In this first scenario, we consider urban VANETs where the scene of the accident is captured by the first vehicle on the scene. Then, this vehicle will transmit the video to the rescue teams so that they can manage the emergency more effectively. In such a situation, the total transmission delay for a multimedia message is limited to a few seconds to ensure notification in real time (Javed et al . 2014). For this type of traffic (Table 1.1), the delay and the flow are considered dominant attributes.
As Figure 1.3 shows, the network architecture in a city is based on the vehicles with OBUs and infrastructures such as RSUs, WiFi access points and LTE eNB base stations for the 4G cell phone network. We suppose that each vehicle is equipped with three radio interfaces: 4G interface, WiFi interface and 802.11p interface.
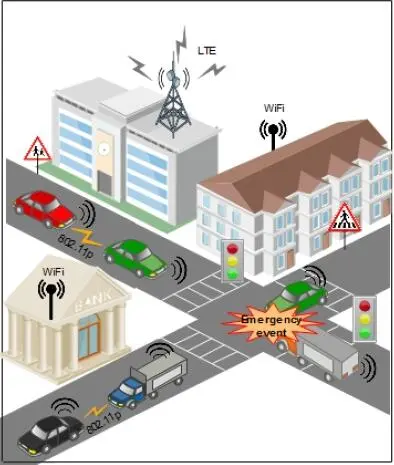
Figure 1.3. Transmission of video from the scene of an accident in VANET networks
The simulation of this scenario, under the network simulator ns3, involves a WiFi access point and a LTE base station offering a theoretical flow of 11 Mbps and 24 Mbps, respectively. At the start, the number of active users is 4 for the WiFi cell and 10 for the LTE cell. The simulation parameters are listed in Table 1.3.
The effective data flow observed by the user of an LTE or WiFi network may be much lower than the theoretical flows stated and defined by the norms. The main factors influencing the effective flow are the number of active users sharing the bandwidth within a cell, the bandwidth frequency allocated to the network operator and the distance between the terminal and the relay antenna. These factors will also influence other QoS parameters such as latency and the average loss rate. For these reasons, the suggested multicriteria decision-making module will calculate the scores of the different networks detected depending on the estimated available bandwidth, the average delay measured and the packet rate loss measured.
Table 1.3. Simulation parameters for scenario 1
| Parameters |
Values |
| Duration of simulation |
50 s |
| Traffic video |
Send interval 1 ms Packet size 1,000 octets |
| Witness vehicle |
Speed: stationary Distance – AP WiFi: 20 m Distance – LTE BS: 60 m |
| Mobility model |
Random Waypoint Model |
| Number of active users |
At t = 10 s, WiFi (4), LTE (10) At t = 20 s, WiFi (10), LTE (20) At t = 30 s, WiFi (20), LTE (10) At t = 40 s, WiFi (10), LTE (4) At t = 50 s, WiFi (10), LTE (10) |
| Theoretical flow for WiFi |
11 Mbps |
| Theoretical flow for LTE |
24 Mbps |
The number of active users may vary during the simulation (Table 1.3) as vehicles or pedestrians depart or arrive. The variation in this parameter influences the QoS parameters characterizing the candidate networks and, consequently, their scores. Figure 1.4 shows the effect of the dynamic network environment on optimal network selection for the service video. Depending on the configuration adopted for this scenario, the results of the simulation show that LTE is selected as an optimal network. In fact, when the LTE score increases because of the dynamic network environment, the optimal network passes from the WiFi to the LTE for the network selection decision. To ensure the stability of the decision and avoid the ping-pong effect, we wait for the following period to make the decision to be sure that the right decision is made.
Considering this example, if (1) the execution period of the suggested decision-making module is not adjusted automatically and (2) the transfer is made after the new trend is confirmed, the transfer will take place at 40 s. This is much later than the changeover time estimated at 23 s. This is why, as we said previously, it is very important to adjust the execution period of the suggested decision-making module automatically.

Figure 1.4. Score variation in VANET networks for transmission of a video message
1.4.3.2. Scenario 2: selecting the radio channel – the case of CR-VANET
Thanks to its cognitive capacity, the compatible intelligent radio vehicle can search for spectrum holes (white spaces) and take opportune decisions to transmit without interfering with the primary users. It can also make adaptations such as modifying the transmission power or the radio channels to meet QoS requirements for vehicle applications.
In this second scenario, we will consider a CR-VANET highway environment in the countryside and we will focus on infotainment applications, especially restaurant reservation. On the topology of CR-VANET highways, the speed of vehicles on the highways is significantly higher than in urban scenarios.
To evaluate performances, we consider the network architecture of a CR-VANET (Figure 1.5) where each vehicle is equipped with wireless communication interfaces (such as a 4G interface and a WiFi interface) and has intelligent radio capacities.
The simulations were made using ns3 paired with SUMO to generate real traffic mobility. The simulation parameters are listed in Table 1.4. For the same reasons cited in the previous scenario, the energy aspect will not be considered here.
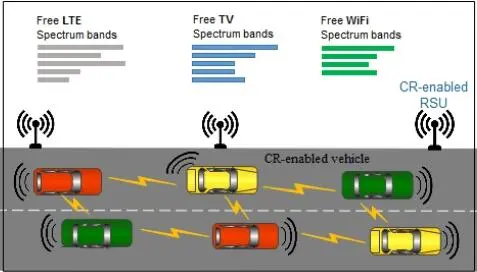
Figure 1.5. Entertainment service on a highway in CR-VANET networks
Table 1.4. Simulation parameters for scenario 2
| Parameters |
Values |
| Simulation duration |
50 s |
| Data traffic |
Flow: 64 kbps |
| Vehicle mobility model |
Car Following Model |
| Intelligent radio channels available |
TV white space bandWiFi white space bandLTE white space band |
For the vehicle behavior model, we have adopted the Car Following Model , which is based on the following parameters: vehicle acceleration, vehicle deceleration, vehicle length, maximum speed of the vehicle and driver imperfection. The values of these parameters are presented in Table 1.5.
Based on the spectral resources detected, the suggested multicriteria decision-making module will calculate the scores of different channels and select the one with the highest score.
Table 1.5. Simulation parameters for the SUMO vehicle
| Parameters |
Values |
| Vehicle acceleration |
2.5 m/s 2 |
| Vehicle deceleration |
4.6 m/s 2 |
| Average vehicle length |
5 m |
| Maximum vehicle speed |
140 km/h |
| Driver imperfection |
0.5 |
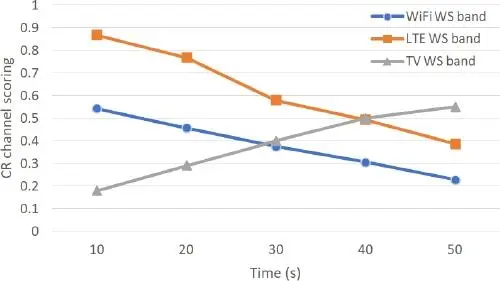
Figure 1.6. Variation of the scores of intelligent radio channels for the entertainment service
Figure 1.6 shows the impact of the dynamic network environment (such as the available bandwidth, the channel’s availability probability and the speed of the vehicle) on selecting the channel best adapted to the infotainment service (restaurant reservation). In Figure 1.6, we can observe that with the high mobility of candidate vehicles on the highways, the channel corresponding to the WiFi bandwidth is not a good candidate. We also observe a degradation of the score of the radio channel corresponding to the bandwidth of the LTE and an increase in the score of the channel corresponding to the TV bandwidth. The evolution of the scores over time justifies the decision to carry out a spectrum handoff, from the suggested module to the TVWS channel. Before running the spectrum handoff, we wait for the choice of the best channel to be confirmed for the following period. This will enable us to avoid unhelpful transfers. And to avoid running the spectrum handoff very late, this wait time will be adjusted automatically. In this scenario, we observe that the choice of TVWS is fully adapted to this context, not only in terms of QoS but also from the perspective of mobility. Indeed, this spectral band is characterized by a long range that is best suited to scenarios with high mobility.
Читать дальше
















