Айзек Азимов - The Genetic Effects of Radiation
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Айзек Азимов - The Genetic Effects of Radiation» весь текст электронной книги совершенно бесплатно (целиком полную версию без сокращений). В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Год выпуска: 2018, Издательство: epubBooks Classics, Жанр: Медицина, Биология, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The Genetic Effects of Radiation
- Автор:
- Издательство:epubBooks Classics
- Жанр:
- Год:2018
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
The Genetic Effects of Radiation: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The Genetic Effects of Radiation»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The Genetic Effects of Radiation — читать онлайн бесплатно полную книгу (весь текст) целиком
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «The Genetic Effects of Radiation», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
The Genetic Effects of Radiation
The Authors

ISAAC ASIMOV received his academic degrees from Columbia University and is Associate Professor of Biochemistry at the Boston University School of Medicine. He is a prolific author who has written over 65 books in the past 15 years, including about 20 science fiction works, and books for children. His many excellent science books for the public cover subjects in mathematics, physics, astronomy, chemistry, and biology, such as The Genetic Code, Inside the Atom, Building Blocks of the Universe, The Living River, The New Intelligent Man’s Guide to Science, and Asimov’s Biographical Encyclopedia of Science and Technology. In 1965 Dr. Asimov received the James T. Grady Award of the American Chemical Society for his major contribution in reporting science progress to the public.

THEODOSIUS DOBZHANSKY was graduated from Kiev University and is now a professor at the Rockefeller University. He has done research in genetics and biological evolution on every continent except Antarctica. Among his distinguished published works are Radiation, Genes, and Man, Heredity and the Nature of Man, Mankind Evolving, and Evolution, Genetics, and Man. Mr. Dobzhansky received the Daniel G. Elliot Prize and Medal and the Kimber Genetics Award from the National Academy of Sciences in 1958, and the National Medal of Science awarded by the President of the United States, in 1965.
Part 1:
The Machinery of Inheritance
Introduction
There is nothing new under the sun, says the Bible. Nor is the sun itself new, we might add. As long as life has existed on earth, it has been exposed to radiation from the sun, so that life and radiation are old acquaintances and have learned to live together.
We are accustomed to looking upon sunlight as something good, useful, and desirable, and certainly we could not live long without it. The energy of sunlight warms the earth, produces the winds that tend to equalize earth’s temperatures, evaporates the oceans and produces rain and fresh water. Most important of all, it supplies what is needed for green plants to convert carbon dioxide and water into food and oxygen, making it possible for all animal life (including ourselves) to live.
Yet sunlight has its dangers, too. Lizards avoid the direct rays of the noonday sun on the desert, and we ourselves take precautions against sunburn and sunstroke.
The same division into good and bad is to be found in connection with other forms of radiation—forms of which mankind has only recently become aware. Such radiations, produced by radioactivity in the soil and reaching us from outer space, have also been with us from the beginning of time. They are more energetic than sunlight, however, and can do more damage, and because our senses do not detect them, we have not learned to take precautions against them.
To be sure, energetic radiation is present in nature in only very small amounts and is not, therefore, much of a danger. Man, however, has the capacity of imitating nature. Long ago in dim prehistory, for instance, he learned to manufacture a kind of sunlight by setting wood and other fuels on fire. This involved a new kind of good and bad. A whole new technology became possible, on the one hand, and, on the other, the chance of death by burning was also possible. The good in this case far outweighs the evil.
In our own twentieth century, mankind learned to produce energetic radiation in concentrations far surpassing those we usually encounter in nature. Again, a new technology is resulting and again there is the possibility of death.
The balance in this second instance is less certainly in favor of the good over the evil. To shift the balance clearly in favor of the good, it is necessary for mankind to learn as much as possible about the new dangers in order that we might minimize them and most effectively guard against them.
To see the nature of the danger, let us begin by considering living tissue itself—the living tissue that must withstand the radiation and that can be damaged by it.
Cells and Chromosomes
The average human adult consists of about 50 trillion cells —50 trillion microscopic, more or less self–contained, blobs of life. He begins life, however, as a single cell, the fertilized ovum .
After the fertilized ovum is formed, it divides and becomes two cells. Each daughter cell divides to produce a total of four cells, and each of those divides and so on.
There is a high degree of order and direction to those divisions. When a human fertilized ovum completes its divisions an adult human being is the inevitable result. The fertilized ovum of a giraffe will produce a giraffe, that of a fruit fly will produce a fruit fly, and so on. There are no mistakes, so it is quite clear that the fertilized ovum must carry “instructions” that guide its development in the appropriate direction.
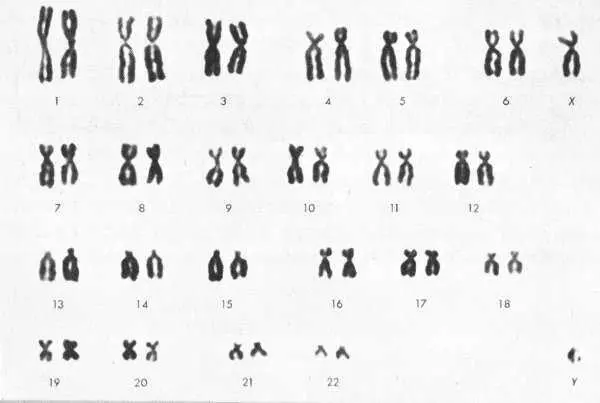
These “instructions” are contained in the cell’s chromosomes , tiny structures that appear most clearly (like stubby bits of tangled spaghetti) when the cell is in the actual process of division. Each species has some characteristic number of chromosomes in its cells, and these chromosomes can be considered in pairs. Human cells, for instance, contain 23 pairs of chromosomes—46 in all.
When a cell is undergoing division ( mitosis ), the number of chromosomes is temporarily doubled, as each chromosome brings about the formation of a replica of itself. (This process is called replication .) As the cell divides, the chromosomes are evenly shared by the new cells in such a way that if a particular chromosome goes into one daughter cell, its replica goes into the other. In the end, each cell has a complete set of pairs of chromosomes; and the set in each cell is identical with the set in the original cell before division.
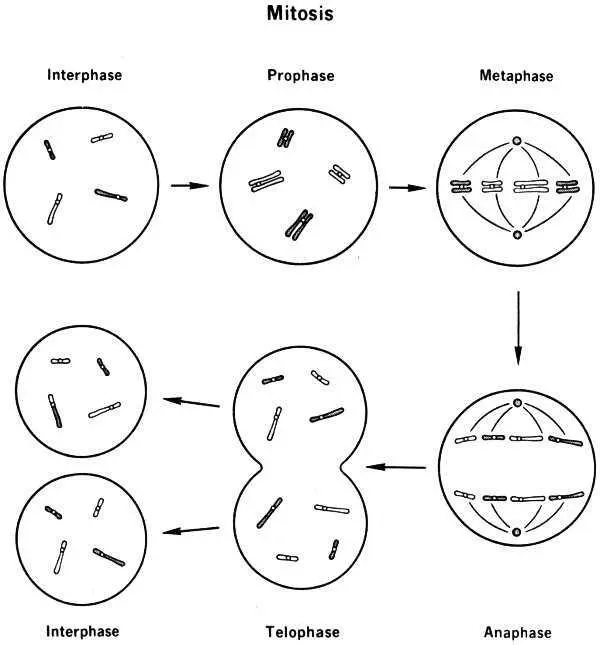
Mitosis. Diagram depicting Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Interphase
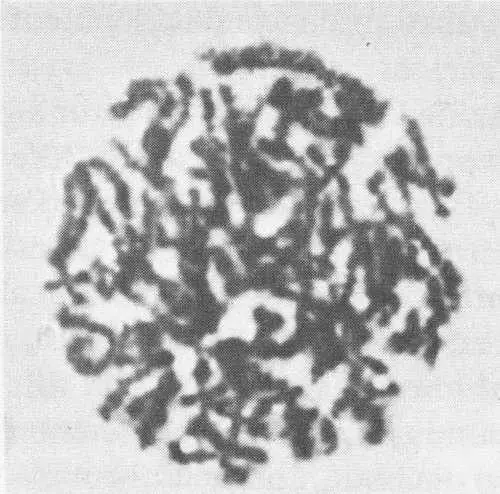
To study chromosomes, scientists begin with a cell that is in the process of dividing, when chromosomes are in their most visible form. Then they treat the cell with a chemical, a derivative of colchicine, to arrest the cell division at the metaphase stage (see mitosis diagram on preceding page). This brings a result like the photomicrograph above; the chromosomes are visible but still too tangled to be counted or measured. Then the cell is treated with a low–concentration salt solution, which swells the chromosomes and disperses them so they become distinct structures, as below.
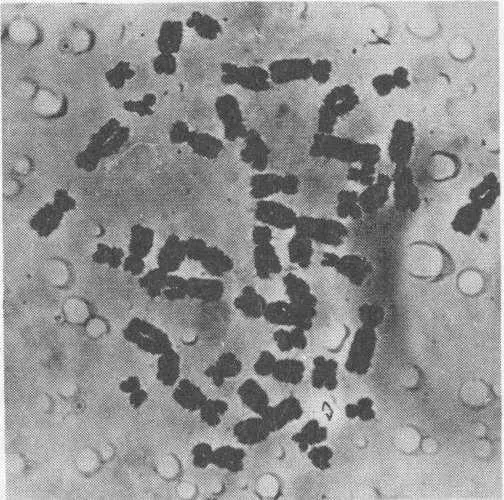
Cell after treatment with salt solution
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «The Genetic Effects of Radiation»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «The Genetic Effects of Radiation» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «The Genetic Effects of Radiation» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.








![Айзек Азимов - Земля Ханаанская. Родина иудаизма и христианства[The Land of Canaan]](/books/172206/ajzek-azimov-zemlya-hanaanskaya-rodina-iudaizma-i-h-thumb.webp)



