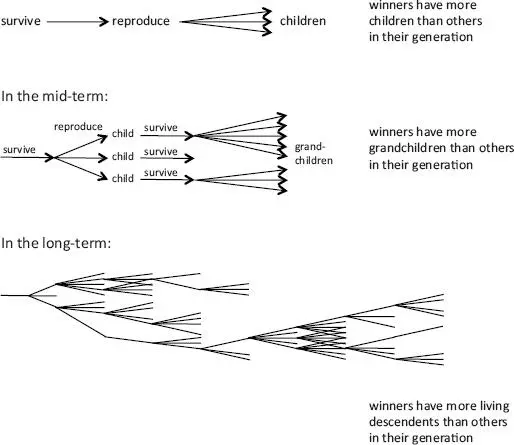
FIGURE 2.1. The game of life: evolution. The goal is to stay alive long enough to reproduce, to reproduce more than others in your generation, and to make offspring that are, in their own generation, successful reproducers. Winners and champions are recognized and distinguished by how well they do relative to others, not on an absolute point scale. As generations pass, results can change if short-term winners leave few descendents in the long term.
In the real game of life most players, even humans, don’t evaluate the evolutionary effectiveness of their behavior. How can we, when most of us don’t even know that we’re playing the game? Instead, the game is played through instinct, gut-level emotional reactions to the circumstances that present themselves. Even if you know that you’re a player, know the rules, and know what it takes to win, you can only guess as to what might make your children successful at making grandchildren. You can’t see the future and the chance events that may alter the conditions on the playing field. We are playing blind.
Although you as an individual may not score points through the three rules described above, you are, in fact, part of a team, and you get some points for just being part of a team that has players that are reproducing. [2] Scoring points by helping your relatives raise kin is formally recognized as “inclusive fitness.”
You can help other members of your familial team reproduce or raise children. But please don’t misunderstand: if you are personalizing this, thinking about your own play in the game of life, then you may be getting bummed out right about now, because I may have conveyed that without children and grandchildren you are a loser. That’s not my intent. I’m just trying to show you a different way to think about evolution—by thinking of it as “differential reproduction.”
Understanding the fundamentals of evolution is key because we so often get it wrong. Think of Darwin’s lament. Evolution is part of our everyday parlance, and even though the game of life is a fact of life, we intentionally and unintentionally misrepresent, steadily. We think, incorrectly, that individuals evolve, that individuals act for the good of the species, that some species are primitive and others are advanced, that a ladder of life describes descent with modification, and that evolution is always working to make species better. We incorrectly intuit that complexity is always more evolutionarily advanced than simplicity, that evolution is goal driven, that evolutionary change is linear and in one direction, that any anatomical structure evolved long ago for the function it fulfills today, and that humans aren’t evolving anymore—wrong, wrong, wrong!
These same poison apples will tempt us when we talk about evolving robots. Our intuitive, mistaken expectations will bear fruit in the form of disappointment, disapproval, and denial. So keep this in mind: nowhere in the rules of the game of life does it say that the players in the future will always be smarter or better in any way than those playing the game right now. The rules don’t say that different strategies that work at one time and place will work at other times and places. And the rules are silent regarding the behavior of other players toward one another, the number of players, the kinds of players, the availability of resources, the use of the environment, and accidents and other chance events that may occur. When robots evolve, we simply don’t know what will happen. That’s life. [3] Although it probably seems crazy at first, I’m not sure that evolving robots aren’t alive. The quality that we recognize scientifically as “life” is usually a suite of characteristics that include the ability of a self-contained entity to (1) make additional and similar versions of itself, (2) gather energy, (3) convert and use the gathered energy to perform chemical and mechanical work (e.g., build or repair itself, gather more energy, make copies of itself), and (4) decrease entropy (disorder) locally and temporarily. These ideas are influenced, in part, by the physicist Erwin Schrödinger in his 1944 book, What Is Life? (based on lectures delivered under the auspices of the Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Dublin, February 1943). From cognitive science, I would include, in our life list, the ability of a self-contained entity to (5) react to changes in the patterns of the global energy array with the goal of reproducing and gathering energy. What do you think?
INDIVIDUALS ARE SELECTED BUT DON’T EVOLVE
I have more bad news: individuals don’t evolve. As much as it makes good science fiction when Captain Jean-Luc Picard “devolves” into a lemur on Star Trek: The Next Generation , individuals are trapped in time and space. An individual human carries a genome—the total complement of genes and DNA within that individual—that is the product of genes from mom’s egg and dad’s sperm. This new combination of genes interacts with the world to create an embryo, just like our autonomous agents interact with the world to create behavior. The behavior of the genome, in this case, creates the ongoing interaction with the world known as development, the splitting of one cell into two, two cells into four, and so on, creating a multicellular animal from a single cell in a matter of a few hours.
The inside of each cell—with its aquatic world of chemicals in solution, lattice-like network of tiny skeletal structures, and membrane-bound micromachines—is the world of the genome. The genes interact with proteins that wind up and organize the DNA; the genes interact with other kinds of proteins that signal when the gene should make RNA; the DNA interacts with itself in order to make copies prior to cell division.
Each cell also has a world with which to interact. Other cells cling to it, pull on it, and exchange chemicals and electric charge. Fluid not in cells can be present in some tissues, and that extracellular fluid can bring hormones that the cell reacts to, setting up a cascade of molecular signals that results in changing how the genome is working. In response to being in different positions in the multicellular embryo, some cells “differentiate”—that is, their genes start making different kinds of RNA, and the RNA starts making different kinds of proteins. Those different proteins self-assemble into different structures. Quickly, you have cells in a particular neighborhood of the embryo that are working together to make a notochord, the skeletal rod that runs from head to tail in all vertebrate embryos and is retained in the adults of some fish and amphibian species. The cells making a notochord, in turn, release compounds that cause neighboring cells to start making a central nervous system and so on, throughout the lifetime of that individual: the genome, copied and partitioned into cells, interacts with its local world inside the cell, outside the cell, and embedded in differentiating tissues that are, in turn, interacting with the world outside the individual.
How, given all this developmental interaction of the genome and the world, is an individual trapped in time and space? Each individual is literally a product of their time and place (where time and place = “world” as I’m using the word). Take the same genome and put it in a different time and place, and you will get a different individual. Interaction of the genome and the world unfolds in development, and development reflects that particular history of that agent. Each agent is “trapped” in the sense that their agent-world interactions—which are unique—make them what they are as they continuously become what they are.
Читать дальше













