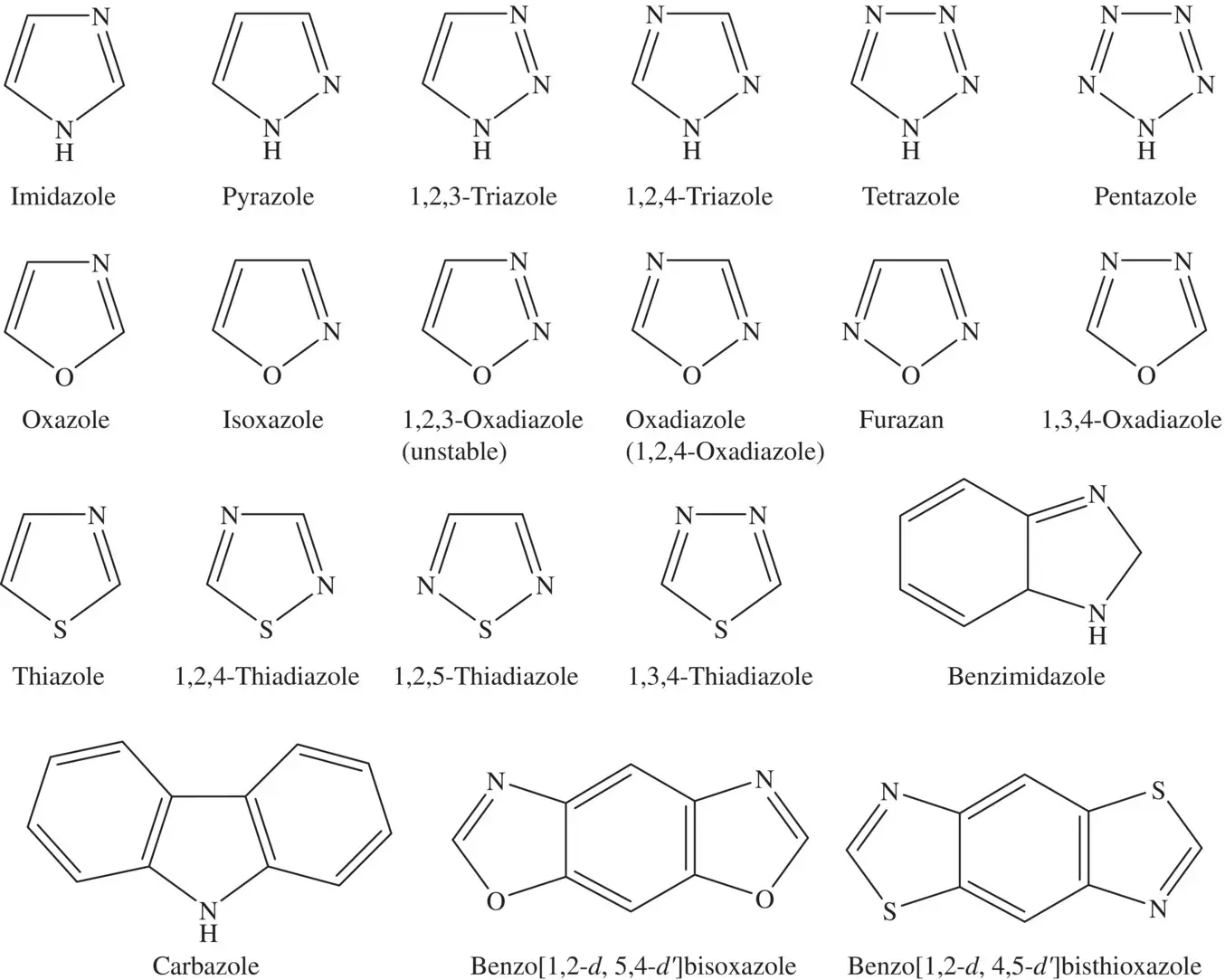
Figure 4.2 The chemical structures of the main azole compounds.
Azepines with seven‐membered as a subgroup of heterocyclic organic compounds and their effects are generally well known in medicinal fields [19] ( Figure 4.3). Potential use of waste drugs as corrosion inhibitors has received increasing attention in recent years. In 2009, Arslan et al. suggested that drug molecules with quantum chemical methods can show inhibitory properties for mild steel in an acidic environment [20]. It has also been reported that different groups of heterocyclic compounds used in many medical fields are promising as environmentally friendly corrosion inhibitors [21]. For a series of triazoloazepine derivatives, the corrosion and protection constants on steel 45 with a concentration of 1 M have been evaluated and suggested that Cl atom substitutions make the main structure more potent against corrosion among all substituents (H, F, Cl, I, CH 3O, and CH 3on different position of the molecule) [22]. In addition, the inhibitory characteristics of acetonitrile and secondary amines containing triazoloazepine ring for carbon steel corrosion in HCl and hydrogen sulfate have been investigated and reported that the reciprocal effects of triazoloazepine and p‐tolyl groups in the secondary amines provide a maximum synergetic effect during inhibition of steel corrosion in the HCl [23]. In the past, the corrosion inhibition properties of the carbamazepine unused drug on steel in different solvent environments have been examined, and the inhibition efficiency of the carbamazepine has been determined as 85% [24]. Besides, carbamazepine has effective role in both anodic processes and cathodic hydrogen evaluation, and thus the amount of carbamazepine does not affect the corrosion potency [24].
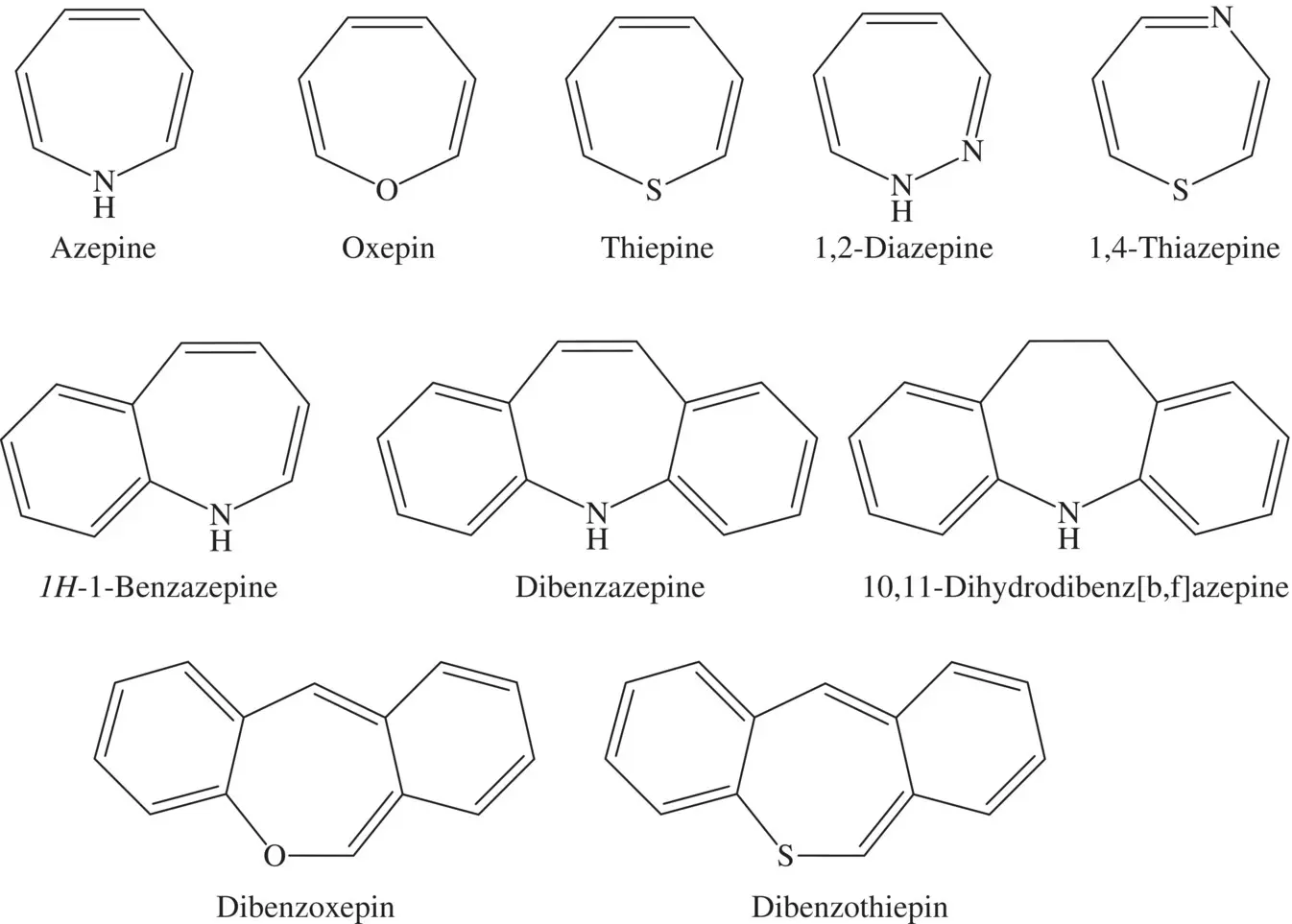
Figure 4.3 The chemical structures of the main azepine compounds.
4.2.1.3 Pyridine and Azines
Pyridine is a heterocyclic organic compound shown by the simple structural formula C 5H 5N and is widely used in many production areas due to its aromatic structure [25] ( Figure 4.4). The lone pair of the nitrogen atom in the structure has sp 2hybridization but does not contribute to the aromaticity of the compound as it lies outside the plane of the ring like sigma bonds and facilitates bond formation with an external system through an electrophilic attack. On the other hand, Azines are an organic compound group with the functional group RR′C = N‐N = CRR′, obtained by the condensation of hydrazine with ketones and aldehydes [26]. In the past, many papers have been reported on pyridine and its derivatives and suggested that they have sufficient potency for inhibition of iron, aluminum, carbon steel, N80 steel, mild steel, and zinc in different acidic media [27–34]. Furthermore, Kurmakova and coworkers [35], with empirical and theoretical support, have evaluated the effects of quaternary pyridinium, imidazopyridinium, and imidazoazepinіum salts for the inhibition of biocorrosion of steel; they have suggested that the observed inhibition capability of the salts have been largely proportional to both the polarizability and energy gap values of the salts. In addition, a lot of papers also have reported that azine derivatives have been potential corrosion inhibitors for mild steel [36–39], carbon steel [40], iron [41] and copper [42], an acidic environment. In a recent study, it has been suggested that the newly synthesized polybenzoxazine compound is promising as a highly corrosion‐resistant material for mild steel and similar alloys under different conditions, including marine conditions [43].
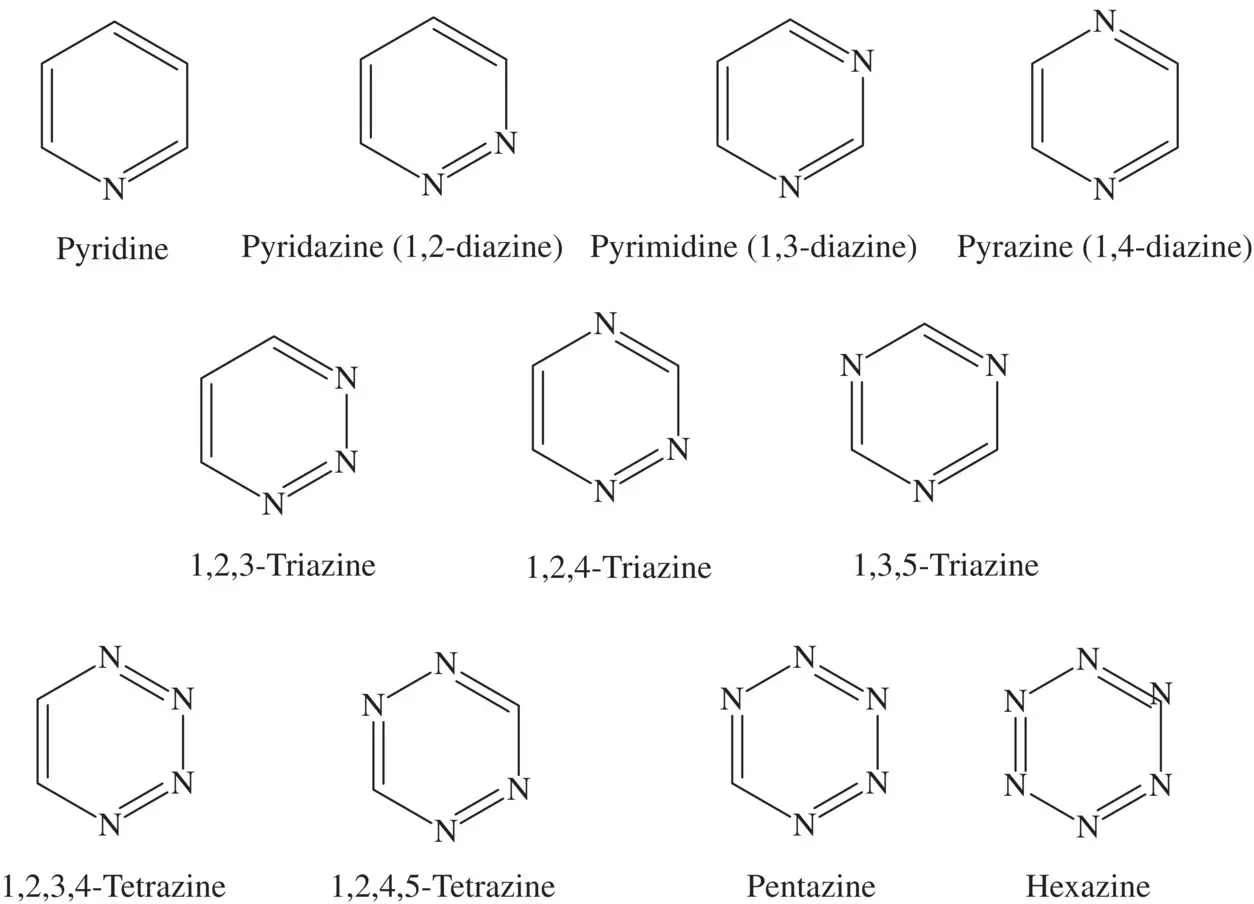
Figure 4.4 The chemical structures of the main pyridine and azine compounds.
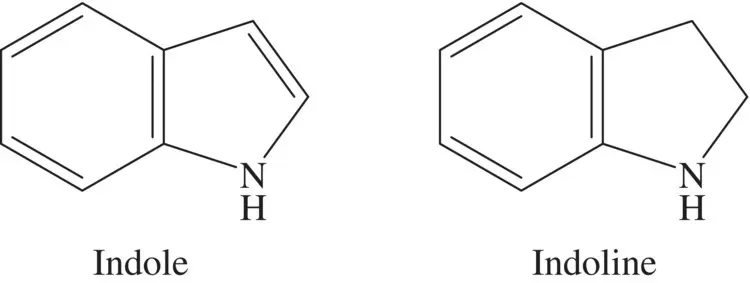
Figure 4.5 The chemical structures of the main indole compounds.
Indoles having a formula C8H7N has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six‐membered benzene ring fused to a five‐membered pyrrole ring, which provides the usefulness in many production and manufacturing sectors, as well as in the medicinal importance of them [44, 45] ( Figure 4.5). In the past, the inhibition capabilities of the indole‐based melatonin compound at 30 and 60 °C with a concentration of 10 mM on the steel surface have been determined [46] as 98.3 and 88.6%.In addition, the corrosion efficiencies of 12‐(2,3‐dioxoindolin‐1‐yl)‐N, N, N‐trimethyldodecan‐1‐ammonium bromide [47] and 1‐(2‐hydroxyethyl)‐2‐imidazolidinone [48] compounds on mild steel have been determined as 95.9% (in 1 M HCl) at 298 K and 85.4% (in 0.5 M HCl) at 293 K, respectively. In addition, the inhibition efficiency of 4‐((1H‐indol‐3‐yl) methyl) phenol (IMP) and 4‐ (di (1H‐indol‐3‐yl) methyl) phenol compounds to protect copper corrosion at 2 mM concentration has been determined [49] to be 99.3 and 97.5%, respectively. In another study, the inhibition potency of new synthesized 3,3‐((4‐(methylthio)phenyl)methylene)bis(1H‐indole) compound on copper corrosion has been examined; it has been suggested to have a good corrosion inhibition capability based on the electrochemical techniques; the adsorption process of the compound on copper surface has been contributed by both physisorption and chemisorption [50].
Quinoline is a compound with the formula C9H7N, usually soluble in organic solvents. Although it has little application area with its simple form, its derivatives have a wide range of applications in the literature, which from basic sciences to industrial engineering [51–56] ( Figure 4.6). Besides, quinoline derivatives containing highly polarizable groups such as –OH, –OMe, –NH 2, and so on in addition to having with both nitrogen atom and π ‐electronic system, it facilitates interaction with the metal surface, making this group of compounds very important among anticorrosive materials, especially in green corrosion inhibitors [57]. Recently, the anticorrosive behavior or corrosion inhibition potency of “oxoquinolinecarbohydrazide N‐phosphonate” [58], “8‐hydroxyquinoline” [59–61], “N,N′‐((ethane‐1,2‐diylbis(azanediyl))bis(ethane‐2,1‐diyl))bis(quinoline‐2‐carboxamide)” [62], “5‐{[(4‐dimethylamino‐benzylidene)‐amino]‐methyl}‐quinolin‐8‐ol” [63] derivatives on mild steel in acidic medium has been extensively studied. In a recent work, the inhibition capability of quinoline derivative “5‐benzyl‐8‐propoxyquinoline” [64] on Q235 steel in sulfuric acid medium has been determined as 97.7%, and it was shown that the inhibition efficiency has quite high even at high concentrations and temperatures. Furthermore, in another comprehensive study on mild steel in 15% HCl solution, the authors have found that the inhibition potential of quinoline derivative “dibenzylamine‐quinoline” [65] has reached its highest value at 363 K with 95.4%, which is quite sufficient to corrosion inhibitor of oil and gas acidification. Mohammadloo and coworkers have investigated the possible usage of “8‐ hydroxyquinoline” [66] in smart coating applications and have suggested that intelligent corrosion detection can be achieved using 8‐HQ as corrosion indicator and inhibitor, based on results obtained from fluorescence microscope.
Читать дальше
















