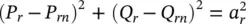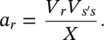
Figure 1-27 Ranges of Q rversus P rat the receiving end of the transmission line for the range of modified power angle  from 0º to 90º when V s= V r= 1 pu, X = 0.5 pu, and R = 0 ( X / R = ∞) using Shunt–Shunt and Shunt–Series configurations, respectively.
from 0º to 90º when V s= V r= 1 pu, X = 0.5 pu, and R = 0 ( X / R = ∞) using Shunt–Shunt and Shunt–Series configurations, respectively.
In an alternate approach to the Shunt–Shunt compensation, the same active and reactive power flows ( P rand Q r) can be obtained using a PFC with a Shunt–Series configuration that applies a series‐compensating voltage ( 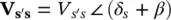 ), such that
), such that
(2‐94b) 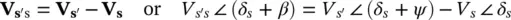
or when δ s= 0°,
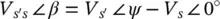
where the phase‐shift angle,
(2‐51b) 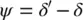
or
(2‐51c) 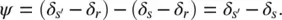
The magnitude ( V s′s) and the relative phase angle ( β ) of the series‐compensating voltage ( V s′s) are
(2‐100) 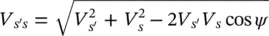
and
(2‐101) 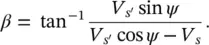
For a Shunt–Shunt Compensator, the relationship between the active and reactive power flows ( P rand Q r) at the receiving end is shown by a quarter circle, the radius ( a′ ) of which is varied within the upper and lower limits by the modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′) as shown in Figure 1-27. The relationship is given by the following equation:
(2‐79) 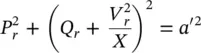
where
(2‐61) 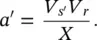
Equation (2‐79)represents the locus of a circle, centered at 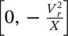 with a radius of a′ .
with a radius of a′ .
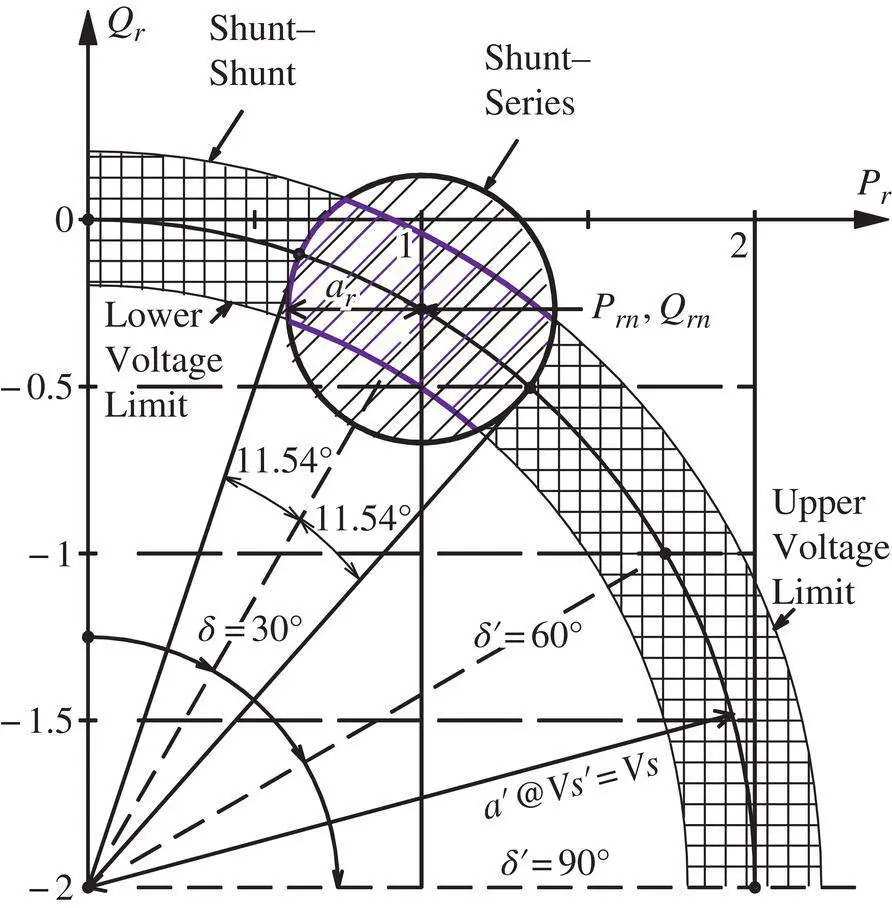
For a Shunt–Series Compensator, the relationship between active and reactive power flows ( P rand Q r) at the receiving end is shown by the small circle in Figure 1-27and is given by the following equation:
(2‐136) 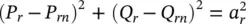
where P rnand Q rnare the natural active and reactive power flows at the receiving end of the line and
(2‐132) 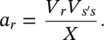
Equation (2‐136)represents the locus of a circle, centered at [ P rn, Q rn], with a radius of a rthat is given in Equation (2‐132).
An ideal PFC controls the values of the power flow control parameters (line voltage magnitude, its phase angle, and line reactance) to regulate the magnitude and the phase angle of the line voltage simultaneously by adding a series‐compensating voltage to the original voltage with the use of a Shunt–Series Compensator as shown in Figure 1-28. The compensating voltage is variable in magnitude and phase angle with respect to the line voltage. The series‐connected VSC is rated for a fraction of the line voltage, but carries the full line current. The shunt‐connected VSC is rated for the full line voltage, but carries only a fraction of the line current. Therefore, each VSC carries only a fraction of the full transmitted power. In an actual installation, both shunt‐ and series‐connected VSCs are designed to be of the same voltage and current ratings, which reduces the inventory of spare parts. Therefore, their different interface voltages with the line are accomplished with selection of proper turns‐ratios of the respective coupling transformers. For example, in the world’ first UPFC at the AEP Inez substation, the two VSCs were designed identically to be rated at ±160 MVA and 37 kV phase‐to‐phase voltage. However, the shunt VSC was connected to a 138 kV‐line through a coupling transformer and the series VSC was designed to inject 13.33 kV (~16% of the phase voltage) in series with the line through a coupling transformer.
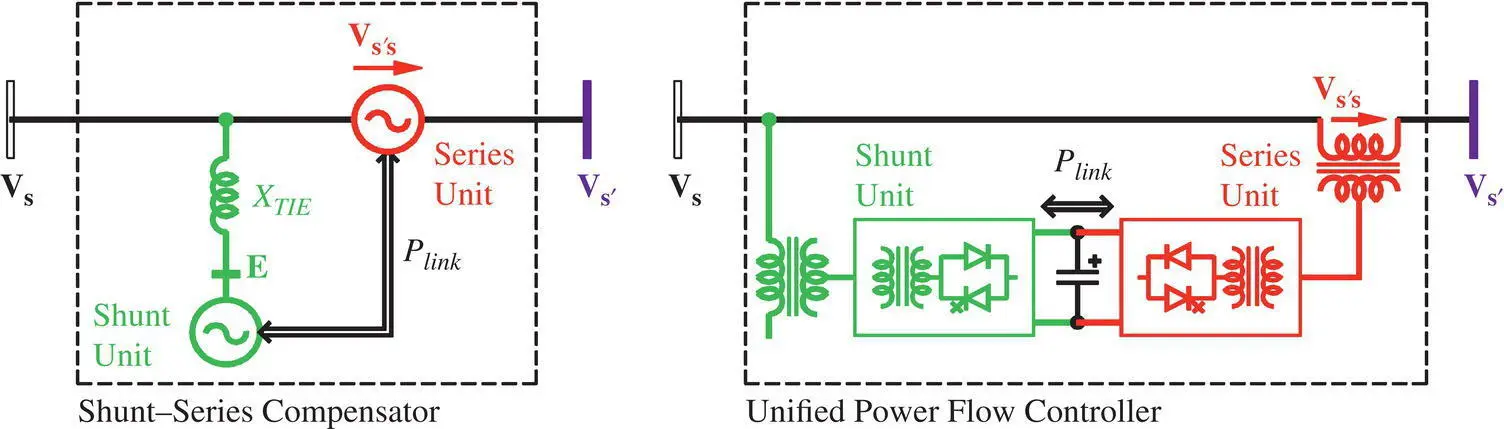
Figure 1-28 Independent active and reactive power flow controller with local reactive power compensation using a Shunt–Series Compensator‐based UPFC.
The Shunt–Series Compensator connects a compensating voltage in series with the line at any relative phase angle in the range of 0 °≤ β ≤ 360 °with respect to the line voltage at the POC. Figure 1-27shows that a series‐compensating voltage of 0.2 pu modifies the power angle by 11.54 °, which may be near the allowable limit. The most important and unique feature of the Shunt–Series configuration is that for a given amount of transmission line power, the series‐connected VSC has a large leverage between its own rating and the controlled transmission line power. The series‐compensating voltage needs to be rated for only a fractional amount of transmitted power, whereas the shunt‐connected VSC in the Shunt–Shunt configuration has no such leverage and it needs to be rated for the full amount of transmitted power. Because of this uniqueness, the Shunt–Series configuration is a preferred topology for a PFC. However, in some special cases for point‐to‐point transfer of power between two isolated networks with POC voltages ( V sand V s′) as shown in Figure 1-26or interconnection of two transmission lines with different voltages or phase angles (or frequencies), Shunt–Shunt configuration may be the preferred solution. One such system, called the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) Interconnections, consists of Eastern Interconnection, Western Interconnection, and Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) Interconnection, which are three separate systems of 60 Hz frequency that are asynchronous to each other. Another such system exists in Japan, connecting a 50 Hz frequency system in the North and the East with a 60 Hz frequency system in the South and the West, that is asynchronous to each other.
Читать дальше


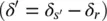 from 0º to 90º when V s= V r= 1 pu, X = 0.5 pu, and R = 0 ( X / R = ∞) using Shunt–Shunt and Shunt–Series configurations, respectively.
from 0º to 90º when V s= V r= 1 pu, X = 0.5 pu, and R = 0 ( X / R = ∞) using Shunt–Shunt and Shunt–Series configurations, respectively.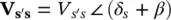 ), such that
), such that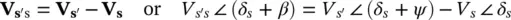
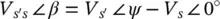
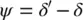
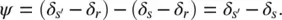
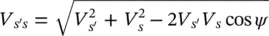
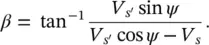
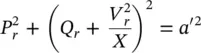
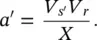
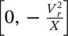 with a radius of a′ .
with a radius of a′ .