Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A robust treatment of traditional and new techniques in sustainable agriculture Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies,
Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies
Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
2.7.3 Diversification with Horticultural Crops
The fruits, vegetables, spices, condiments, and flowering ornamental plants are very useful for developing high productive and profitable diversification plan in many areas. Depending upon the resource availability, prevailing market conditions and available technological support, different crops components may be selected. Under semiarid conditions a similar diversified fruit tree‐based diversified system was developed. The IFS refers to combining one or more agriculture and allied activities with field crop cultivation. This will certainly help in making rainfed areas a stable, sustainable agroecosystem (Rathore et al. 2019). Many studies have identified the important role of perennial vegetation in supporting biodiversity in general and beneficial organisms in particular (Perfecto and Vandermeer 2008).
Table 2.4 Possible new niches for pulses.
Source : Based on Singh et al. 2009.
| Cropping systems | Possible niches | Suitable varieties |
|---|---|---|
| Tur‐wheat system | North‐West U.P., Haryana, Punjab, and North Rajasthan | Virat, Pusa Vishal, UPAS 120, Manak, Pusa33, AL 15, AL201 |
| Maize‐ rabi pigeonpea | Central and Eastern U.P., North Bihar, West Bengal, Assam | Pusa 9, Sharad |
| Maize‐potato/mustard + mungbean/urdbean | Punjab, Haryana, and West U.P. | Mungbean:Pant Mung 2, PDM11,HUM 2, SML668, Pusa Vishal Urdbean: PDU 1, NarendraUrd 1, Uttara |
| Spring sugarcane + mungbean/urdbean | East U.P., Bihar, West Bengal | Mungbean:Pant Mung 2, PDM 11, Narendra Mung 1 Urdbean:PDU 1, Pant Urd 19 |
| Rice‐mungbean | Orissa, Part of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, A.P. | TARM 1, Pusa 9072 |
| Rice‐urdbean | Coastal area of A.P., Karnataka, Tamil Nadu | LBG 17, LBG 402 |
| Rice wheat mungbean | Western U.P., Haryana, Punjab | Pant Mung 2, Narendra Mung 1, PDM 139, HUM 2 |
The agri‐horti system has been developed for round the year cultivation of the crops and generation of produce for regular income and employment. During kharif season, intercropping of legume crops were taken in the rows in between the fruit crops. In fruits crops falsa ( Grewia asiatica ), karonda ( Carissa carandas ), drum stick ( Moringa oleifera ), aonla ( Phyllanthus emblica ), guava ( Psidium guajava ), and pomegranate were grown and in field crops during kharif season vegetable cowpea, mung bean was cultivated as intercrops and in this intercrop space, vegetable pea, Bengal gram, and cole crops will be taken during the rabi season. The whole system is designed to be irrigated by drip irrigated system from the pond. The well designed micro irrigation system along with fertigation device and appropriate filters ensures the risk of crop failure due to moisture shortage. The rain water is harvested and stored in the pond for life saving irrigation through micro irrigation system. Thus, every drop of water is efficiently utilized for production of different crops. The data revealed that the different agri‐horti systems are economically viable, productive, and employment generator round the year ( Figure 2.4). The inclusion of horticultural crops not only guarantee higher productivity and profitability but also ensure nutritional security of a family household ( Table 2.5).
2.8 Constraints in Crop Diversification
The crop diversification approach has been identified as one of the potential agronomic intervention to address many of the present challenges in farming across the globe. Even out of the 17 sustainable development goals (SDGs), 6–7 SDGs have been identified as having greater involvement of CD to achieve them within set time framework.
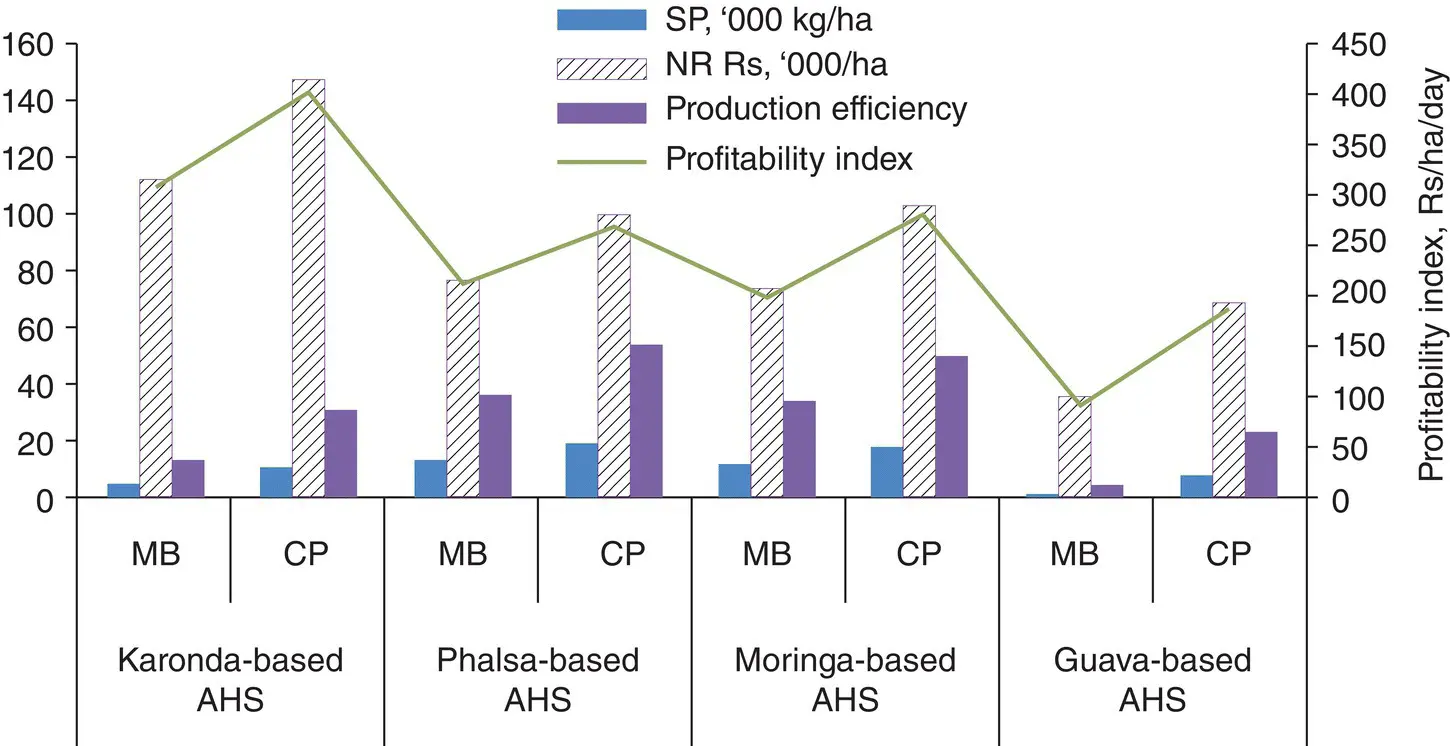
Figure 2.4 Diversified agri‐horti system for higher system yield and income.
Table 2.5 Nutritional importance of vegetable crops.
Source : Jogendra et al. 2019.
| S.No. | Dietary factors | Source vegetables |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | High energy | Immature seeds of broad bean and peas, lima bean, tapioca, yam, colocasiacorms, potato, brussels sprouts, onion and garlic, sweet potato |
| 2 | Proteins | Leguminous vegetable crops such as vegetable peas, beans, garlic, brussels sprouts, cowpea, lima bean seeds, amaranthus leaves, drumstick leaves, and menthe |
| 3 | Vitamin A (beta carotene) | Carrot, spinach, turnip green, palak, sarson sag, amaranth, coriander, sweet potato, pumpkin, tomato |
| 4 | Vitamin B complex | Peas, broad bean, lima bean, garlic, asparagus, colocasia and tomato |
| 5 | Vitamin C | Turnip green, green chilies, brussels sprouts, mustard green, amaranth, coriander, drumstick leaves, cauliflower, KnollKhol Spinach, cabbage, bitter gourd and reddish leaves |
| 6 | Calcium | Amaranth, parsley, palak, Chinese cabbage, kale, collard greens, broccoli, spinach |
| 7 | Iron | Amaranth, beans, peas, spinach, radish leaves, turnip greens |
| 8 | Potassium | Cowpea, peas, sword bean, colocasia, melons, potato, sweet potato, spinach, turnip green, collard greens, peas, beans |
In spite of all advantages being offered due to crop diversification, its adoption is poor due to following constraints:
Over 117.5 mha (63%) of the cropped area in the country is completely dependent on rainfall.
Both suboptimal and over‐use of resources.
Inadequate supply of seed and planting material for crop diversification
Fragmentation of landholdings which discourage modernization and mechanization of agriculture.
Poor basic infrastructure like rural, roads, power, transport, communication, etc.
Inadequate postharvest technologies and weak agro‐based industries.
Weak research‐extension and farmer linkage
Decreased investment in the agriculture sector over the years.
2.9 Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Crop diversification is of vital significance to improve livelihood, enhanced system productivity and at the same time maintain many of the ecosystem services. Diversified crop production systems are of 10 less risky, if managed proficiently, they are benefitted from synergisms among different compatible crops. The system productivity also increases by two to four times over sole cropping under diversified system of farming. The core characteristics of crop diversification is to ensure complementarily, among the selected crops in spatial and temporal dimension. Hence, the resource use efficiency is also increasing with minimal wastage of the inputs. By 2050, the food supply must double to cope for rising population pressure, and impact of climate change will further create complexity in ensuring food security. It is high time to address the constraints as explained above for wider adoption. The crop diversification has also been identified as a climate smart technology to combat the risks due to climate change in agricultural production system. Under stressed ecologies like drought and flood‐prone areas, CD is an ideal approach for mitigating the negative impact of adverse weather conditions. Another vital characteristic of the agricultural diversification is efficient use of on‐farm resources, better recycling of by‐products which maintain ecosystem services for improving long‐term system sustainability.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Sustainable Agriculture Systems and Technologies» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.











