Saeid Sanei - EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Saeid Sanei - EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
11 Chapter 11Figure 11.1 Two segments of EEG signals each from a patient suffering: (a) g...Figure 11.2 The CNN architecture proposed in [48]. The first layer (Conv2D) ...Figure 11.3 (a) A sample of IED recorded using intracranial foramen ovale el...Figure 11.4 The main three different neonate seizure patterns. (a) Low ampli...Figure 11.5 Eight seconds of EEG signals from eight out of 16 scalp electrod...Figure 11.6 The four independent components obtained by applying BSS to the ...Figure 11.7 The smoothed λ 1evolution over time for two intracranial electro...Figure 11.8 Smoothed λ 1evolution over time for two independent components I...Figure 11.9 (a) A segment of eight seconds of EEG signals (with zero mean) f...Figure 11.10 (a) Intracranial EEG analysis: three‐point smoothed λ 1evolutio...Figure 11.11 Smoothed λ 1evolution for a focal seizure estimated from the in...Figure 11.12 (a) Smoothed λ 1evolution of four intracranial electrodes for a...Figure 11.13 The schematic for the proposed LRCN seizure prediction algorith...Figure 11.14 Foramen ovale holes where the subdural electrodes are inserted ...Figure 11.15 Basal (left) and lateral (right) X‐ray images showing the inser...Figure 11.16 A segment of concurrent multichannel data. The first 22 signals...Figure 11.17 The scoring histogram provided by an expert in epilepsy.Figure 11.18 Classification accuracy of the ensemble classifier with respect...Figure 11.19 The ratio of detected IEDs (from the scalp EEG), to the total n...Figure 11.20 Detected scalp‐invisible IEDs with true positive on the top and...Figure 11.21 Examples of single‐channel reconstructed intracranial signals f...Figure 11.22 Topology of the DNN for mapping scalp to iEEGs. Xis the scalp ...Figure 11.23 A schematic comparison between the proposed method (left) and a...Figure 11.24 Estimation of iEEG for two IED segments and a non‐IED segment (...Figure 11.25 A segment of EEG signals affected by the scanner ballistocardio...Figure 11.26 Schematic diagram of the topographic map correlation procedure....
12 Chapter 12Figure 12.1 Exemplar EEG signals recorded during drowsiness.Figure 12.2 During Stage III sleep, 26 s of brain waves were recorded.Figure 12.3 Twenty‐six seconds of brain waves recorded during the REM state....Figure 12.4 A typical concentration of melatonin in a healthy adult man (ext...Figure 12.5 Typical waveforms for (a) spindles and (b) K‐complexes, adopted ...Figure 12.6 Time–frequency energy map of 20 seconds epochs of sleep EEG in d...Figure 12.7 Block diagram of the sleep scoring system proposed in [34].Figure 12.8 The scoring result of the proposed system in [34] (bottom) compa...Figure 12.9 I × K matrix Xis converted to tensor 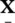 where J is the number of...Figure 12.10 Block diagram of the single‐channel source separation system us...Figure 12.11 A model for neuronal slow‐wave generation;
where J is the number of...Figure 12.10 Block diagram of the single‐channel source separation system us...Figure 12.11 A model for neuronal slow‐wave generation; 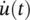 is the derivative ...Figure 12.12 A sample PSG record of multichannel five seconds long data. The...
is the derivative ...Figure 12.12 A sample PSG record of multichannel five seconds long data. The...
13 Chapter 13Figure 13.1 Inter‐hemisphere coherency of beta, alpha, and theta rhythms; to...Figure 13.2 Inter‐hemisphere phase synchronization of beta, alpha, and theta...Figure 13.3 Tracking variability of P3a and P3b before and during fatigue; t...Figure 13.4 Comparison of three methods (spatial PCA, exact match and mismat...Figure 13.5 (a) Single‐trial ERPs (40 trials related to the infrequent tones...Figure 13.6 Selection of reference signals for P3a and P3b. In each row, the...Figure 13.7 Scalp projections of P3a (top row) and P3b (bottom row) in four ...Figure 13.8 Forty single‐trial ERPs and their average from the Cz channel be...Figure 13.9 Forty single‐trial ERPs and their average from the Cz channel du...Figure 13.10 The ERP achieved by averaging 40 EEG trials before and during t...Figure 13.11 The estimated scalp projections of P3a (top row) and P3b (botto...Figure 13.12 The estimated scalp projections of P3a (top row) and P3b (botto...Figure 13.13 Theta phase synchronization of F3–F4: (a) before stimulus and (...Figure 13.14 Alpha phase synchronization of C3–C4: (a) before stimulus and (...Figure 13.15 Beta phase synchronization of F3–F4: (a) before stimulus and (b...Figure 13.16 Two‐stage PCANet block diagram proposed in [55].
14 Chapter 14Figure 14.1 The limbic system and the location of the amygdala.Figure 14.2 The generators of respiration‐related anxiety potentials are in ...Figure 14.3 Valence–arousal space showing high and low positive and negative...Figure 14.4 Emotion neural circuitry regions involved in emotion regulation....Figure 14.5 Direct and indirect pathways to the amygdala.Figure 14.6 Time course of an EPN and its corresponding topography images [9...Figure 14.7 Time course of the late positive potential; grand‐averaged ERP w...Figure 14.8 Olfactory bulb.Figure 14.9 Group comparison between anterior and posterior P300 amplitudes ...Figure 14.10 Negative and positive magnitudes of activity for the main regio...
15 Chapter 15Figure 15.1 Distribution of the MEG sensors into left central (LC), anterior...Figure 15.2 Block diagram of the spectral coherency, c ( f ), measure.Figure 15.3 (a) A 10 second segment of one EMG channel and (b) its correspon...Figure 15.4 Reference selection using the k ‐means algorithm.Figure 15.5 Spectral coherency levels without (left) and with (right) region...Figure 15.6 ERPs recorded using the Cz electrode for (a) healthy and (b) AD ...Figure 15.7 Mean GC magnitudes across subjects for all links in control, AD–...Figure 15.8 Results of the multitask diffusion adaptation method in [5] for ...Figure 15.9 Ten brain regions used to estimate the functional connectivity u...Figure 15.10 A sample of 10‐channel EEG of a CJD patient showing clear perio...Figure 15.11 EEG in the very early stages of CJD, showing right‐lateralised ...
16 Chapter 16Figure 16.1 Stimulus‐locked and response‐locked ERPs. Stimulus‐locked grand ...Figure 16.2 Typical faces and labels for congruent and incongruent stimuli u...Figure 16.3 Block diagram of the system developed in [55] for classification...Figure 16.4 Typical ERPs recorded (and averaged over trials) from the Fz ele...Figure 16.5 The mean asymmetry between the left and right brain hemisphere c...Figure 16.6 The 13 EEG electrode groups used in [74].
17 Chapter 17Figure 17.1 A cross‐section of the motor cortex and the links to different o...Figure 17.2 Readiness potential elicited around the finger movement time ins...Figure 17.3 The averaged RPs from C 3 and C 4 during left and right finger mov...Figure 17.4 ERD/ERS patterns over the central region ( C 3 and C 4) during imag...Figure 17.5 A typical BCI system using scalp EEGs when visual feedback is us...Figure 17.6 A hybrid BSS‐SVM system for EEG artefact removal [98].Figure 17.7 Classification of left/right finger movements using space–time–f...Figure 17.8 Left finger imagination: two components. The upper figure repres...Figure 17.9 Right finger imagination: two components. The upper figures repr...Figure 17.10 The EEG signals before the removal of eye‐blinking artefacts in...Figure 17.11 Illustration of source propagation from the coherency spectrum ...Figure 17.12 Illustration of source propagation from the coherency spectrum ...Figure 17.13 A block diagram of the system proposed in [128] for classificat...Figure 17.14 The results of applying CSP to classify the cortical activity o...Figure 17.15 The electrodes highlighted in dark grey are those which are ove...Figure 17.16 A typical stimulus grid for the speller BCI.Figure 17.17 (a) The user operates the real‐time feedback loop to freely typ...Figure 17.18 The locations of the most popular neurotechnology products [157...
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












