(2/24): esound-0.2.36-0.f 100% |=========================| 127 kB 00:00
...(Lines snipped)...
Running Transaction Test
Repackage : bind-utils ####################### [ 0/43]
Repackage : esound ####################### [ 0/43]
...(Lines snipped)...
Installing: GFS-kernel ####################### [22/43]
Updating : bind-libbind-devel ####################### [23/43]
Installed: GFS-kernel.i686 0:2.6.11.8-20050601.152643.FC4.17 cman-kernel.i686
...(Lines snipped)...
pam.i386 0:0.79-9.6 pam-devel.i386 0:0.79-9.6 sudo.i386 0:1.6.8p8-2.3
Complete!
For each of the currently installed packages, yum checks to see if a newer version exists in any of the repositories and queues the update of those packages plus the installation of any packages required for dependency resolution. After confirming the package set with the user, the packages are downloaded and the update/installation is performed through the RPM system.
To update one specific package (and dependencies), list the package name as an argument:
# yum update kernel
yum also offers a number of information and miscellaneous options; the most useful are shown in Table 5-5 . However, most of these operations are more easily performed using the graphical user interface (GUI).
Table 5-5. Information and miscellaneous commands for yum
| Option |
Description |
| list |
Lists available packages. |
| check-update |
Verifies whether any updates are available. An exit code of 100 indicates that updates are ready for installation. |
| whatprovides capability |
Displays the name of any packages that provide the listed capability , which may be an RPM-style capability name or a filename. |
| provides capability |
| search keyword |
Searches for a package with keyword in the description, summary, packager name, or package name metadata. The search is case-insensitive. |
| info package |
Displays metadata about package (similar to rpm -qi). |
| deplist package |
Displays the dependencies of package , including the names of the packages that will resolve those dependencies. |
| localinstall rpm_file |
Installs or removes the package contained in the local rpm_file and, if necessary, resolves any dependencies using the repositories. |
| localupdate rpm_file |
| -C |
Runs the specified command from cache (doesn't contact each repository to check for updates). |
5.3.1.2. Using yum with a GUI
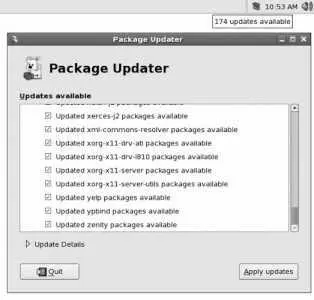
Fedora Core also provides graphical tools for using yum . When updates are available for any of the packages on your system, an update icon (which looks like a cardboard box) will appear in the upper GNOME panel. If you place your mouse cursor over this icon, a tool tip message will appear showing the number of available updates, as shown in the upper-right corner of Figure 5-1.
The yum-updatesd service must be running to make the update icon appear.
To install the available updates, right-click on the update icon and select Apply Updates (or select Applications→System Tools→Software Updater, or enter the command pup ). You will be prompted for the root password, and then the window shown in Figure 5-1 will appear; click "Apply updates" to install the updates listed.
Figure 5-1. The package updater window and notification icon
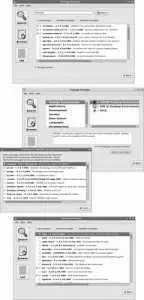
Fedora Core also provides a tool for graphically installing and removing software, named Pirut (pronounced "pirate"). To start this program, select the menu option Applications→Add/Remove Software; you will be prompted for the root password. Pirut offers three main modes of operation, as shown in Figure 5-2; these modes are selected using the buttons on the left side of the window and permit you to search for a specific package (the top window in Figure 5-2), browse by package groups (middle window, along with the window that appears when you click on "Optional packages"), or scroll through a list of all packages (bottom window).
If the browse-package-groups window looks familiar, you have a good memory. The same display is used for software package customization during installation.
Select the checkbox in front of the packages that you wish to install, and deselect the checkbox of the packages that you wish to uninstall; then click Apply. After confirmation, the selected actions will be performed.
Figure 5-2. The three operating modes of Pirut, the Install/Remove Software tool
Fedora Extras also provides the Yumex tool, which provides an alternate graphical frontend to yum .
5.3.1.3. Adding repositories
Fedora Core ships with configuration files for the six repositories listed in Table 5-6 . The three prerelease repositories are disabled by default, and the rest are enabled.
Table 5-6. Fedora Core repositories
| Repository |
Enabled by default |
Description |
| base |
Y |
Fedora Core base packages (same as CD/DVD) |
| development |
N |
Prerelease Fedora Core packages (also known as "Rawhide") |
| updates-released |
Y |
Updates to Fedora Core packages |
| updates-testing |
N |
Prerelease update packages |
| extras |
Y |
Add-on software for Fedora |
| extras-development |
N |
Prerelease add-on software |
The repositories are configured by files in /etc/yum.repos.d . Here is the content of the Fedora Extras file /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora-extras.repo :
[updates-released]
name=Fedora Core $releasever - $basearch - Released Updates
#baseurl=http://download.fedora.redhat.com/pub/fedora/linux/core/updates/$releasever/$basearch/
mirrorlist=http://fedora.redhat.com/download/mirrors/updates-released-fc$releasever
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-fedora
After the section identifier [updates-released] , there are several name/value pairs, each on a separate line, joined with equal signs:
name
The repository name as it will be shown to the user. The variables $releasevar and $basearch are replaced with the distribution release ( 6 ) and the system architecture ( i386 , x86_64 , or ppc ).
baseurl
The master URL for the repository.
mirrorlist
The URL of a text file listing all of the mirrors (alternate servers that are loaded from the master server) for the repository. It is better to use a mirrorlist than a baseurl entry to avoid overloading the master server and to provide multiple servers for redundancy.
enabled
Читать дальше














