10 Chapter 11Figure 11.1 The quantum circuit employed in Shor’s algorithm for finding the...Figure 11.2 The quantum circuit of the quantum phase estimation algorithm, w...Figure 11.3 Grover operator’s quantum circuit including an oracle, two n‐qub...Figure 11.4 Example of Grover’s QSA, OO‐Oracle Operator, and DO‐Diffusion Op...Figure 11.5 Flowchart of the Boyer–Brassard–Høyer–Tapp (BBHT) quantum search...Figure 11.6 Flowchart of the Dürr–Høyer (DH) quantum search algorithm (QSA)....Figure 11.7 Quantum circuit of the quantum counting algorithm (QCA).Figure 11.8 Quantum circuit of the quantum mean algorithm (QMA).Figure 11.9 Quantum circuit of the quantum weighted sum algorithm (QWSA)....Figure 11.10 Interferometer with two phase shifters.Figure 11.11 Network representation for the phase shift transformation of Eq...Figure 11.12 Network representation of Deutsch’s algorithm.Figure 11.13 Network representation of Deutsch–Jozsa and Bernstein–Vazirani ...Figure 11.14 Network for 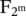 shown acting on the basis state ∣a1a2⋯am〉...Figure 11.15 Network illustrating estimation of phase φ with j ‐bit precision...Figure 11.16 Network representation of Grover’s algorithms. By repeating the...
shown acting on the basis state ∣a1a2⋯am〉...Figure 11.15 Network illustrating estimation of phase φ with j ‐bit precision...Figure 11.16 Network representation of Grover’s algorithms. By repeating the...
11 Chapter 12Figure 12.1 Circuit‐centric quantum classifier.Figure 12.2 The circuit‐centric quantum classifier representation.Figure 12.3 Generic model circuit architecture for eight qubits.Figure 12.4 Graphical representation of quantum gates.Figure 12.5 (a) Parameter t 1and its derivative.Figure 12.5b Parameter t 7and its derivative.Figure 12.6 Schematic of the quantum neural network (QNN) on a quantum proce...
12 Chapter 13Figure 13.1 Illustration of the three common steps of hybrid quantum‐classic...Figure 13.2 Quantum circuit to evaluate the n‐ th component of the grad...Figure 13.3 Fraction of satisfied clauses R 7( γ , β ) for circuits o...Figure 13.4 Processing steps of HHL algorithm.Figure 13.5 Quantum circuit for solving a 4 × 4 system of linear equation Ax ...
13 Chapter 14Figure 14.1 Braess’s paradox.Figure 14.2 Simulation results.Figure 14.3 Simulation results.Figure 14.4 Cognitive network architecture.Figure 14.5 Circuit that generates the initial entangled state ∣ψ e 〉....Figure 14.6 Ctrl − F 1gate circuit, where 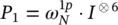 . Looking fro...Figure 14.7 Empirical probability p ( L 1) (choice frequency of the risky prosp...Figure 14.8 Empirical probability p ( L 1) (choice frequency of the risky prosp...
. Looking fro...Figure 14.7 Empirical probability p ( L 1) (choice frequency of the risky prosp...Figure 14.8 Empirical probability p ( L 1) (choice frequency of the risky prosp...
14 Chapter 15Figure 15.1 Integration of satellite and ground communication networks.Figure 15.2 Principle of trusted‐repeater‐based satellite QKD.Figure 15.3 Basic structure of QKP‐enabled satellite QKD system.Figure 15.4 Architecture of double‐layer quantum satellite networks (QSNs)....Figure 15.5 Route selection for key‐relay services in two scenarios over the...Figure 15.6 Contact and resource graph of quantum satellite network (QSN)....Figure 15.7 Success probability (SP) and SP‐a versus traffic load under diff...Figure 15.8 (a) Success probability (SP) versus traffic load with different ...Figure 15.9 (a) Success probability (SP) versus traffic load with different ...Figure 15.10 Social overlay network.Figure 15.11 Social relationship graph form.Figure 15.12 Adaptive QoS‐QKD network model.Figure 15.13 Simple topology showing the calculation of the threshold 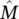 .Figure 15.14 Network parameters.Figure 15.15 An example of greedy forwarding.Figure 15.16 The number and average sizes of routing packets.Figure 15.17 Packet delivery ratio (PDR).
.Figure 15.14 Network parameters.Figure 15.15 An example of greedy forwarding.Figure 15.16 The number and average sizes of routing packets.Figure 15.17 Packet delivery ratio (PDR).
15 Chapter 16Figure 16.1 Schematic illustration of the adopted quantum network architectu...Figure 16.2 Expected link entanglement rate ξ i, j(T ch) between adjacent...Figure 16.3 Expected end‐to‐end entanglement rate 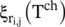 between nodes v iand v j...Figure 16.4 Minimum coherence time
between nodes v iand v j...Figure 16.4 Minimum coherence time 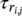 required for the successful utilization ...Figure 16.5 (a) Butterfly, (b) inverted crown network.Figure 16.6 (a) The G knetwork, (b) the grail network.Figure 16.7 Probability distributions of 100‐step discrete quantum walks on ...Figure 16.8 The probability distribution obtained from a computer simulation...Figure 16.9 A graph with various degrees and a labeling of the edges for eac...Figure 16.10 The hypercube in d = 3 dimensions. Vertices correspond to 3‐bit...Figure 16.11 The classical simple random walk on the three‐dimensional hyper...Figure 16.12 The graph G 4. Two binary trees of n = 4 levels are glued togeth...Figure 16.13 The elements of the Hamiltonian of the quantum random walk on GFigure 16.14 Approximation of the finite line by an infinite homogeneous lin...Figure 16.15 A random walk on assignments to the 2‐SAT formula of our exampl...Figure 16.16 The modified graph of Figure 16.12. A big random cycle has been...
required for the successful utilization ...Figure 16.5 (a) Butterfly, (b) inverted crown network.Figure 16.6 (a) The G knetwork, (b) the grail network.Figure 16.7 Probability distributions of 100‐step discrete quantum walks on ...Figure 16.8 The probability distribution obtained from a computer simulation...Figure 16.9 A graph with various degrees and a labeling of the edges for eac...Figure 16.10 The hypercube in d = 3 dimensions. Vertices correspond to 3‐bit...Figure 16.11 The classical simple random walk on the three‐dimensional hyper...Figure 16.12 The graph G 4. Two binary trees of n = 4 levels are glued togeth...Figure 16.13 The elements of the Hamiltonian of the quantum random walk on GFigure 16.14 Approximation of the finite line by an infinite homogeneous lin...Figure 16.15 A random walk on assignments to the 2‐SAT formula of our exampl...Figure 16.16 The modified graph of Figure 16.12. A big random cycle has been...
16 Chapter 17Figure 17.1 Quantum internet graph G with deterministically chosen virtual l...Figure 17.2 Quantum internet graph G with deterministically chosen virtual l...Figure 17.3 Comparison of different routing algorithms on deterministic virt...Figure 17.4 Recursively generated physical graph and virtual graph at the 0‐...Figure 17.5 Recursively generated physical graph and virtual graph at the fi...Figure 17.6 Network example with three switches (boxes with multiple vertica...Figure 17.7 A quantum network protocol stack comprising four layers: physica...Figure 17.8 Setting of layers 1 and 2.Figure 17.9 Settings of layers 3 and 4.Figure 17.10 Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger (GHZ) states are very fragile.Figure 17.11 (a) Static phase, (b) adaptive phase.Figure 17.12 (a) Static phase, (b) adaptive phase.Figure 17.13 The goal of a quantum routing protocol.Figure 17.14 Regions and how they connect.Figure 17.15 The state for connecting nine networks in hierarchical regions ...Figure 17.16 Symmetrizing a network state between regions (shown for a three...Figure 17.17 Example network for illustration of Protocol 2.Figure 17.18 (a) Generating the state |GHZ 4〉, (b) generating the state...
1 Cover Page
2 Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks
3 Copyright
4 Preface
5 Table of Contents
6 Begin Reading
7 Index
8 WILEY END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
1 iii
2 iv
3 xiii
4 1
5 3
6 4
7 5
8 6
9 7
10 8
11 9
12 10
13 11
14 12
15 13
16 14
17 15
18 16
19 17
20 18
21 19
22 20
23 21
24 22
25 23
26 24
27 25
28 26
29 27
30 28
31 29
32 30
33 31
34 32
35 33
36 34
37 35
38 36
39 37
40 38
41 39
42 40
43 41
44 42
45 43
46 44
47 45
48 46
49 47
50 48
51 49
52 50
53 51
54 52
55 53
56 54
57 55
58 56
59 57
60 58
61 59
62 60
63 61
64 62
65 63
66 64
67 65
68 66
Читать дальше

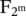 shown acting on the basis state ∣a1a2⋯am〉...Figure 11.15 Network illustrating estimation of phase φ with j ‐bit precision...Figure 11.16 Network representation of Grover’s algorithms. By repeating the...
shown acting on the basis state ∣a1a2⋯am〉...Figure 11.15 Network illustrating estimation of phase φ with j ‐bit precision...Figure 11.16 Network representation of Grover’s algorithms. By repeating the...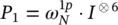 . Looking fro...Figure 14.7 Empirical probability p ( L 1) (choice frequency of the risky prosp...Figure 14.8 Empirical probability p ( L 1) (choice frequency of the risky prosp...
. Looking fro...Figure 14.7 Empirical probability p ( L 1) (choice frequency of the risky prosp...Figure 14.8 Empirical probability p ( L 1) (choice frequency of the risky prosp...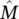 .Figure 15.14 Network parameters.Figure 15.15 An example of greedy forwarding.Figure 15.16 The number and average sizes of routing packets.Figure 15.17 Packet delivery ratio (PDR).
.Figure 15.14 Network parameters.Figure 15.15 An example of greedy forwarding.Figure 15.16 The number and average sizes of routing packets.Figure 15.17 Packet delivery ratio (PDR).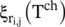 between nodes v iand v j...Figure 16.4 Minimum coherence time
between nodes v iand v j...Figure 16.4 Minimum coherence time 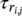 required for the successful utilization ...Figure 16.5 (a) Butterfly, (b) inverted crown network.Figure 16.6 (a) The G knetwork, (b) the grail network.Figure 16.7 Probability distributions of 100‐step discrete quantum walks on ...Figure 16.8 The probability distribution obtained from a computer simulation...Figure 16.9 A graph with various degrees and a labeling of the edges for eac...Figure 16.10 The hypercube in d = 3 dimensions. Vertices correspond to 3‐bit...Figure 16.11 The classical simple random walk on the three‐dimensional hyper...Figure 16.12 The graph G 4. Two binary trees of n = 4 levels are glued togeth...Figure 16.13 The elements of the Hamiltonian of the quantum random walk on GFigure 16.14 Approximation of the finite line by an infinite homogeneous lin...Figure 16.15 A random walk on assignments to the 2‐SAT formula of our exampl...Figure 16.16 The modified graph of Figure 16.12. A big random cycle has been...
required for the successful utilization ...Figure 16.5 (a) Butterfly, (b) inverted crown network.Figure 16.6 (a) The G knetwork, (b) the grail network.Figure 16.7 Probability distributions of 100‐step discrete quantum walks on ...Figure 16.8 The probability distribution obtained from a computer simulation...Figure 16.9 A graph with various degrees and a labeling of the edges for eac...Figure 16.10 The hypercube in d = 3 dimensions. Vertices correspond to 3‐bit...Figure 16.11 The classical simple random walk on the three‐dimensional hyper...Figure 16.12 The graph G 4. Two binary trees of n = 4 levels are glued togeth...Figure 16.13 The elements of the Hamiltonian of the quantum random walk on GFigure 16.14 Approximation of the finite line by an infinite homogeneous lin...Figure 16.15 A random walk on assignments to the 2‐SAT formula of our exampl...Figure 16.16 The modified graph of Figure 16.12. A big random cycle has been...










