Legal metrology concerns activities which result from statutory requirements and concern measurement, units of measurement, measuring instruments and methods of measurement and which are performed by competent bodies.
Ex. 2. Answer the questions
1. What is metrology ?
2. What is legal metrology ?
3. What are the three main activities of metrology ?
4. What organization gave the definition for metrology ?
5. What is necessary to ensure confidence in measurements?
Ex. 3. Are these sentences true or false ?
1. Metrology deals with measurements.
2. The BIPM provides people wi th reference standards in different fields.
3. In the area of measurement the BIPM has identified ten areas.
4. These areas of measurement defined by the BIMP include mass, time, length.
5. Applied metrology is connected with applying measurement science for only research process.
6. The activities which are concerned by legal metrology result from statutory requirements.
7. Measuring devices provide the confidence of measurement.
Ex. 4. Fill the blanks using the words from the text: «Metrology» .
Metrology studies measurements. This science include both theoretical and practical …According to the definition given by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures(BIPM): metrology is a science of measurement which gives theoretical and experimental … at any level of uncertainty. The main goals of metrology is to … units of measurements, to realize … into practice and t o apply the chains of traceability which connects measurements made in practice with …
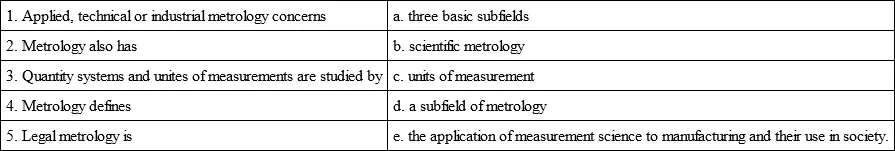
Ex. 5. Match the beginning with the endings based on the text
Ex. 6. Put the question to the bold-typed words:
1. Scientific metrology concerns the establishment of quantity systems.
2. The Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology (JCGM) maintains the international vocabulary of metrology(VIM).
3. BIPM has identified nine areas
4. These metrological areas include time, mass, length.
5. Legal metrology is a subfield of metrology.
Ex. 7. Make the summary of the text:«Metrology» using the following plan:
1. Definition of metrology;
2. Subfields of metrology;
3. The object of study of scientific metrology;
4. The object of study of the applied metrology;
5. The object of study of legal metrology.
Project Work:
«Do I know any organization on metrology in my country?»
Tell about any organization on metrology functioning in your country on the following plan:
1. When was this organization founded?
2. Where is it situated?
3. What kind of services does this organization provide?
4. Is it the only organization in metrology in your country?

5. What specialists work there?
6. In what spheres of human activity does this organization provide metrological services? Give the examples.
7. What metrological laboratories does this organization include?
8. Is this organization important in your country?
9. Are you planning to work in this organization in the future?
10. Have you ever visited this organization ?
Vocabulary
metrological traceability – метрологическая прослеживаемость – метрологиялық бақылау
core сoncept – основное понятие – негізгі түсінік
to establish – устанавливать – құру, қою; орнату, орналасу
property – свойство – қасиет
value – значение – мән; мағына
reference – эталон – эталон, үлгі, өлшем
standard – стандарт – стандарт
to perform – осуществлять, проводить – істеу; жүзеге асыру, іске асу
measuring instrument – измерительный прибор – өлшеуіш аспап
range – диапазон – ауқым
quality – качество – сапа; қасиет
quality management system – система управления качеством – сапаны басқару жүйесі
accuracy – правильность – ұқыптылық; дұрыстық
systematic bias – систематическая ошибка – жүйелі қате
precision – точность – дәлдік; бірдейлік
evaluation – оценка – бағалау, баға кесу; баға
primary standard – первичный стандарт – алғашқы стандарт
error – погрешность, серьезная ошибка – қате, адасу, жаңылу, маңызды қате
ratio – соотношение – қатыс, арақатынас, өзара қатынас; байланыс
previous – предыдущий – бұдан бұрынғы, осыдан ілгері, өткен
comparability – сопоставимость – салыстыру
to use – использовать – пайдалану
equipment – оборудование – жабдық
voltmeter – вольтметр – вольтметр
triple point – тройная точка – үштік нүкте
specimen – образец – үлгі
X-rays – рентгеновские лучи – рентгендік сәулелер
electron beam – пучок электронов – электрондар шоғы
to read – показывать – көрсету; әйгілеу; байқату; таныту; білдіру
constant – постоянный – тұрақты; бірқалыпты, өзгермейтін
to verify – проверять – тексеру, қарап шығу; сынап байқау
to adjust – устанавливать (прибор) – (аспапты) орнату, орналастыру
to allow for – предусматривать – алдын ала ескеру; назарда ұстау
to settle – устанавливать – қоныстану, орналасу; ретке келтіру
distinction – различие – айырма; ерекшелік
inexact – неточный – дәл емес
critical part – важная часть – маңызды бөлім
measurement uncertainty – погрешность измерений – өлшем қателігі
to reserve for – предназначать – арнау, белгілеу; жарату; тағайындау
lead – провод – бастау, көрсету; алып жүру; апару
establishment – установление – орнату
Ex. 1. Read and translate the text
Metrological traceability
A core concept in metrology is metrological traceability, defined by the BIPMas «the property of the result of a measurement or the value of a st andard whereby it can be related to stated references, usually national or international standards, through an unbroken chain of comparisons, all having stated uncertainties)). The level of traceability establishes the level of comparability of the measurement: whether the result of a measurement can be compared to the previous one, a measurement result a year ago, or to the result of a measurement performed anywhere else in the world.
Читать дальше














