
Figure 2.11. The average recompense with the adaptive controller
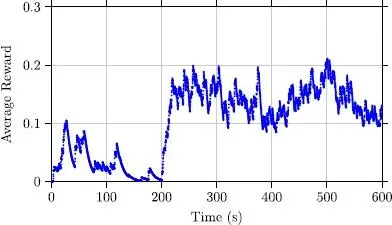
Figure 2.12. The average recompense with the controller using TD3
We can note that in Figure 2.13 the adaptive technique does not make it possible to control correctly the number of attempts. In fact, we very often reach numbers significantly higher than the optimum. This triggers many collisions at access and new access attempts. We also see that the number of abandonments remains relatively significant compared to the TD3 controller (Figure 2.14). The latter, after the exploration stage, succeeds in significantly reducing the number of abandonments, which demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
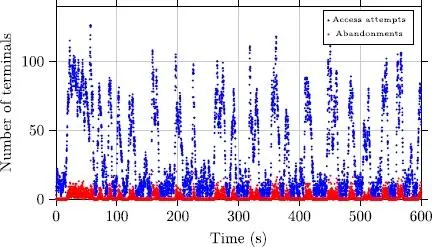
Figure 2.13. Access attempts (blue) and abandonments (red) with the adaptive controller. For a color version of this figure, see www.iste.co.uk/chalouf/intelligent.zip
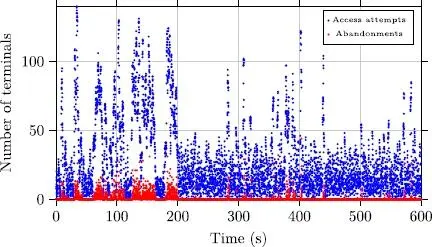
Figure 2.14. Access attempts (blue) and abandonments (red) with the controller using TD3. For a color version of this figure, see www.iste.co.uk/chalouf/intelligent.zip
It should be noted that having recourse to our approach based on reinforcement learning, we have an improvement in performance with each access attempt. The limit, however, is found in the estimation errors, which lead to errors in calculating the recompense, hence the importance of having precise estimators.
In this chapter, we proposed a mechanism to control congestion of the access network, which is considered one of the most critical problems for IoT objects. We have proposed tackling congestion at its root by effectively managing random accesses from these devices thanks to use of the ACB mechanism.
The proposed access control mechanism is different from conventional methods, which generally rely on simple heuristics. Indeed, the proposed technique relies on recent advances in deep reinforcement learning, through use of the TD3 algorithm. The proposed approach has, in addition, the advantage of learning from its environment and could therefore enable it to adapt to variation of the access schema.
The simulation results make it possible to show the superiority of the proposed approach, which succeeds in maintaining a number of access attempts close to the optimum, despite the absence of exact information on the number of access attempts. This work also makes it possible to show the potential of using learning techniques in environments where the state cannot be known with precision.
In the context of our future work, we envisage improving estimation of the number of attempts using learning techniques.
3GPP (2011). RAN improvements for machine-type communications. TR 37.868, version 11.0.0 [Online]. Available at: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2630[Accessed 14 October 2020].
3GPP (2015). Cellular system support for ultra-low complexity and low throughput Internet of Things (CIoT). TR 45.820 [Online]. Available at: https://portal.3gpp.org/ChangeRequests.aspx?q=1&versionId=46751&release=187[Accessed 14 October 2020].
3GPP (2016). E-UTRA and E-UTRAN; LTE physical layer, general description (Release 13) . TR TS 36.201 [Online]. Available at: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2424[Accessed 14 October 2020].
3GPP (2017a). Physical layer measurements (Release 13). TS 36.214, version 13.5.0 [Online]. Available at: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2428 [Accessed 14 October 2020].
3GPP (2017b). User equipment (UE) radio transmission and reception (Release 13). TS 36.101, version 13.9.0 [Online]. Available at: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2411[Accessed 14 October 2020].
3GPP (2018a). Consideration on self-evaluation of IMT-2020 for mMTC connection density. R1-1801796 [Online]. Available at: http://www.3gpp.org/ftp/TSG_RAN/WG1_RL1/TSGR1_92/Docs/R1-1801796.zip[Accessed 14 October 2020].
3GPP (2018b). Radio Resource Control (RRC); protocol specification. TS 36.331 [Online]. Available at: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2440[Accessed 14 October 2020].
3GPP (2019a). Study on cellular Internet of Things (IoT) support and evolution for the 5G System. TR 23.724, version 16.1.0 [Online]. Available at: http://www.3gpp.org/DynaReport/23724.htm[Accessed 14 October 2020].
3GPP (2019b). Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol specification. TS 36.321, V14.12.0 [Online]. Available at: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2437[Accessed 14 October 2020].
3GPP (2020). Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); physical channels and modulation (Release 16). TS 36.211, version 16.2.0, June 2020 [Online]. Available at: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2425[Accessed 14 October 2020].
Adhikary, A., Lin, X., Wang, Y.-P.-E. (2016). Performance evaluation of NB-IoT coverage. In The IEEE 84th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall). IEEE, Montreal.
Ali, M.S., Hossain, E., Kim, D.I. (2017). LTE/LTE-A random access for massive machine-type communications in smart cities. IEEE Communications Magazine , 55(1), 76–83.
Baracat, G. and Brito, J. (2018). NB-IoT random access procedure analysis. In The Latin-American Conference on Communications (LATINCOM) . IEEE, Guadalajara.
Bicheno, S. (2015). Intel, Nokia and Ericsson collaborate on NB-LTE wireless for IoT [Online]. Available at: https://telecoms.com/441951/intel-nokia-and-ericsson-collaborate-on-nb-lte-wireless-for-iot/[Accessed 1 February 2022]
Bouzouita, M., Hadjadj-Aoul, Y., Zangar, N., Rubino, G., Tabbane, S. (2015). Multiple access class barring factors algorithm for M2M communications in LTE-advanced networks. In 18th ACM International Conference on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems, MSWiM’15. ACM, New York.
Bouzouita, M., Hadjadj-Aoult, Y., Zangar, N., Tabbane, S. (2016). On the risk of congestion collapse in heavily congested M2M networks. In 2016 International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications (ISNCC). IEEE, Yasmine Hammamet.
Bouzouita, M., Hadjadj-Aoul, Y., Zangar, N., Rubino, G. (2019). Estimating the number of contending IoT devices in 5G networks: Revealing the invisible. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies , 30(4), e3513.
Cheng, R.C., Chen, J., Chen, D.W., Wei, C.H. (2015). Modeling and analysis of an extended access barring algorithm for machine-type communications in LTE-A Networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications , 14(6), 2956–2968.
Читать дальше
















