Saeid Sanei - EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Saeid Sanei - EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
3 Chapter 3 Figure 3.1 (a) A network of three neurons that exchange electric signals, na... Figure 3.2 A pair of oscillators weakly coupled via the perturbation functio... Figure 3.3 The Hodgkin–Huxley excitation model. Figure 3.4 A single AP in response to a transient stimulation based on the H... Figure 3.5 The AP from a Hodgkin–Huxley oscillatory model with reduced maxim... Figure 3.6 Simulation of an AP within the Morris–Lecar model. The model para... Figure 3.7 An illustration of the bursting behaviour that can be generated b... Figure 3.8 A nonlinear lumped model for generating the rhythmic activity of ... Figure 3.9 The local EEG model (LEM). The thalamocortical relay neurons are ... Figure 3.10 Simplified model for brain cortical alpha generation. The input ... Figure 3.11 A two‐column model for generation of VEP. Two connectivity const... Figure 3.12 A linear model for the generation of EEG signals. Figure 3.13 Mixture of Gaussian (dotted curves) models of a multimodal unkno... Figure 3.14 The Lewis membrane model [57]. Figure 3.15 Circuits simulating (a) potassium and (b) sodium conductances in... Figure 3.16 The Lewis neuron model from 1968 [57]. Figure 3.17 The Harmon neuron model [60]. Figure 3.18 The Lewis model for simulation of the propagation of the action ...
4 Chapter 4 Figure 4.1 An EEG set of tonic–clonic seizure signals including three segmen... Figure 4.2 (a) An EEG seizure signal including preictal, ictal, and posticta... Figure 4.3 Single‐channel EEG spectrum. (a) A segment of an EEG signal with ... Figure 4.4 TF representation of an epileptic waveform in (a) for different t... Figure 4.5 Morlet's wavelet: real and imaginary parts shown respectively in ... Figure 4.6 Mexican hat wavelet. Figure 4.7 The filter bank associated with the multiresolution analysis. Figure 4.8 (a) A segment of a signal consisting of two modulated components,... Figure 4.9 Illustration of 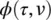 for the Choi–Williams distribution. Figure 4.10 Cross‐spectral coherence for a set of three electrode EEGs, one ... Figure 4.11 An adaptive noise canceller. Figure 4.12 The general application of PCA. Figure 4.13 Adaptive estimation of the weight vector w( n ).
for the Choi–Williams distribution. Figure 4.10 Cross‐spectral coherence for a set of three electrode EEGs, one ... Figure 4.11 An adaptive noise canceller. Figure 4.12 The general application of PCA. Figure 4.13 Adaptive estimation of the weight vector w( n ).
5 Chapter 5 Figure 5.1 Separation of EMG and ECG using the SSA technique; top signal is ... Figure 5.2 BSS concept; mixing and blind separation of the EEG signals. Figure 5.3 A sample of an EEG signal simultaneously recorded with fMRI. Figure 5.4 The EEG signals after removal of the scanner artefact. Figure 5.5 Estimated independent components of a set of EEG signals, acquire... Figure 5.6 Topographic maps, each illustrating an IC. It is clear that the s... Figure 5.7 Tensor and its various modes. Figure 5.8 Tensor factorization using: (a) Tucker and (b) PARAFAC models. Figure 5.9 A tensor representation of a set of multichannel EEG signals. (a)... Figure 5.10 The extracted factors using STF–TS modelling. (a) and (b) illust... Figure 5.11 Restoration of the EEG signals in (a) from multiple eye blinks a... Figure 5.12 Representation of the first two components (a, b) in the time–sp... Figure 5.13 The results of application of the FOBSS algorithm to a set of sc... Figure 5.14 The intracranial records from three electrodes. These signals we...
6 Chapter 6Figure 6.1 Generated chaotic signal using the model x ( n ) → αx ( n )(1 − x (Figure 6.2 The attractors for (a) a sinusoid and (b) the above chaotic time ...Figure 6.3 The reference and the model trajectories, evolution of the error,...Figure 6.4 (a) The signal and (b) prediction order measured for overlapping ...
7 Chapter 7Figure 7.1 A two‐dimensional feature space with three clusters, each with me...Figure 7.2 Schematic diagram of deep clustering [16]. The deep features are ...Figure 7.3 An example of a decision tree to show the humidity level at 9:00 ...Figure 7.4 The SVM separating hyperplane and support vectors for a separable...Figure 7.5 Soft margin and the concept of a slack parameter.Figure 7.6 Nonlinear discriminant hyperplane (separation margin) for SVM.Figure 7.7 Output class distributions for (a) close to zero and (b) non‐zero...Figure 7.8 A biological neuron that expresses the fundamental elements of a ...Figure 7.9 A simple three‐layer NN for node localization in sensor networks ...Figure 7.10 Sigmoid (a) and ReLU (b) activation functions.Figure 7.11 An example of a CNN and the operations in different layers.Figure 7.12 Structure of an autoencoder NN.Figure 7.13 The schematic of the VAE structure. 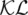 refers to Kullback–Leibler...Figure 7.14 (a) The association of biological neuron activity and an artific...Figure 7.15 Rate‐based encoding (on the left) and temporal encoding (on the ...Figure 7.16 A synthetic ECG segment of a healthy individual and its correspo...Figure 7.17 An HMM for detection of a healthy heart from an ECG sequence.Figure 7.18 CSP patterns related to right‐hand movement (a) and left‐hand mo...
refers to Kullback–Leibler...Figure 7.14 (a) The association of biological neuron activity and an artific...Figure 7.15 Rate‐based encoding (on the left) and temporal encoding (on the ...Figure 7.16 A synthetic ECG segment of a healthy individual and its correspo...Figure 7.17 An HMM for detection of a healthy heart from an ECG sequence.Figure 7.18 CSP patterns related to right‐hand movement (a) and left‐hand mo...
8 Chapter 8Figure 8.1 Cross‐spectral coherence for a set of three electrode EEGs, one s...Figure 8.2 Connectivity pattern imposed in the generation of simulated signa...Figure 8.3 The result of application of S‐transform to a set of simulated so...Figure 8.4 Representation of node k and its neighbouring nodes for diffusion...Figure 8.5 The use of brain connectivity for diffusion adaptation filtering....Figure 8.6 An illustration of brain connectivity pattern. EEG signals collec...Figure 8.7 Variation of combination weights (brain connectivity parameters) ...Figure 8.8 Example of modelling the multirelational social network as a tens...Figure 8.9 Conceptual model of tensors decomposition for linked multiway BSS...
9 Chapter 9Figure 9.1 Four P100 components: (a) two normal P100 and (b) two abnormal P1...Figure 9.2 The average ERP signals for normal and alcoholic subjects. The cu...Figure 9.3 Typical P3a and P3b subcomponents of a P300 ERP signal viewed at ...Figure 9.4 Block diagram of the ICA‐based algorithm proposed in [43]. Three ...Figure 9.5 Synthetic ERP templates including a number of delayed Gaussian an...Figure 9.6 The results of the ERP detection algorithm [47]. The scatter plot...Figure 9.7 The average P3a and P3b for a schizophrenic patient (a) and (b) r...Figure 9.8 Construction of an ERP signal using a WN. The nodes in the hidden...Figure 9.9 Dynamic variations of ERP signals. (a) First stimulus and (b) twe...Figure 9.10 Estimated ERPs by applying KF and PF, (a) and (b) ERP latency ov...Figure 9.11 Estimated (a) amplitude and (b) latency of P3a (bold line) and P...Figure 9.12 The chirplets extracted from a simulated EEG‐type waveform [75]....
10 Chapter 10Figure 10.1 The magnetic field B at each electrode is calculated with respec...Figure 10.2 The magnetic field B at each electrode is calculated with respec...Figure 10.3 The steps in using MRI data to build up a head model. (a) Origin...Figure 10.4 Localization results for (a) the schizophrenic patients and (b) ...Figure 10.5 Flow diagram of inverse methods used for EEG source localization...Figure 10.6 The locations of the P3a and P3b sources for five patients in a ...Figure 10.7 The locations of the P3a and P3b sources for five healthy indivi...Figure 10.8 Localization plot for one source uncorrelated with other sources...Figure 10.9 Percentage of successful localizations for various SNRs for the ...Figure 10.10 Percentage of successful localizations for various SNRs for the...Figure 10.11 Localization plot for P3a, circles, o, and P3b, squares, □, for...Figure 10.12 Localization plot for the P3a, circles, o, and P3b, squares, □,...Figure 10.13 Topographies or power profiles of real MEG data obtained using ...
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












