private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) {
LogError("File not found.", "Form1.cs");
}
private void LogError(string message, string SourceFile) {
Console.WriteLine(SourceFile + ": " + message);
}
Debugging is an important part of the development cycle. Naturally, Visual Studio 2008 contains debugging tools that enable you to observe the runtime behavior of your program. This section takes a look at those tools.
Suppose that you have the following program:
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 {
public partial class Form1 : Form {
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) {
Console.WriteLine("Start");
printAllOddNumbers(9);
Console.WriteLine("End");
}
private void printAllOddNumbers(int num) {
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 1) {
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
}
}
}
The following sections show how you can insert breakpoints into the application so that you can debug the application during runtime.
To set a breakpoint in your application, in the Visual Studio 2008 Code Editor, click in the left column beside the statement at which you want to set the breakpoint (see Figure 2-60).

Figure 2-60
Press F5 to debug the application. When the execution reaches the statement with the breakpoint set, Visual Studio 2008 pauses the application and shows the breakpoint (see Figure 2-61).
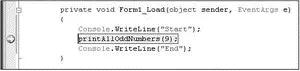
Figure 2-61
Stepping through the Code
With the application stopped at the breakpoint, you have a choice of what to do:
□ Step Into— Press F11 (see Figure 2-62). Stepping into the code means that if the breakpoint statement is a function call, execution is transferred to the first statement in the function and you can step through the function one statement at a time.
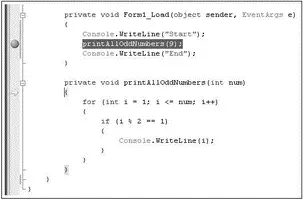
Figure 2-62
□ Step Over— Press F10. Stepping over the code means that if the breakpoint statement is a function call, the entire function is executed and control is transferred to the next statement after the function.
□ Step Out— Press Shift+F11 to step out of the code (Step Out). If the statement at the breakpoint is part of a function, execution is resumed until the function exits. The control is transferred to the returning point in the calling function.
Step Into and Step Over are basically the same, except when it comes to executing functions.
While you are at a breakpoint stepping through the code (using either F10 or F11), you can also examine the values of variables by hovering the mouse over the object you want to examine. Figure 2-63 shows value of i when the mouse is over i.

Figure 2-63
You can also right-click on the object you want to monitor and select Add Watch or QuickWatch (see Figure 2-64).
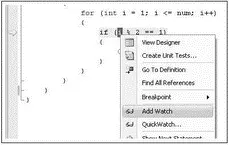
Figure 2-64
When you use the Add Watch feature, the variable you are watching will be displayed in the Watch window (see Figure 2-65). As you step through your code, changes in the variable are reflected in the Watch window. In addition, you have the option to change the value of the variable directly in the Watch window.
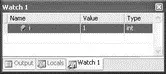
Figure 2-65
The QuickWatch feature also enables you to monitor the value of variables, except that the execution cannot continue until you have closed the QuickWatch window (see Figure 2-66). You can also enter an expression to evaluate and at the same time add a variable into the Add Watch window.
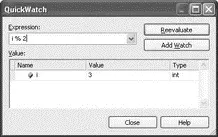
Figure 2-66
Autos and Immediate Windows
To automatically view all the relevant variables in scope, you can launch the Autos window (see Figure 2-67) during a breakpoint by selecting Debug→Windows→Autos.
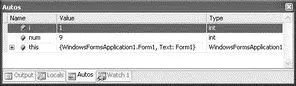
Figure 2-67
You can use the Immediate Window (see Figure 2-68) at runtime to evaluate expressions, execute statements, print variable values, and so on. You can launch the Immediate window during a breakpoint by selecting Debug→Windows→Immediate.
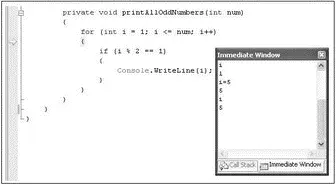
Figure 2-68
Application testing is one of the tasks that every programmer worth his salt needs to do. For example, after writing a class, you often need to write additional code to instantiate the class and test the various methods and properties defined within it. Visual Studio 2008 Professional (and higher) provides a Unit Testing feature to auto-generate the code needed to test your application.
This section demonstrates how unit testing is performed in Visual Studio 2008. Use the following Pointclass definition located within a Class Library project:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace UnitTesting {
class Point {
public Point() { }
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int x { get; set; }
public int y { get; set; }
//--- calculates the length between 2 points
public double length(Point pointOne) {
return Math.Sqrt(
Math.Pow(this.x - pointOne.x, 2) +
Math.Pow(this.y - pointOne.y, 2));
}
}
}
For this example, create a unit test to test the length()method. To do so, right-click on the length()method and select Create Unit Tests (see Figure 2-69).
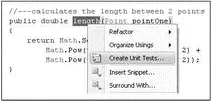
Figure 2-69
Читать дальше






















