* * *
The best way to appreciate the general direction of history is to count the number of separate human worlds that coexisted at any given moment on planet Earth. Today, we are used to thinking about the whole planet as a single unit, but for most of history, earth was in fact an entire galaxy of isolated human worlds.
Consider Tasmania, a medium-sized island south of Australia. It was cut off from the Australian mainland in about 10,000 BC as the end of the Ice Age caused the sea level to rise. A few thousand hunter-gatherers were left on the island, and had no contact with any other humans until the arrival of the Europeans in the nineteenth century. For 12,000 years, nobody else knew the Tasmanians were there, and they didn’t know that there was anyone else in the world. They had their wars, political struggles, social oscillations and cultural developments. Yet as far as the emperors of China or the rulers of Mesopotamia were concerned, Tasmania could just as well have been located on one of Jupiter’s moons. The Tasmanians lived in a world of their own.
America and Europe, too, were separate worlds for most of their histories. In AD 378, the Roman emperor Valence was defeated and killed by the Goths at the battle of Adrianople. In the same year, King Chak Tok Ich’aak of Tikal was defeated and killed by the army of Teotihuacan. (Tikal was an important Mayan city state, while Teotihuacan was then the largest city in America, with almost 250,000 inhabitants – of the same order of magnitude as its contemporary, Rome.) There was absolutely no connection between the defeat of Rome and the rise of Teotihuacan. Rome might just as well have been located on Mars, and Teotihuacan on Venus.
How many different human worlds coexisted on earth? Around 10.000 BC our planet contained many thousands of them. By 2000 BC, their numbers had dwindled to the hundreds, or at most a few thousand. By AD 1450, their numbers had declined even more drastically. At that time, just prior to the age of European exploration, earth still contained a significant number of dwarf worlds such as Tasmania. But close to 90 per cent of humans lived in a single mega-world: the world of Afro-Asia. Most of Asia, most of Europe, and most of Africa (including substantial chunks of sub-Saharan Africa) were already connected by significant cultural, political and economic ties.
Most of the remaining tenth of the world’s human population was divided between four worlds of considerable size and complexity:
1. The Mesoamerican World, which encompassed most of Central America and parts of North America.
2. The Andean World, which encompassed most of western South America.
3. The Australian World, which encompassed the continent of Australia.
4. The Oceanic World, which encompassed most of the islands of the south-western Pacific Ocean, from Hawaii to New Zealand.
Over the next 300 years, the Afro-Asian giant swallowed up all the other worlds. It consumed the Mesoamerican World in 1521, when the Spanish conquered the Aztec Empire. It took its first bite out of the Oceanic World at the same time, during Ferdinand Magellan’s circumnavigation of the globe, and soon after that completed its conquest. The Andean World collapsed in 1532, when Spanish conquistadors crushed the Inca Empire. The first European landed on the Australian continent in 1606, and that pristine world came to an end when British colonisation began in earnest in 1788. Fifteen years later the Britons established their first settlement in Tasmania, thus bringing the last autonomous human world into the Afro-Asian sphere of influence.
It took the Afro-Asian giant several centuries to digest all that it had swallowed, but the process was irreversible. Today almost all humans share the same geopolitical system (the entire planet is divided into internationally recognised states); the same economic system (capitalist market forces shape even the remotest corners of the globe); the same legal system (human rights and international law are valid everywhere, at least theoretically); and the same scientific system (experts in Iran, Israel, Australia and Argentina have exactly the same views about the structure of atoms or the treatment of tuberculosis).
The single global culture is not homogeneous. Just as a single organic body contains many different kinds of organs and cells, so our single global culture contains many different types of lifestyles and people, from New York stockbrokers to Afghan shepherds. Yet they are all closely connected and they influence one another in myriad ways. They still argue and fight, but they argue using the same concepts and fight using the same weapons. A real ‘clash of civilisations’ is like the proverbial dialogue of the deaf. Nobody can grasp what the other is saying. Today when Iran and the United States rattle swords at one another, they both speak the language of nation states, capitalist economies, international rights and nuclear physics.
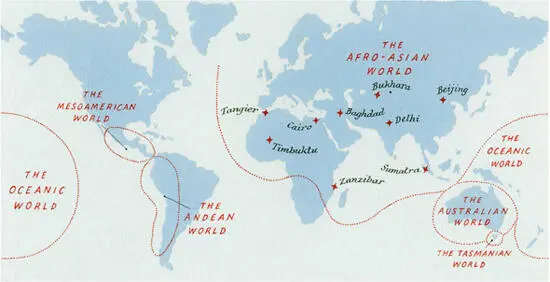
Map 3. Earth in AD 1450. The named locations within the Afro-Asian World were places visited by the fourteenth-century Muslim traveller Ibn Battuta. A native of Tangier, in Morocco, Ibn Battuta visited Timbuktu, Zanzibar, southern Russia, Central Asia, India, China and Indonesia. His travels illustrate the unity of Afro-Asia on the eve of the modern era.
We still talk a lot about ‘authentic’ cultures, but if by authentic’ we mean something that developed independently, and that consists of ancient local traditions free of external influences, then there are no authentic cultures left on earth. Over the last few centuries, all cultures were changed almost beyond recognition by a flood of global influences.
One of the most interesting examples of this globalisation is ‘ethnic’ cuisine. In an Italian restaurant we expect to find spaghetti in tomato sauce; in Polish and Irish restaurants lots of potatoes; in an Argentinian restaurant we can choose between dozens of kinds of beefsteaks; in an Indian restaurant hot chillies are incorporated into just about everything; and the highlight at any Swiss café is thick hot chocolate under an alp of whipped cream. But none of these foods is native to those nations. Tomatoes, chilli peppers and cocoa are all Mexican in origin; they reached Europe and Asia only after the Spaniards conquered Mexico. Julius Caesar and Dante Alighieri never twirled tomato-drenched spaghetti on their forks (even forks hadn’t been invented yet), William Tell never tasted chocolate, and Buddha never spiced up his food with chilli. Potatoes reached Poland and Ireland no more than 400 years ago. The only steak you could obtain in Argentina in 1492 was from a llama.
Hollywood films have perpetuated an image of the Plains Indians as brave horsemen, courageously charging the wagons of European pioneers to protect the customs of their ancestors. However, these Native American horsemen were not the defenders of some ancient, authentic culture. Instead, they were the product of a major military and political revolution that swept the plains of western North America in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, a consequence of the arrival of European horses. In 1492 there were no horses in America. The culture of the nineteenth-century Sioux and Apache has many appealing features, but it was a modern culture – a result of global forces – much more than authentic’.
The Global Vision
From a practical perspective, the most important stage in the process of global unification occurred in the last few centuries, when empires grew and trade intensified. Ever-tightening links were formed between the people of Afro-Asia, America, Australia and Oceania. Thus Mexican chilli peppers made it into Indian food and Spanish cattle began grazing in Argentina. Yet from an ideological perspective, an even more important development occurred during the first millennium BC, when the idea of a universal order took root. For thousands of years previously, history was already moving slowly in the direction of global unity, but the idea of a universal order governing the entire world was still alien to most people.
Читать дальше




![Юваль Ной Харари - Sapiens. Краткая история человечества [litres]](/books/34310/yuval-noj-harari-sapiens-kratkaya-istoriya-cheloveche-thumb.webp)





![Юваль Ной Харари - 21 урок для XXI века [Версия с комментированными отличиями перевода]](/books/412481/yuval-noj-harari-21-urok-dlya-xxi-veka-versiya-s-ko-thumb.webp)


