To service the ItemRemovedevent in the Branchclass, modify the code as follows:
static void Main(string[] args) {
Branch b = new Branch();
b.ItemRemoved += new EventHandler(b_ItemRemoved);
b.BranchNames.Add("ABC");
b.BranchNames.Add("XYZ");
b.BranchNames.Remove("XYZ");
foreach (string branchName in b.BranchNames) {
Console.WriteLine(branchName);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void b_ItemRemoved(object sender, EventArgs e) {
Console.WriteLine("Item removed!");
}
And here's the code's output:
Item removed!
As a rule of thumb, use the generic Collectionclass (because it is more extensible) as a return type from a public method, and use the generic Listclass for internal implementation.
Generics allow you define type-safe data structures without binding to specific fixed data types at design time. The end result is that your code becomes safer without sacrificing performance. In addition to showing you how to define your own generic class, this chapter also examined some of the generic classes provided in the .NET Framework class library, such as the generic LinkedListand Collectionclasses.
Today's computer runs at more than 2GHz, a blazing speed improvement over just a few years ago. Almost all operating systems today are multitasking, meaning you can run more than one application at the same time. However, if your application is still executing code sequentially, you are not really utilizing the speed advancements of your latest processor. How many times have you seen an unresponsive application come back to life after it has completed a background task such as performing some mathematical calculations or network transfer? To fully utilize the extensive processing power of your computer and write responsive applications, understanding and using threads is important.
A thread is a sequential flow of execution within a program. A program can consist of multiple threads of execution, each capable of independent execution.
This chapter explains how to write multithreaded applications using the Thread class in the .NET Framework. It shows you how to:
□ Create a new thread of execution and stop it
□ Synchronize different threads using the various thread classes available
□ Write thread-safe Windows applications
□ Use the BackgroundWorkercomponent in Windows Forms to program background tasks.
The Need for Multithreading
Multithreading is one of the most powerful concepts in programming. Using multithreading, you can break a complex task in a single application into multiple threads that execute independently of one another. One particularly good use of multithreading is in tasks that are synchronous in nature, such as Web Services calls. By default, Web Services calls are blocking calls — that is, the caller code does not continue until the Web Service returns the result. Because Web Services calls are often slow, this can result in sluggish client-side performance unless you take special steps to make the call an asynchronous one.
To see how multithreading works, first take a look at the following example:
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
DoSomething();
Console.WriteLine("Continuing with the execution...");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void DoSomething() {
while (true) {
Console.WriteLine("Doing something...");
}
}
}
This is a simple application that calls the DoSomething()function to print out a series of strings (in fact, it is an infinite loop, which will never stop; see Figure 10-1). Right after calling the DoSomething()function, you try to print a string (" Сontinuing with the execution...") to the console window. However, because the DoSomething()function is busy printing its own output, the " Console.WriteLine("Continuing with the execution...");" statement never gets a chance to execute.
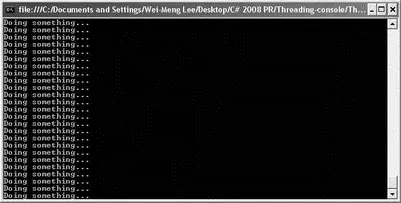
Figure 10-1
This example illustrates the sequential nature of application — statements are executed sequentially. The DoSomething()function is analogous to consuming a Web Service, and as long as the Web Service does not return a value to you (due to network latency or busy web server, for instance), the rest of your application is blocked (that is, not able to continue).
You can use threads to break up statements in your application into smaller chunks so that they can be executed in parallel. You could, for instance, use a separate thread to call the DoSomething()function in the preceding example and let the remaining of the code continue to execute.
Every application contains one main thread of execution. A multithreaded application contains two or more threads of execution.
In C#, you can create a new thread of execution by using the Threadclass found in the System.Threadingnamespace. The Threadclass creates and controls a thread. The constructor of the Threadclass takes in a ThreadStartdelegate, which wraps the function that you want to run as a separate thread. The following code shows to use the Threadclass to run the DoSomething()function as a separate thread:
Import the System.Threadingnamespace when using the Threadclass.
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(new ThreadStart(DoSomething));
t.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Continuing with the execution...");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void DoSomething() {
while (true) {
Console.WriteLine("Doing something...");
}
}
}
Note that the thread is not started until you explicitly call the Start()method. When the Start()method is called, the DoSomething()function is called and control is immediately returned to the Main()function. Figure 10-2 shows the output of the example application.
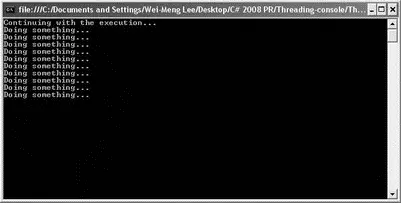
Figure 10-2
Figure 10-3 shows graphically the two different threads of execution.
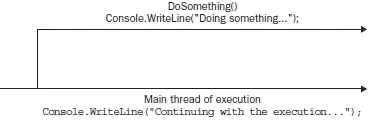
Figure 10-3
As shown in Figure 10-2, it just so happens that before the DoSomething()method gets the chance to execute, the main thread has proceeded to execute its next statements. Hence, the output shows the main thread executing before the DoSomething()method. In reality, both threads have an equal chance of executing, and one of the many possible outputs could be:
Читать дальше















