William Josephus Robinson - Woman. Her Sex and Love Life
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «William Josephus Robinson - Woman. Her Sex and Love Life» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: psy_sex_and_family, foreign_antique, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Woman. Her Sex and Love Life
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Woman. Her Sex and Love Life: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Woman. Her Sex and Love Life»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Woman. Her Sex and Love Life — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Woman. Her Sex and Love Life», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
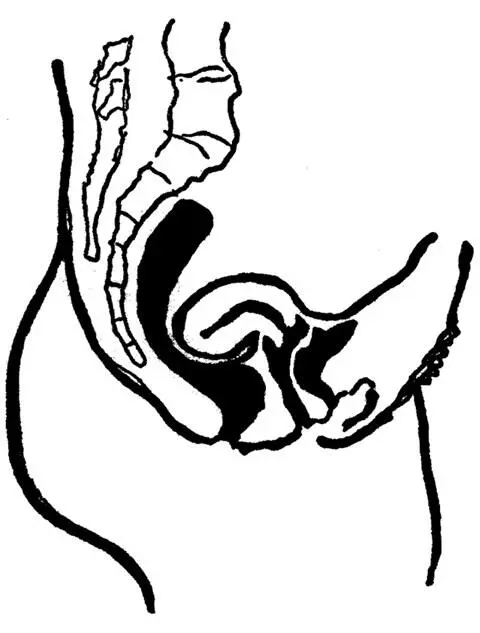
Retroflexion of the Uterus.
The Hymen[hymen in Greek—a membrane]. The external opening of the vagina, in virgins, that is, in girls or women who have not had sexual intercourse, is almost entirely closed by a membrane called the hymen. The vulgar name for hymen is "maidenhead." The hymen may be of various shapes, and of different consistency. In some girls it is a very thin membrane, which tears very readily; in others it is quite tough. On the upper margin or in the center of the hymen there is an opening which permits any secretion from the vagina and the blood from the uterus to come through. In rare cases there is no opening in the hymen, that is, the vagina is entirely closed. Such a hymen is called imperforate (not perforated). When the girl begins to menstruate, the blood cannot come out and it accumulates in the vagina. In such cases the hymen must be opened or slit by a doctor. In some cases the hymen is congenitally absent; that is, the girl is born without any hymen. While the hymen is usually ruptured during the first intercourse, it, in some cases, being elastic and stretchable, persists untorn after sexual intercourse. It will therefore be seen that just as the presence of the hymen is no absolute proof of virginity, so is the absence of the hymen no absolute proof that the girl has had sexual relations, She might have been born without any hymen, or it might have been ruptured by vaginal examination, by a vaginal douche, by scratching to relieve itching, or by some accident.
The remains of the hymen after it is ruptured shrink and form little elevations which can be easily felt; they are known as caruncles. [In Latin, carunculæ myrtiformes , which means in English myrtleberry-shaped caruncles; caruncle is a small fleshy elevation; derived from caro , which in Latin means flesh.]
SUBCHAPTER B
THE EXTERNAL GENITALS
The Vulva.The external genitals of the female are called the vulva . The vulva consists of the labia majora (meaning the larger lips), which are on the outside and which in the grown-up girl are covered with hair, and the labia minora (the smaller lips), which are on the inside and which are usually only seen when the labia majora are taken apart.
[Vulva in Latin means folding-door. The ancients Were fond of giving fancy names to things.]
The Mons Veneris.The elevation above the vulva, which during puberty becomes covered with hair, is called by the fanciful name, mons Veneris , or Venus' mountain. It is usually well padded with fatty tissue.
The Clitoris.The clitoris is a small body about an inch in length, situated beneath the mons Veneris and partly or entirely covered by the upper borders of the labia minora.
The Urethra.Between the clitoris above and the opening of the vagina below is situated the opening of the urethra , or the urinary meatus, through which the urine passes. Many women are so ignorant, or, let us say innocent, that they think the urine passes out through the vagina. This is not so. The vagina has nothing to do with the process of urination.
Again enumerating the female sex organs, but in the reverse order, from before backward, or from out inward, we have: The mons Veneris and the labia majora, or the external lips of the vulva; these are the plainly visible parts of the female genital organs. When the labia majora are taken apart we see the labia minora; when the labia majora and minora are taken apart we can see or feel the clitoris and the hymen, or the remains of the hymen. We then have the vagina, a large, stretchable musculo-membranous canal, in the upper portion of which the neck of the womb, or the cervix, can be seen (when a speculum is used), or felt by the finger. Only the cervix, or neck of the womb, can be seen, but the rest of the womb, the broader portion, can be easily felt and examined by one hand in the vagina and the other hand over the abdomen. Continuous with the uterus are the Fallopian tubes, and below the trumpet-shaped ends of the Fallopian tubes are the ovaries, embedded in the broad ligaments, one on each side.
The Breasts.The breasts, also called mammary glands, or mammæ [mamma in Latin, breast], may be considered as accessory organs of reproduction. They are of no importance in the male, in whom they are usually rudimentary, but they are of great importance in the female. They manufacture milk, which is necessary for the proper nutrition of the infant, and they add a great deal to the beauty and attractiveness of the woman. They are thus a help to the woman in getting a mate or a husband. The projecting elevation of the breast, which the child takes in his mouth when nursing, is called the nipple; the darker colored area surrounding the nipple is called the areola.
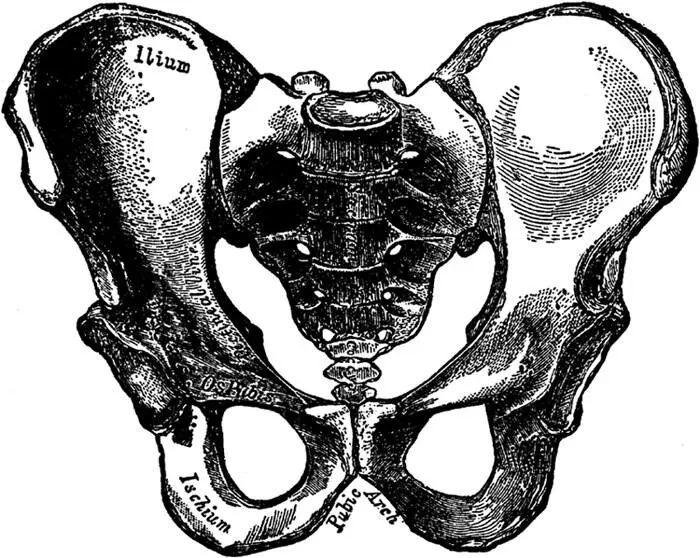
The Pelvis of the Male.
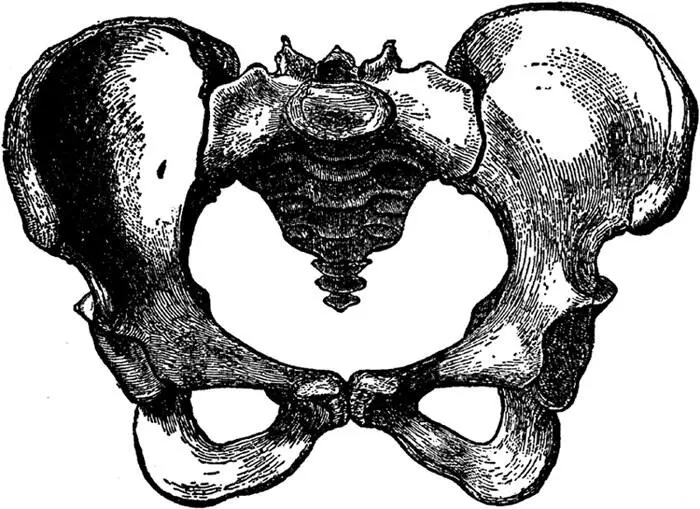
The Pelvis of the Female.
SUBCHAPTER C
THE PELVIS
The internal sex organs are situated in the lower part of the abdominal cavity, the part that is called the pelvis , or pelvic cavity. The meaning of the word pelvis in Latin is basin. The pelvis, also referred to as the pelvic girdle or pelvic arch, forms a bony basin, and is composed of three powerful bones: the sacrum, consisting of five vertebræ fused together and constituting the solid part of the spine, or vertebral column, in the back, and the two hipbones, one on each side. The two hipbones meet in front, forming the pubic arch .
The hipbones are called in Latin the ossa innominata (nameless bones) and each hipbone is composed of three bones: the ilium, the ischium, and the os pubis. The thighs are attached to the hipbones, and to the hipbones are also attached the large gluteal muscles, which form the buttocks, or the "seat."
The pelvis of the female differs considerably from the pelvis of the male. The female pelvis is shallower and wider, less massive, the margins of the bones are more widely separated, thus giving greater prominence to the hips; the sacrum is shorter and less curved, and the pubic arch is wider and more rounded. All this is necessary in order to permit the child's head to pass through. If the female pelvis were exactly like the male pelvis, a full-term living child could never pass through it. The two illustrations show the differences between the male and female pelvis very clearly.
Note particularly the differences in the pubic arches: in the male pelvis it is really more of an angle than an arch. Also note how much longer and more solid the sacrum (with its attached bone, called the coccyx 2 2 The coccyx consists of three rudimentary vertebræ; it is the vestige of an organ which we once possessed in common with many other animals, namely—a tail.
) is in the male pelvis. The differences in the pelves (the plural of pelvis is pelves) of the male and female become fully marked at puberty, but they are present as early as the fourth month of intra-uterine life.
Chapter Three
THE PHYSIOLOGY OF THE FEMALE SEX ORGANS
Function of the Ovaries—Internal Secretion of the Ovaries—Function of the Internal Secretion—Number of Ova in the Ovaries—The Graafian Follicles—Ovulation—Corpora Lutea—Function of the Fallopian Tubes—Function of the Vagina—Functions of the Vulva, Clitoris and Mons Veneris—Function of the Breasts—Besides Secreting Milk Breast Has Sexual Function—The Orgasm—Pollutions in Women—Secondary Sex Characters—Differences Between Woman and Man.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Woman. Her Sex and Love Life»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Woman. Her Sex and Love Life» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Woman. Her Sex and Love Life» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












