Signals carried by the Lamb waves a) S 0
and b) A 0for different prop...Figure 4.7. Phase velocities (solid lines) and group velocities (dashed line) of...Figure 4.8. The Love wave propagates in a structure composed of a plate of thick...Figure 4.9. Phase velocity (solid lines) and group velocity (dashed lines) for t...Figure 4.10.
Love waves: a) tangential displacement u 3
and b) stress σ 23in the ...Figure 4.11.
The propagation medium, inhomogeneous along x 2, is divided into N s...Figure 4.12.
Arrangement of the axes. The plate thickness is d = 2
h Figure 4.13. Lamb wave displacement. a) Symmetric: on either side of the median ...Figure 4.14.
The (
ω, k ) plane is divided into three sectors, depending on the va...Figure 4.15. Dispersion curves of the first Lamb modes in a duralumin plate. Sym...Figure 4.16. a) Phase velocities and b) group velocities of the first Lamb modes...Figure 4.17.
Particle displacements for a duralumin plate of thickness d =2 mm, ...Figure 4.18. Lamb wave in an isotropic plate. Mechanical displacement of the fir...Figure 4.19.
Dispersion curves of the S 5
and S 8modes for different values of th...Figure 4.20. Normalized cut-off frequencies fcd/VT (solid lines) and fcd/VL (das...Figure 4.21.
Variation with Poisson’s ratio ( 0 ≤
ν ≤ 0.49) of Lamb waves in a fr...Figure 4.22.
Specific behavior for ν = 0 (rigid solid). a) Segments of the line ...Figure 4.23. Lamé modes. a) The guided wave is a transverse wave propagating at ...Figure 4.24.
a) Dispersion curves of Lamb modes S 0
, S 1
, S 2
, S 2band of the first...Figure 4.25. Immersed plate. Disposition of axes and components of the wave vect...Figure 4.26. Duralumin plate immersed in water. a) Phase velocity of the fundame...Figure 4.27. a) Plate immersed in water, map of the intensity reflection coeffic...Figure 4.28. Unidirectional composite material made of carbon fibers embedded in...Figure 4.29. Lamb wave slowness curves for a unidirectional composite plate of t...Figure 4.30.
Cylindrical waveguide of radius a and coordinates r, θ, z Figure 4.31.
Steel cylinder (ν = 0.27). Dispersion curves for the first longitud...Figure 4.32. First three longitudinal modes propagating in a steel cylinder. Var...Figure 4.33. Dispersion curves for the first flexural modes of a steel wire with...Figure 4.34. Dispersion curves for the first torsional modes. The mode T(0,1) is...Figure 4.35. Steel tube (mean radius: 3.75 mm, thickness: 1.5 mm). Variation of ...
5 Appendix 1Figure A1.1. Cylindrical coordinate system. For a color version of this figure, ...Figure A1.2. Spherical coordinate system. For a color version of this figure, se...
6 Appendix 2Figure A2.1. a) Two-dimensional crystalline lattice: all nodes are equivalent, a...Figure A2.2. Rows. The nodes in a two-dimensional lattice are located at the int...Figure A2.3. Miller indices. The spacing between two neighboring lattice planes ...Figure A2.4. A twofold inverse axis ( A 2) is equivalent...Figure A2.5. Stereographic projection. a) Triangles SOp and SPN are similar, so ...Figure A2.6. Association of an n-fold direct axis with n perpendicular binary ax...Figure A2.7. The symmetry elements of a cube are 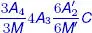 Figure A2.8. The 32-point symmetry classes of crystals
Figure A2.8. The 32-point symmetry classes of crystals
7 Appendix 3Figure A3.1. The waves propagate along the x 1axis of the waveguide. Quantities ...
1 Chapter 1 Table 1.1. Values of Lamé constants, Young’s modulus, Poisson’s ratio and mass d...
Table 1.2. Bulk wave velocities for various isotropic materials. The media that ...
Table 1.3. Remarkable values for the Poisson’s ratio ν, the bulk modulus K and t...
Table 1.4. Relations between the various elastic constants and the Poisson’s rat...
Table 1.5. Components of the stiffness tensor CIJ for crystals, according to the...
Table 1.6. Mass density (in kg.m −3) and stiffness constants (in GPa) for some an...
Table 1.7. Components of the elastic, piezoelectric and dielectric tensors: | an...Table 1.8. Piezoelectric constants (C/m 2 ) and dielectric constants ( 10 −11F/m) o...
2 Chapter 3Table 3.1. Characteristics of Rayleigh waves for different piezoelectric materia...
3 Chapter 4Table 4.1. Cut-off frequency and mechanical displacement of higher order Lamb mo...Table 4.2. Critical values of the velocity ratio VL/VT, of Poisson’s ratio ν and...Table 4.3. Characteristic velocities of elastic waves propagating in an isotropi...
1 Cover
2 Table of Contents
3 Title Page Series Editors Pierre-Noël Favennec† and Frédérique de Fornel
4 Copyright First published 2022 in Great Britain and the United States by ISTE Ltd and John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Apart from any fair dealing for the purposes of research or private study, or criticism or review, as permitted under the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988, this publication may only be reproduced, stored or transmitted, in any form or by any means, with the prior permission in writing of the publishers, or in the case of reprographic reproduction in accordance with the terms and licenses issued by the CLA. Enquiries concerning reproduction outside these terms should be sent to the publishers at the undermentioned address: ISTE Ltd 27-37 St George’s Road London SW19 4EU UK www.iste.co.uk John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 111 River Street Hoboken, NJ 07030 USA www.wiley.com © ISTE Ltd 2022 The rights of Daniel Royer and Tony Valier-Brasier to be identified as the authors of this work have been asserted by them in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s), contributor(s) or editor(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of ISTE Group. Library of Congress Control Number: 2021951482 British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data A CIP record for this book is available from the British Library ISBN 978-1-78630-814-6
5 Preface
6 List of Main Symbols
7 Begin Reading
8 Appendix 1 Differential Operators in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates
9 Appendix 2 Symmetry and Tensors
10 Appendix 3 Transport of Energy
11 References
12 Index
13 End User License Agreement
1 v
2 iii
3 iv
4 ix
5 x
6 xi
7 xii
8 xiii
9 xiv
10 xv
11 1
12 2
13 3
14 4
15 5
16 6
17 7
18 8
19 9
20 10
21 11
22 12
23 13
24 14
25 15
26 16
27 17
28 18
29 19
30 20
31 21
32 22
33 23
34 24
35 25
36 26
37 27
38 28
39 29
40 30
41 31
42 32
43 33
44 34
45 35
46 36
47 37
48 38
49 39
50 40
51 41
52 42
53 43
54 44
55 45
56 46
57 47
58 48
59 49
60 50
61 51
62 52
63 53
64 54
65 55
66 56
67 57
68 58
69 59
70 60
71 61
72 62
73 63
74 64
75 65
76 66
77 67
78 68
79 69
80 70
81 71
82 72
83 73
84 74
85 75
86 76
87 77
88 78
89 79
90 80
91 81
Читать дальше

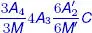 Figure A2.8. The 32-point symmetry classes of crystals
Figure A2.8. The 32-point symmetry classes of crystals










