Application of Nanotechnology in Mining Processes
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Application of Nanotechnology in Mining Processes» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Application of Nanotechnology in Mining Processes
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Application of Nanotechnology in Mining Processes: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Application of Nanotechnology in Mining Processes»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Nanotechnology has revolutionized processes in many industries but its application in the mining industry has not been widely discussed. This unique book provides an overview of the successful implementation of nanotechnology in some of the key environmental and beneficiation mining processes.
Audience
Application of Nanotechnology in Mining Processes — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Application of Nanotechnology in Mining Processes», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Rare earth elements consist of the 15 lanthanide elements including yttrium (Y) and scandium (Sc) on the periodic table. These elements exhibit similarities in geochemical behavior because of their identical stable trivalent oxidation state (except Ce and Eu), systematic decrease in ionic radius and increasing atomic number [24]. Mineral deposits of REE typically occur in low concentrations as oxides or carbonates in a broad array of geologic formations in very few countries, and over 90% of REE production occurs in China [25]. This near-monopoly has created a conceivable handicap for other countries where REEs are not readily produced [10]. The demand for these REEs has increased tremendously over the years due to their extensive application in several scientific advancements ( Table 1.3) owing to their unique magnetic, phosphorescent, and catalytic properties [26]. The extraction of these elements from their conventional ores is energy-intensive and alone is insufficient to satisfy the rising demand in the foreseeable future due to their strategic importance in modern technology [27, 28]. Consequently, it has prompted researchers, national governments, and private entities to develop possible techniques for recovering these elements from unconventional sources, such as AMD, to meet the rising demand. In the United States, a significant concentration of REE was found in precipitates formed during acid mine drainage treatment from coal tailings [10]. In Brazil, acid water generated in a uranium mine in the state of Minas Gerais was found to contain a total concentration of 126 ppm of REE significantly higher than acid waters generated from different mines worldwide [29]. Also, in the Guizhou province in southwestern China, the Xingren coalfield mine is reported to contain REE concentrations varying between 0.1 and 0.9 ppm [30]. Although the recovery of rare earth metals from AMD remains a great challenge as it is several orders of magnitude lower in this product than the conventional REE ores, it can be recovered using a low-cost nano-adsorbent if concentrated out of the liquid solution during the neutralization processes [31]. The emergence of nanotechnology has contributed tremendously to economic prosperity by providing solutions to some challenges facing modern-day technology [32]. In this chapter, a state-of-the-art technique will be presented using modified magnetic dendrimer nanoparticles to effectively recover REE from AMD after alkaline treatment. First, the generation of AMD and its environmental effect are highlighted, and then in the following sections the shortcomings of various remediation methods for AMD as background motivation for this method design are discussed.
1.2.3 Classical AMD Remediation and Treatment Methods
The effects of AMD on the environment are enormous, and several remediation technologies have been implemented ( Figure 1.2) depending on the geographical conditions and weather effects of the mining sites to ensure environmental compliance. Over the past decades, neutralization techniques involving active and passive methodologies have been employed, and a detailed description of these technologies was reported by Naidu et al ., including a few case studies on actual mining sites [46]. However, these technologies still have some shortcomings and call for logical approaches to enhance their effectiveness. Active treatment technologies use neutralizing agents, such as CaCO 3, Ca (OH) 2, CaO, Na 2CO 3, NaOH, and NH 3, that produce sludge or precipitates heavily laden with metals and REEs, which require suitable disposal methods, making the procedure very expensive [47].
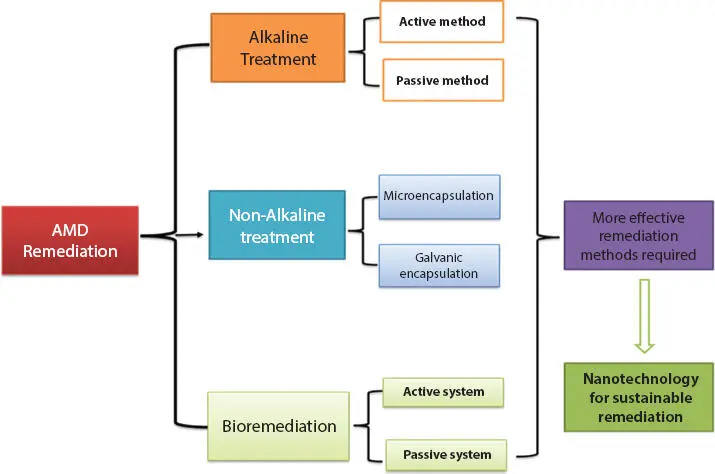
Figure 1.2 Schematic of the different types of remediation techniques for ARD neutralization or prevention.
Similarly, passive treatments, although being the least expensive approach, also make use of neutralizing agents. This technology is effective in mine waste with low acidic content and minimal water flow rate fluctuation. The major drawback of passive technology is that it requires a lengthier operative time for effective remediation, compromising its usage in modern mining activities [48]. Although investigations and pilot analysis have indicated that active and passive approaches can positively handle AMD [49], the continuous use of chemicals to neutralize AMD has raised some environmental concerns, making this procedure unsustainable and costly. In avoiding the use of excess chemicals, Tabelin and coworkers introduced two passivation techniques known as microencapsulation and galvanic microencapsulation techniques that could potentially prevent pyrite oxidation at the point source. The microencapsulation technique uses a redox-reactive organic carrier that is highly sensitive to pyrite in mine tailings to coat pyrite surfaces and thus prevent AMD formation. Meanwhile, galvanic encapsulation is based on galvanic interactions between pyrite and metals with lower rest potentials to suppress the oxidation of sulfide minerals [50]. However, these methods are not sufficient as they only suppress sulfide oxidation on a temporary basis, besides which sulfide oxidation is a natural process that is slow and difficult to prevent. A recent study has shown that active and passive biological remediation techniques offer great advantages, permanently removing sulphate and metals from mine drainage and having a high ability to recover the valuable metals [51]. However, the shortcomings of these methods is the high cost involved and the difficulty in setting up the processes, calling for a more sustainable and cost-effective technique for the remediation of AMD from mining MSWs.
1.3 Dendrimer as Extraction Agent of Rare Earth Element in AMD
Polymeric materials such as dendrimer nanoparticles have been proven to effectively recover metals from wastewater [52, 53]. Dendrimers are three-dimensional, nanosized polymeric material with great surface chemistry consisting of numerous end groups that can be manipulated or functionalized as modules for a thriving nanotechnology industry [54]. Intensive research studies have been conducted to evaluate the feasibility of retrieving REE from unconventional sources using different techniques ( Table 1.4). However, these techniques also have their shortcomings involving cost and, therefore, developing an appropriate cost-effective method to extract them from AMD could make it a perfect source of REE. The use of dendrimers as an absorbent for the removal of metals in solution is a growing trend, and structurally, it has a tree-like branched nature consisting of a central core, an interior and exterior branched cell with the potential of forming more branches through a repetitive synthesis of monomers known as generation growth [55]. The higher generation growth of dendrimers is believed to carry more functional groups on their molecular surfaces. This allows them to interact with solid surfaces, acting as an adsorbent or ligands soluble in water to remove solvated toxic metals [56–58]. The properties of dendrimers are dependent mainly on these functional groups, such as amine, carboxyl, or hydroxyl groups, attached to dendrimers, which are used primarily for adsorption reactions of different targets [55, 59]. For instance, amine-terminated dendrimers, such as polyamido-amine dendrimers (PAMAMs), exhibit a high binding affinity for metal ions to their surface via coordination with the amine or acid functionality [60].
Table 1.4 Recovery of REE using different techniques.
| Types of REEs | Technique(s) used for recovery/extraction |
| Gd | Magnetically retrievable imprinted chitosan/carbon nanotube composite reverse osmosis.Binding on mesoporous silica supports functionalization with diphosphonic acid.Ion exchange on cesium molybdo vanado phosphate immobilized on platelet SBA-15. |
| La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm | Adsorption on silica gel modified with diglycol amic acid. |
| Tb | Nano-Mg (OH) 2reaction column.Extraction using solvent-impregnated resin containing TOPS 99. |
| Eu | Sorption on graphene oxide-supported polyaniline composites.Adsorption on graphene oxide nanosheets. |
| Nd | Adsorption on carboxymethyl chitosan adsorbents entrapped by silica. |
| Lu, Yb | Solid-liquid extraction using Tulsion CH-96 resin. |
1.3.1 Poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) Dendrimers
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Application of Nanotechnology in Mining Processes»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Application of Nanotechnology in Mining Processes» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Application of Nanotechnology in Mining Processes» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












