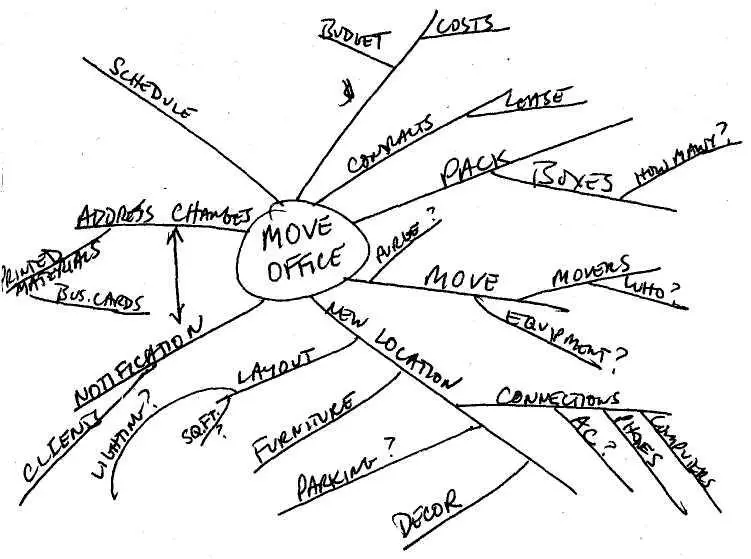
You could do this kind of mind-mapping on Post-its that could be stuck on a white board, or you could input ideas into a word processor or outlining program on the computer.
Distributed Cognition
The great thing about external brainstorming is that in addition to capturing your original ideas, it can help generate many new ones that might not have occurred to you if you didn't have a mechanism to hold your thoughts and continually reflect them back to you. It's as if your mind were to say, "Look, I'm only going to give you as many ideas as you feel you can effectively use. If you're not collecting them in some trusted way, I won't give you that many. But if you're actually doing something with the ideas—even if it's just recording them for later evaluation—then here, have a bunch! And, oh wow! That reminds me of another one, and another," etc.
Nothing is more dangerous than an idea when it is the only one you have.
— Emile Chartier
Psychologists are beginning to label this and similar processes "distributed cognition." It's getting things out of your head and into objective, reviewable formats. But my English teacher in high school didn't have to know about the theory to give me the key: "David," he said, "you're going to college, and you're going to be writing papers. Write all your notes and quotes on separate three-by-five cards. Then, when you get ready to organize your thinking, just spread them all out on the floor, seethe structure, and figure out what you're missing." Mr. Edmund son was teaching me a major piece of the natural planning model!
Only he who handles his ideas lightly is waster of his ideas, and only he who is master of his ideas is not enslaved by them.
— Lin Yutang
Few people can hold their focus on a topic for more than a couple of minutes, without some objective structure and tool or trigger to help them. Pick a big project you have going right now and just try to think of nothing else for more than sixty seconds. This is pretty hard to do unless you have a pen and paper in hand and use those "cognitive artifacts" as the anchor for your ideas. Then you can stay with it for hours.That's why good thinking can happen while you're working on a computer document about a project, mind-mapping it on a legal pad of on a paper tablecloth in a hip restaurant, or just having a meeting about it with other people in a room that allows you to hold the context (a white board with nice wet markers really helps there, too).
Brainstorming Keys
Many techniques can be used to facilitate brainstorming and out-of-the-box thinking. The basics principles, however, can be summed up as follows:
• Don't judge, challenge, evaluate, or criticize.
• Go for quantity, not quality.
• Put analysis and organization in the background.
Don't Judge, Challenge, Evaluate, or Criticize It's easy for the unnatural planning model to rear its ugly head in brainstorming, making people jump to premature evaluations and critiques of ideas. If you care even slightly about what a critic thinks, you'll censure your expressive process as you look for the "right" thing to say. There's a very subtle distinction between keeping brainstorming on target with the topic and stifling the creative process. It's also important that brainstorming be put into the overall context of the planning process, because if you think you're doing it just for its own sake, it can seem trite and inappropriately off course. If you can understand it instead as something you're doing right now, for a certain period, before you move toward a resolution at the end, you'll feel more comfortable giving this part of the process its due.
A good way to find out what something might be is to uncover ail the things it's probably not.
This is not to suggest that you should shut off critical thinking, though—everything ought to be fair game at this stage. It's just wise to understand what kinds of thoughts you're having and to park them for use in the most appropriate way. The primary criterion must be expansion, not contraction.
Go for Quantity, Not Quality Going for quantity keeps your thinking expansive. Often you won't know what's a good idea until you have it. And sometimes you'll realize it's a good idea, or the germ of one, only later on. You know how shopping at a big store with lots of options lets you feel comfortable about your choice? The same holds true for project thinking. The greater the volume of thoughts you have to work with, the better the context you can create for developing options and trusting your choices.
Put Analysis and Organization in the Background Analysis and evaluation and organization of your thoughts should be given as free a rein as creative out-of-the-box thinking. But in the brain-storming phase, this critical activity should not be the driver.
Making a list can be a creative thing to do, a way to consider the people who should be on your team, the customer requirements for the software, or the components of the business plan. Just make sure to grab all that and keep going until you get into the weeding and organizing of focus that make up the next stage.
Organizing
If you've done a thorough job of emptying your head of all the things that came up in the brainstorming phase, you'll notice that a natural organization is emerging. As my high school English teacher suggested, once you get all the ideas out of your head and in front of your eyes, you'll automatically notice natural relation-ships and structure. This is what most people are referring to when they talk about "project plans."
Organizing usually happens when you identify components and subcomponents, sequences or events, and/or priorities. What are the things that must occur to create the final result? In what order must they occur? What is the most important element to ensure the success of the project?
This is the stage in which you can make good use of structuring tools ranging from informal bullet points, scribbled liter-ally on the back of an envelope, to project-planning software like Microsoft Project. When a project calls for substantial objective control, you'll need some type of hierarchical outline with components and subcomponents, and/or a GANTT-type chart showing stages of the project laid out over time, with independent and dependent parts and milestones identified in relationship to the whole.
A "project plan" identifies the smaller outcomes, which can then be naturally planned.
Creative thinking doesn't stop here; it just takes another form. Once you perceive a basic structure, your mind will start trying to "fill in the blanks." Identifying three key things that you need to handle on the project, for example, may cause you to think of a fourth and a fifth when you see them all lined up.
The Basics of Organizing
The key steps here are:
• Identify the significant pieces.
• Sort by (one or more):
• components
• sequences
• priorities
• Detail to the required degree.
I have never seen any two projects that needed to have exactly the same amount of structure and detail developed in order to get things off people's minds and moving successfully. But almost all projects can use some form of creative thinking from the left side of the brain, along the lines of "What's the plan?"
Next Actions
The final stage of planning comes down to decisions about the allocation and reallocation of physical resources to actually get the project moving. The question to ask here is, "What's the next action?"
As we noted in the previous chapter, this kind of grounded, reality-based thinking, combined with clarification of the desired outcome, forms the critical component of knowledge work. In my experience, creating a list of what your real projects are and consistently managing your next action for each one will constitute 90 percent of what is generally thought of as project planning. This "runway level" approach will make you "honest" about all kinds of things: Are you really serious about doing this? Who's responsible? Have you thought things through enough?
Читать дальше












