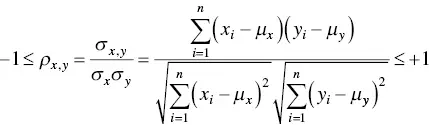
Figure 1.22 (a) Regression analysis, (b) data classification, and (c) data clustering.
The ensemble approach is an alternative method for data classification. An ensemble is a set of classifiers that learn a target function. By combining different outputs of several classifiers, the risk of selecting a poorly performing classifier is reduced. The typical ensemble procedure is provided by the following pseudocode where T denotes the original training dataset, κ is the number of base classifiers, and B is the test data:
1. For i=1 to k do 2. Create training set Ti from T. 3. Build a base classifier Ci from T. 4. end For 5. for each test record x∈ B do: 6. C*(x)=Vote (C1(x),C2(x),…,Ck(x)) 7. end For
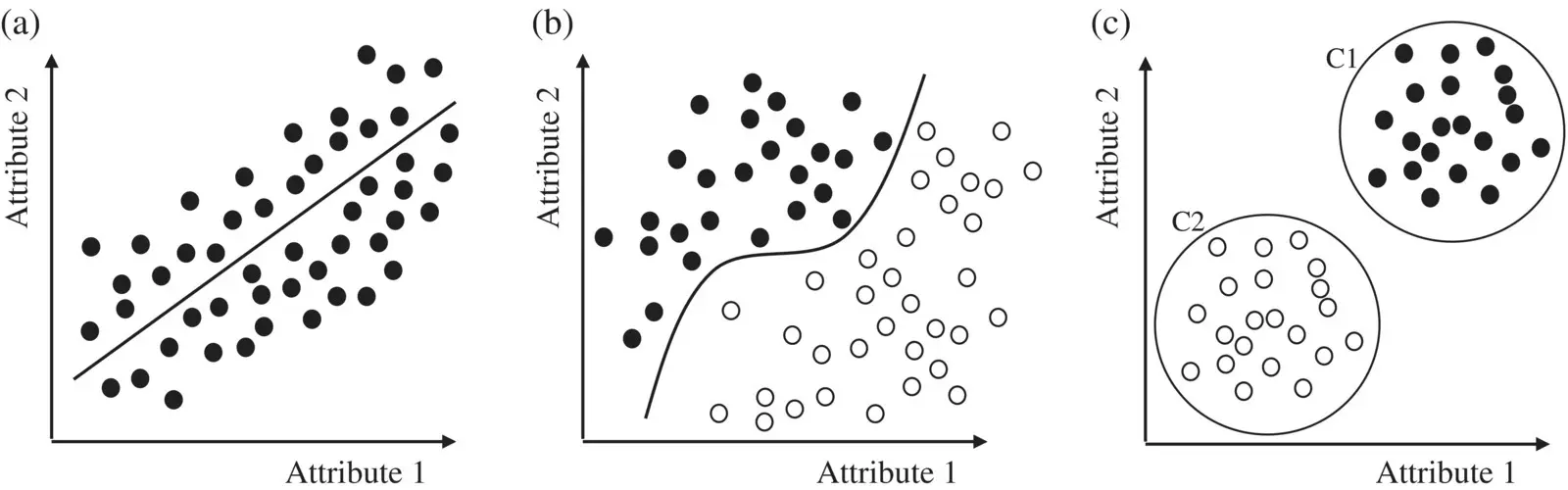
The individual predictions of classifiers are combined to classify new samples, thus optimizing the classifier performance on a specific domain. Figure 1.23shows an example of an ensemble approach based on the best classification of a single feature.
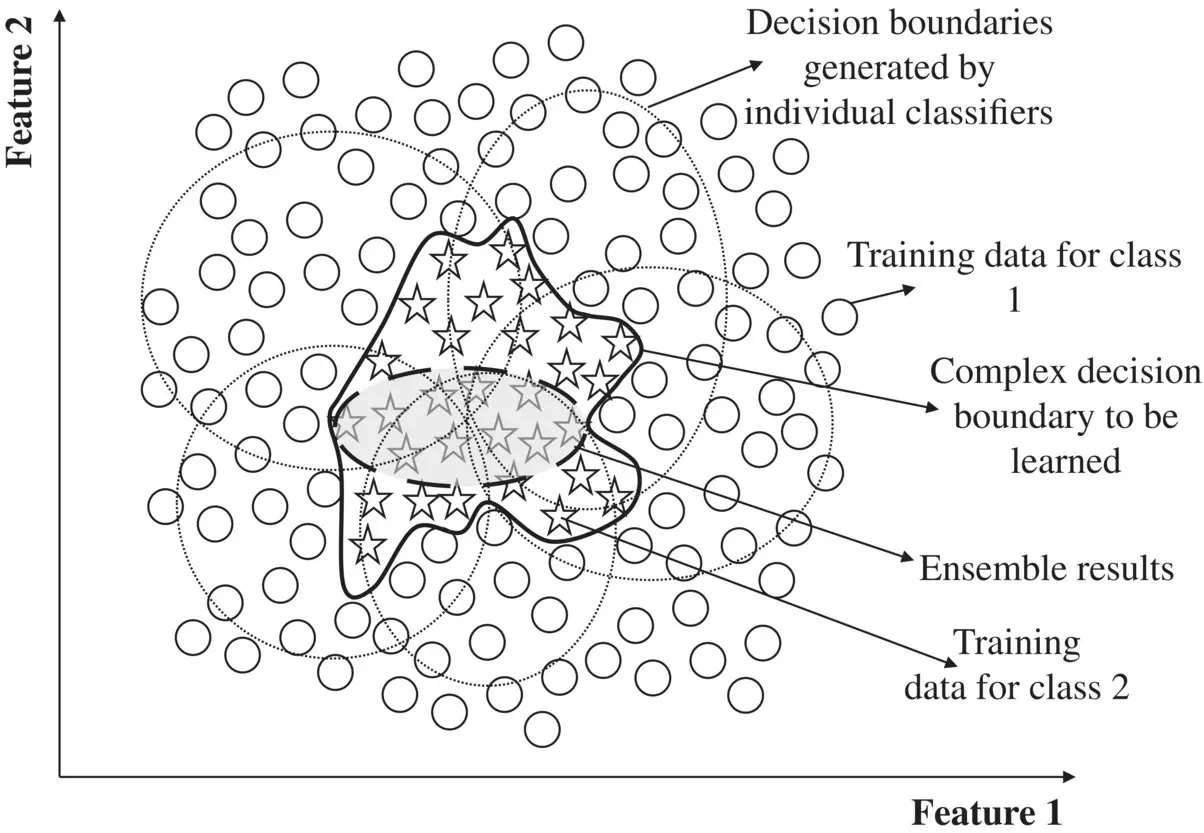
Figure 1.23 Ensemble method and classification.
The RFo method [73] is a class of ensemble methods specifically designed for DT classifiers. The main property is to combine predictions performed by more DT models: each tree is generated from a part of the training dataset and the values are grouped into a set of random vectors. This algorithm is structured as follows ( Figure 1.24):
F input features are randomly selected to split at each node (step 1 of creation of random vectors).
A linear combination of the input features is created to split at each node (step 2 of using a random vector to build multiple DTs).
A combination of DTs is created (step 3).
Figure 1.24 Ensemble method and classification.
The RFo classification technique is also applied in image processing detecting defect features. The logic of the DT algorithm is reported by the following pseudocode:
Decision_Tree Function. 1. Compute Gain values for all attributes and select an attribute having the highest value creating a node for that attribute. 2. Make a branch from this node for every value of the attribute. 3. Assign all possible values of the attributes to branches.
Follow each branch partitioning the dataset to be only instances whereby the value of the branch is present (or for similar values) and then go back to 1 .
A particular feature of neural network algorithms are the long short‐term memory (LSTM) networks, which are artificial recurrent neural network (RNN) architectures [74] used for DL applications. The basic architecture is shown in Figure 1.25a: the structure is a cell (cell state), an input gate (input gate state activated at the time step t ), an output gate (output gate state at the time step t ), and a forget gate (forget gate state at the time step t ). The gates calculate their activations at time step t, by taking into account the activation of the memory cell C at time step t ‐1. Figure 1.25b shows the basic model of a network composed of LSTM nodes.
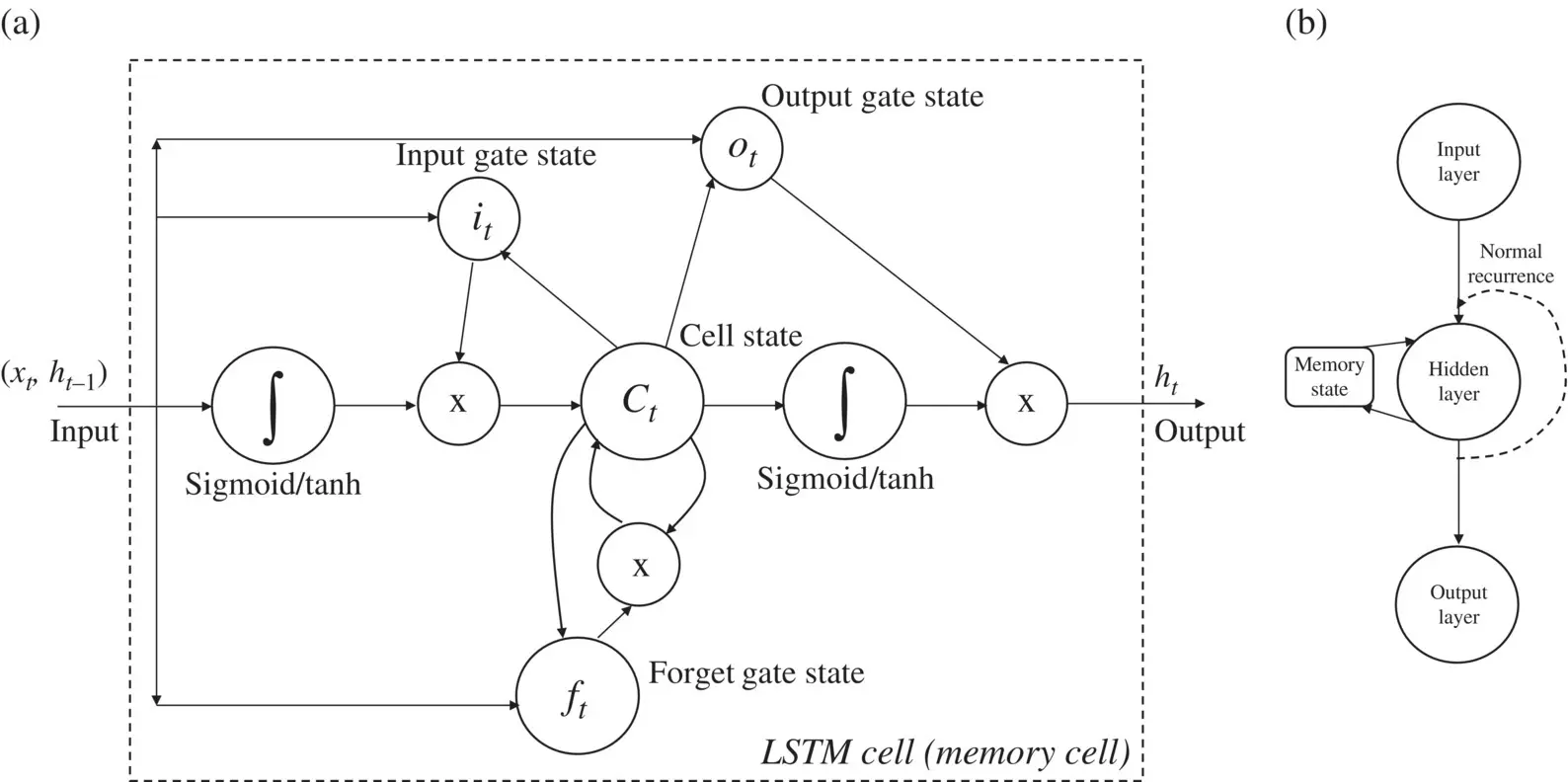
Figure 1.25 (a) LSTM unit cell. (b) LSTM network and its memory.
Another important parameter used for the choice of the training dataset is the correlation coefficient, indicating a relationship between two attributes. The correlation coefficient indicates a value between −1 and 1 (−1 when the attributes are inversely correlated, +1 when the attributes are absolutely correlated, and 0 represents no correlations). The correlation coefficient considers the magnitudes of the deviations from the mean value. In particular, the Pearson–Bravais correlation coefficient is estimated as the ratio between the covariance of the two variables and the product of their standard deviations as follows [75]:
(1.32) 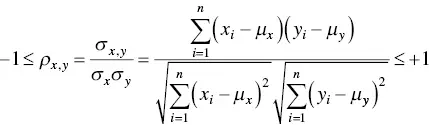
The correlation coefficients are plotted in a correlation matrix with the structure shown in Table 1.9.
Table 1.9 Example of a correlation matrix for a model with five attributes ( v 1, v 2, v 3, v 4, v 5).
|
v 1 |
v 2 |
v 3 |
v 4 |
v 5 |
| v 1 |
1 |
0.4 |
−0.8 |
0.6 |
−0.3 |
| v 2 |
0.4 |
1 |
0.1 |
0.8 |
−0.5 |
| v 3 |
−0.8 |
0.1 |
1 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
| v 4 |
0.6 |
0.8 |
0.2 |
1 |
−0.3 |
| v 5 |
−0.3 |
−0.5 |
0.1 |
−0.3 |
1 |
1.6 Knowledge Upgrading in Industries
KG in industry is achieved by upgrading the information system [32] in different stages, as illustrated in Figure 1.26. The knowledge base (KB) is the starting point representing the industry knowhow provided by the digital information. A first increase of the knowledge is obtained by adding new applications concerning software and tools optimizing production such as:
RE tools.
Design and simulation tools.
Rapid prototyping tools.
Software managing IoT sensor network and monitoring production.
Building information models implemented in AR systems.
Digital sensors to be integrated in analogical machines.
HMI as data entry systems for data digitization according to the Industry 4.0 principle.
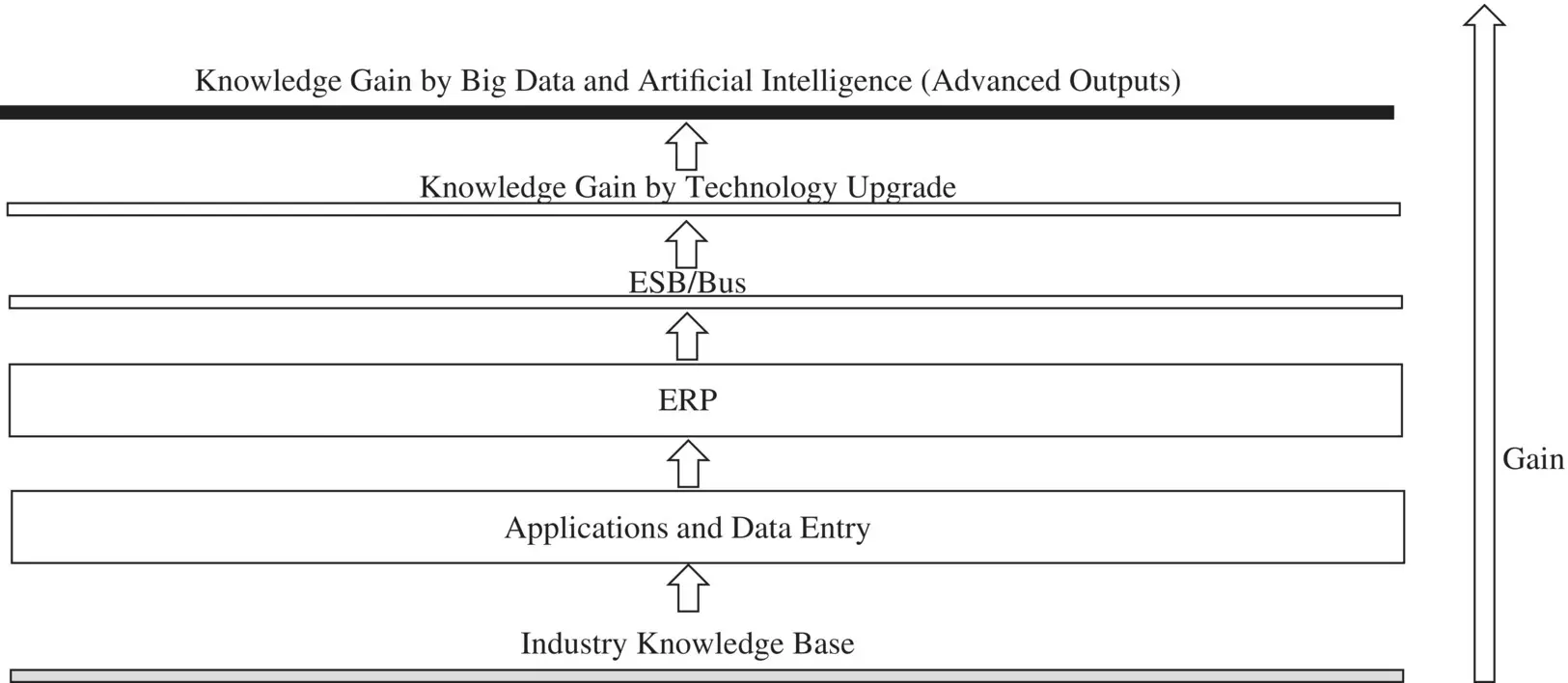
Figure 1.26 Knowledge gain in industry.
All digitized data are typically managed by a unique ERP collecting all data into DB systems. Digitized data travel through the ESB or LAN bus line linking all the software and the information of the industry network [32]. The KG is performed by reading the outputs of advanced analyses related mainly to big data analytics and AI results. The KG is fundamental for industry research. The information system upgrade involves the front‐office, the back‐office, and the whole network infrastructure, powering contact management, E‐commerce, customer relationship management (CRM), BPM, E‐learning, and BI algorithms providing association rules and cost predictions [76]. Big data and data mining are important for BI decision‐making processes, and are able to [77, 78]:
Find possible inefficiencies.
Define human resources KPIs.
Efficiently manage the scheduling of the activities.
Classify human resource skills.
Classify service typologies.
Define strategic marketing.
Classify industry locations based on efficiency estimation.
Читать дальше