application to power electronics and thermal process control A concise treatment of the characterization of passive outputs, incremental models, and Port Hamiltonian and Euler-Lagrange systems Perfect for senior undergraduate and graduate students studying control systems,
will also earn a place in the libraries of engineers who practice in this area and seek a one-stop and fully updated reference on the subject.

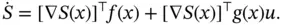
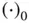 , and is given by
, and is given by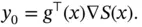
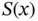 is the energy stored by the system,
is the energy stored by the system, 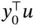 is the supplied power and
is the supplied power and 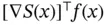 is the system's dissipation. In passivity theory, it is said that the system
is the system's dissipation. In passivity theory, it is said that the system  does not suffer from the dissipation obstacle – at an assignable equilibrium
does not suffer from the dissipation obstacle – at an assignable equilibrium  – if
– if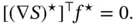
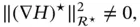
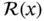 is the dissipation matrix and
is the dissipation matrix and 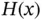 is a bona fide energy function – yielding a clear physical interpretation.
is a bona fide energy function – yielding a clear physical interpretation.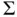 with passive output 2.3 and a dynamic extension
with passive output 2.3 and a dynamic extension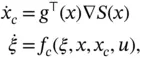
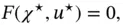
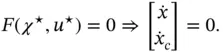
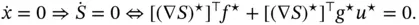
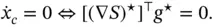
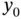 as a particular case of CbI, which is a physically (and conceptually) appealing method to stabilize equilibria of nonlinear systems widely studied in the literature, cf, Duindam et al. (2009), Ortega et al. (2008), and van der Schaft (2016).
as a particular case of CbI, which is a physically (and conceptually) appealing method to stabilize equilibria of nonlinear systems widely studied in the literature, cf, Duindam et al. (2009), Ortega et al. (2008), and van der Schaft (2016). ‐system
‐system 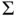 , which we assume passive with storage function
, which we assume passive with storage function 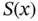 , and the controller
, and the controller










