Shaping Future 6G Networks
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Shaping Future 6G Networks» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Shaping Future 6G Networks
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Shaping Future 6G Networks: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Shaping Future 6G Networks»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Discover the societal and technology drivers contributing to build the next generation of wireless telecommunication networks Shaping Future 6G Networks: Needs, Impacts, and Technologies
Shaping Future 6G Networks
Shaping Future 6G Networks — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Shaping Future 6G Networks», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
To this end, as previously discussed, it is important to provide low‐cost, low‐energy and highly available connectivity in 6G networks. Notably, Smart‐X applications need global coverage and the possibility of transmitting and receiving data with the same connection throughout the whole world. Consider, for example, the current production paradigm where a product may be manufactured in China, shipped to Europe (through either a ship or an airplane), further processed, and then delivered to a customer in the United States. To enable a seamless, global tracking and monitoring, the sensors on the device should be able to authenticate and securely transmit data, irrespective of the area in which the device is located. Moreover, given the scale of the deployment of Smart‐X sensors, it will be important to design 6G networks so that such sensors can be cheap, consume very little energy, and be easily disposable and/or reusable for different applications.
2.3.8 Financial World
6G is positioned to revolutionize the financial sector by allowing companies to launch new products and services not previously possible, move into new markets, and increase productivity.
Along these lines, 6G can enable efficient HFT, a new method of trading where powerful computer programs can transact millions of financial decisions in fractions of a seconds. For these applications, receiving data even a millisecond sooner can represent a clear advantage over the competitors and generate profits. To this aim, financial institutions typically tend to buy computing facilities as close as possible to the trading and exchange offices to get the trading transactions close to the speed of light, which is, however, a very expensive and often impractical approach. In this context, 6G innovations in the wireless architecture design could offer a better (and more accessible) solution for achieving ultralow‐latency communication in comparison to fiber optic equipment and on‐site deployments, especially in those (rural and/or remote) areas where wired connectivity cannot be easily provided.
The blockchain technology has also gained momentum in the financial industry as a solution to decentralize and eliminate intermediaries in financial feeds while guaranteeing transparency and anonymity. In this perspective, blockchain can be considered as an additional component technology to support financial instruments in 6G networks [10]. 6G innovations, in fact, can provide elevated security features, e.g. through quantum computation, as well as reduce processing fees and improve resilience and resistance to external attacks.
Moreover, in the financial world, 6G can facilitate merchants and banks to deploy transformative and highly personalized customer service experiences, including virtual tellers in banking, high‐resolution digital signage with facial recognition in retail, and AR/VR‐enabled e‐commerce (which would allow potential customers to explore virtual showrooms, improve their shopping experience and, in the end, encourage them to complete a purchase). By supporting high‐capacity data communications in real‐time, 6G can also support time‐sensitive banking operations for both ordinary customers and banks, and accelerate inclusion of small financial institutions, e.g. from emerging markets, by transitioning from (expensive) banking facilities to more accessible, ready‐to‐use digital banking experiences. Furthermore, 6G can help implement more robust and secure fraud prevention without consumer intervention or other expensive direct activities.
Large‐scale financial operations could further stress already congested communication networks, which will struggle to guarantee low‐latency connectivity with very high degrees of reliability. For example, for HFT, latency requirements should be in the order of sub‐millisecond (a 1‐millisecond advantage in trading applications may be worth $100 million a year to a major brokerage firm, according to some estimates [11]), in contrast to the more relaxed (though already challenging) 1 ms 5G target. For blockchain operations, in turn, security, as well as energy consumption, will be key concerns. Finally, digitalization in the financial industry and the introduction of artificial‐intelligence‐based procedures will result in very large amounts of data to be exchanged and processed, which will likely saturate 5G capacity: the per‐user data rate may need to reach the Gbps range, at least one order of magnitude up from the 100 Mbps of 5G.
2.4 Conclusions
In this chapter, we analyzed possible business‐oriented use cases, scenarios, and relative KPIs for future 6G networks, as summarized in Figure 2.1. Notably, even though the market verticals we presented have been already considered in 4G and 5G networks, we focused on applications of these verticals that would not be supported by 5G networks in terms of (often combined) throughput, latency, coverage, and reliability requirements. After a brief introduction, we discussed the importance of services that (i) enable remote presence or inspection with high fidelity, including sensory information (teleportation, digital twin); (ii) globally connect goods, vehicles, and machines (Smart‐X IoT, smart transportation and industry); and (iii) provide secure continuous connectivity for critical information (remote healthcare interventions, PS, financial world). We believe that this chapter can provide a basis for a requirement‐driven development of future 6G networks, to enable key digital services for the connected society of 2030 and beyond.
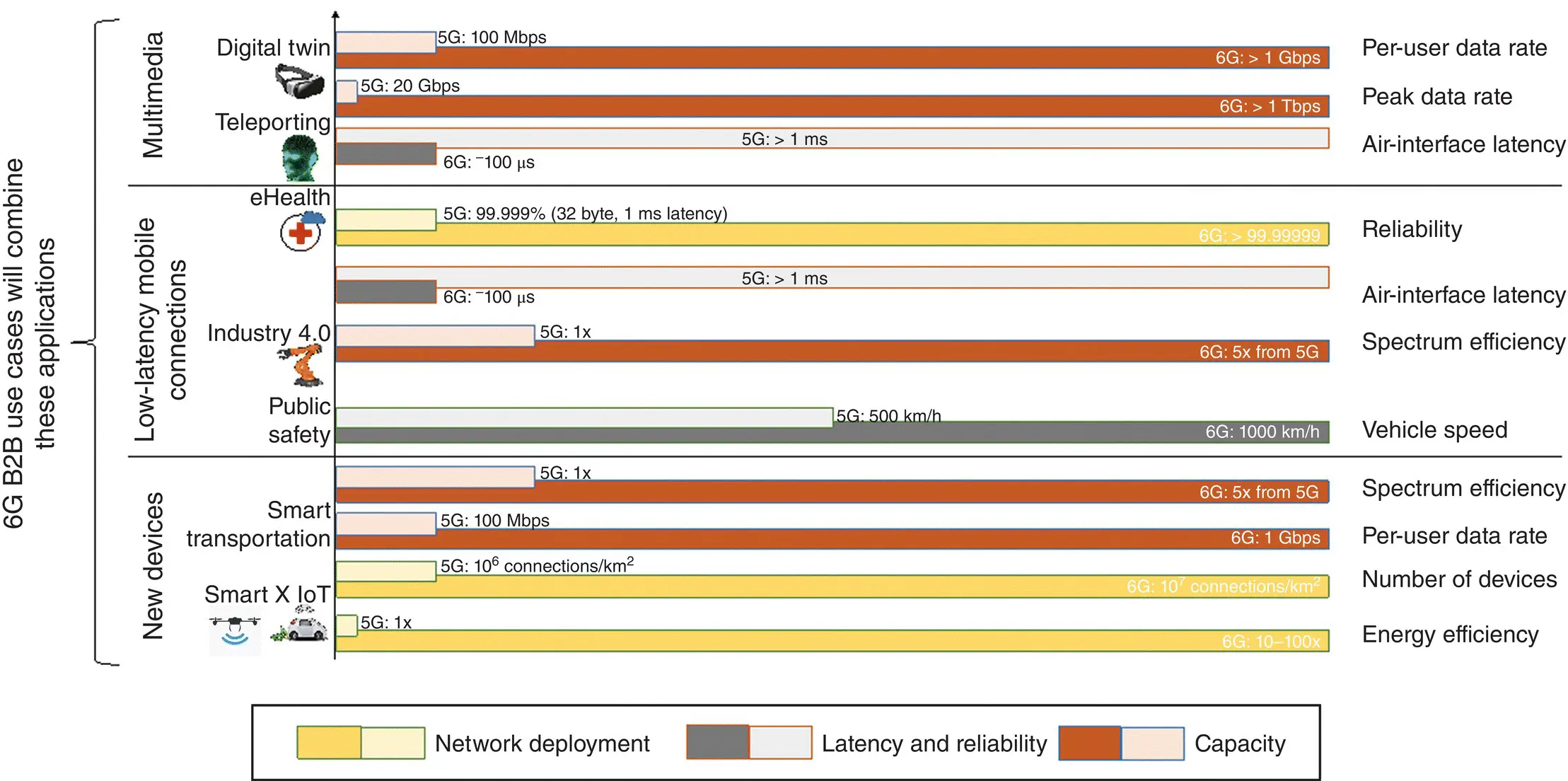
Figure 2.1 Representation of multiple KPIs of 6G use cases and improvements with respect to 5G.
References
1 1 Giordani, M., Polese, M., Mezzavilla, M. et al. (2020). Toward 6G networks: use cases and technologies. IEEE Communications Magazine 58 (3): 55–61.
2 2 Clemm, A., Vega, M.T., Ravuri, H.K. et al. (2020). Toward truly immersive holographic‐type communication: challenges and solutions. IEEE Communications Magazine 58 (1): 93–99.
3 3 Jones, D., Snider, C., Nassehi, A. et al. (2020). Characterising the digital twin: a systematic literature review. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology 29 (Part A): 36–52.
4 4 ITF (2019). ITF Transport Outlook 2019. Paris: OECD Publishing https://doi.org/10.1787/transp_outlook‐en‐2019‐en.
5 5 ETSI TR 103 562 V2.1.1, Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Analysis of the Collective Perception Service (CPS); Release 2, 2019.
6 6 Lin, X., Andrews, J.G., Ghosh, A., and Ratasuk, R. (2014). An overview of 3GPP device‐to‐device proximity services. IEEE Communications Magazine 52 (4): 40–48.
7 7 Pouttu, A., Burkhardt, F., Patachia, C. et al. (2020). 6G white paper on validation and trials for verticals towards 2030. White Paper.
8 8 Laya, A. (2017). The internet of things in health, social care, and wellbeing. Ph.D. dissertation. KTH Royal Institute of Technology.
9 9 Zhang, Q., Liu, J., and Zhao, G. (2018). Towards 5G enabled tactile robotic telesurgery. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.03586.
10 10 Hewa, T., Gür, G., Kalla, A. et al. (2020). The role of blockchain in 6G: challenges, opportunities and research directions. 2nd 6G Wireless Summit.
11 11 Martin, R. (2007). Wall Street’s quest to process data at the speed of light. InformationWeek.
Note
1 1G. Wikström et al, “Ever‐present intelligent communication. A research outlook towards 6G,” Ericsson White Paper, 2020. [Online] Available: https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports‐and‐papers/white‐papers/a‐research‐outlook‐towards‐6g
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Shaping Future 6G Networks»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Shaping Future 6G Networks» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Shaping Future 6G Networks» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












