Active Electrical Distribution Network
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Active Electrical Distribution Network» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Active Electrical Distribution Network
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Active Electrical Distribution Network: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Active Electrical Distribution Network»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Discover the major issues, solutions, techniques, and applications of active electrical distribution networks with this edited resource Active Electrical Distribution Network: A Smart Approach
Active Electrical Distribution Network: A Smart Approach
Active Electrical Distribution Network — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Active Electrical Distribution Network», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
After a takeover, the focus of the DF shifts toward operations and asset management, thus neglecting the prime focus of loss reduction.
Loss handling is weakly addressed as operation and maintenance supersede the loss handling system and method.
Power management status is very poor as the DF is not allowed for market participation.
Investment toward system up-gradation and augmentation related works are poor due to lack of availability of sufficient capitals.
Investment needed for implementations, technologies, and innovations is missing because of the unavailability of adequate capital.
Capital mobilization toward renovation and modernization works are not sufficient.
DF is not able to ensure sufficient capital mobilization toward physical structure development and future investment because the tariff is not within its control.
1.4 Need for a Novel Business Model for Power Distribution under Smart Grid Environment
Poor innovation capability and adaptation of an inappropriate business model for the power distribution sector has acted as an obstacle toward incorporating the latest technologies, especially designed for the sector. For example, specific technologies have been designed for ToD/ToU metering, demand-side management (DSM) initiatives, loss reduction, distributed generation (DG) promotion, etc., but the adopted business model has failed in harnessing benefits from these specially designed technologies. Therefore, developing an appropriate business model that can capture values from these technologies is highly essential for the effective and efficient performance of the power distribution sector.
1.4.1 Description of the Novel Business Model
The power distribution function comprises two major activities, namely distribution network creation and retailing [10]. The development of an electricity distribution infrastructure capable of meeting the present as well as the future demand by the consumer is one of the most valuable assets but is very high capital intensive in almost every nation. After the infrastructure has been developed, increasing power quality, reliability, cost effectiveness, etc., create a demand for various ancillary services that impose various additional infrastructures in addition to the basic distribution infrastructure. For example, metering, communication, IT, controllers, protection infrastructure, etc., impose ancillary needs by the distribution sector. This again adds a huge capital requirement for the distribution infrastructure development. The huge capital required for this development is quite difficult for a government owned distribution company or a private distribution company to invest alone. Hence, outsourcing and partnership can be adopted as a possible solution toward capital mobilization for infrastructural development in the distribution sector.
The novel business model proposed [6] is shown in Figure 1.5. In this model of power distribution, various major tasks of power distribution have been proposed to be carried out through outsourcing. The PPP model, build–own–operate–transfer (BOOT) model, or Opex/Totex model has been adopted as the mode of outsourcing. The total structure of the power distribution business has been divided into three segments, viz. the physical infrastructure unit (PIU), the distribution management and maintenance unit (DMMU), and the control–operation–revenue management unit (CORMU). The following sections describes the various segments along with their functions.
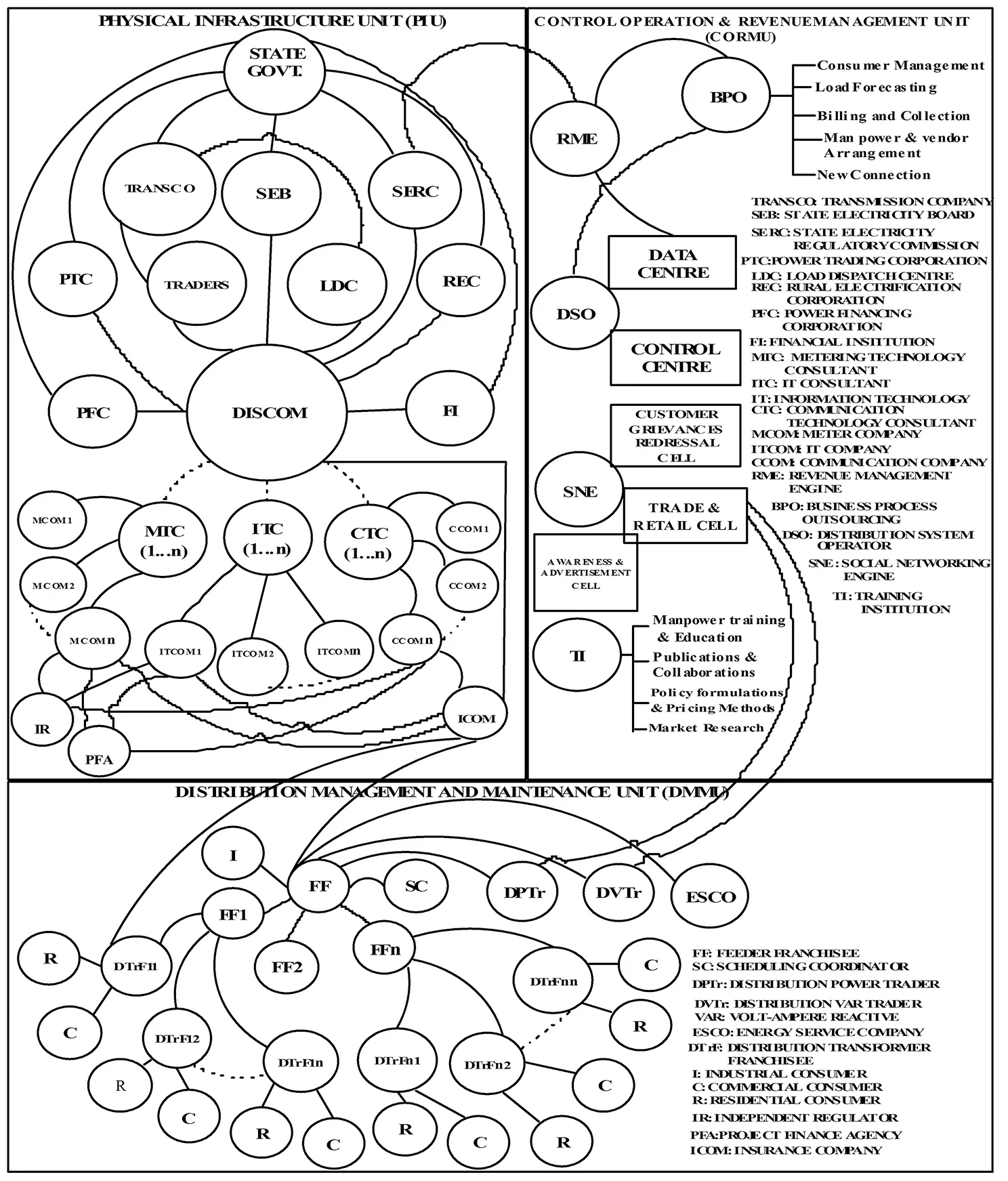
Figure 1.5 Nobel business model for power distribution.
1.4.2 Physical Infrastructure Unit (PIU)
Various physical entities such as DISCOM, metering company (MCOM), information technology company (ITCOM), and communication company (CCOM) are part of this unit, whose roles and functions are now given.
1.4.2.1 DISCOM
DISCOM, which is either government owned or a corporatized government owned or a private company, is responsible for building all the physical infrastructures. Physical infrastructures include: towers and poles, overhead conductors, cables, transformers, etc. DISCOM is responsible for any expansion or upgradation work.
1.4.2.2 MCOM
Metering is an essential task to bring energy accountability, data collection, appropriate planning, device monitoring, risk reduction, etc. Meters are required at all different modes of power transactions, which is very huge in numbers. Therefore, metering activity is a big task in power distribution and hence the metering business can be carried out as a separate segment of power distribution business as MCOMs. An MCOM receives the metering contract from a DISCOM through metering technology consultants (MTC) hired by them.
1.4.2.3 ITCOM
Maintaining and managing a network database is an essential requirement in the power distribution sector, like many other sectors. It helps in planning and monitoring, decision making, creating transparency, keeping records, etc. In a power distribution business, it is required to deal with a very big data base as collecting and managing this large amount of data is not possible manually. Hence automation is highly essential where the information technology plays an important role. Automation should necessarily be preferred over manual activities and this distribution automation (DA) can provide power utilities with a long-term competitive advantage through better power reliability and an improved customer service [11]. As the data maintenance and management activity is a very big activity in a power distribution business, it can be carried out as a distinct business activity. This is the basic function of power distribution and hence there exists scope for involving different ITCOMs for data maintenance and management. To get the business contract from a DISCOM, an ITCOM has to approach it through an IT consultant (ITC).
1.4.2.4 CCOM
Very big data is required to be communicated across different nodes of the power distribution network to ensure the reliable, stable, and secure operation of the distribution networks for which a strong communication channel is essential. As the power distribution system is distributed across a huge area at which millions of nodes are present, the number of communication channels required is also huge. Hence, focusing on the development and management of this communication infrastructure with the focus on electrical infrastructure becomes difficult for the DISCOM. Furthermore, the demand response (DR) is also considered an integral part of the power system and market operational practices [12] and is considered a key focus area, which needs communication that is possible through smart grid initiatives [13]. Hence, the activities related to communication can be segregated as a distinct activity and a separate entity can be allotted to hold the communication related business as a CCOM. To get the business contract from a DISCOM, a CCOM must approach it through communication technology consultants (CTCs).
1.4.2.5 ICOM
There exists a risk of contingent and uncertain losses in every business. Hence to protect the business participants from such risk, involvement of an insurance company (ICOM) is essential, as in other sectors.
1.4.2.6 IR
It is highly essential for any organization to protect the interest of various stakeholders for which regulatory frameworks and standardizations are required. To carry out these tasks, roles of an independent regulator (IR) are necessary in the power distribution sector. An IR functions as a non-profit organization and will help all the stakeholders.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Active Electrical Distribution Network»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Active Electrical Distribution Network» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Active Electrical Distribution Network» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.











