The target class ( tclass ) associated with the object being accessed is determined by the type of object (and in some cases, how it is being accessed); in this example, where init is attempting to access /etc/inittab , the tclass is file . Therefore the SELinux policy is checked to see if access is permitted for an scontext of system_u:system_r:init_t , a tcontext of system_u:object_r:etc_t , and a tclass of file . To speed access, SELinux rules are cached in an area of memory called the access vector cache which explains why SELinux error messages are labeled avc .
The Fedora project has three policies available:
targeted
The default policy installed with Fedora Core. This policy is targeted for the protection of the most frequently attacked portions of the system, including most network services. Programs that are not targeted are unconstrained by SELinux.
strict
This policy denies every action except those explicitly permitted. Although this should be more secure than the targeted policy, it's hard to create a policy that encompasses all possible configurations of all programs that can be installed on a Fedora system, and attempting to use this policy has frustrated many system administrators into turning off SELinux altogether. In other words, the targeted policy is often more secure simply because it's more likely to be used.
MLS
Experimental policy to support multilevel security ( MLS). This is important for some government certifications and is not widely used outside of government. (The future MCS framework appearing in the targeted policy will use specific features of MLS for a type of discretionary access control).
In the default targeted policy, the role element of the security context is not used (all subjects are system_r, and all objects are object_r), and very few users are defined (just system_u , user_u , and root ).
SELinux policies are difficult and time-consuming to write, and even more difficult to write well. Nonetheless, they have to be customized to suit the particular needs of each site. The SELinux booleans provide a compromise between complexity and flexibility, by enabling policy options to be configured without editing, compiling, and retesting the policy code.
The SELinux technology was originally developed by the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA), with several partner organizations. The kernel components of SELinux have been incorporated into the main Linux kernel releases. The Fedora project utilizes those kernel components along with customized policy and some user tools (such as versions of ls and ps that include the -Z options, and SELinux-specific tools such as chcon and getenforce , and the graphical configuration tool system-config-securitylevel ). Red Hat is a major contributor to SELinux development.
8.2.3.1. ...using the strict or MLS policies?
These alternate policies are provided as RPM packages and are installed using yum :
# yum install selinux-policy-strict selinux-policy-mls
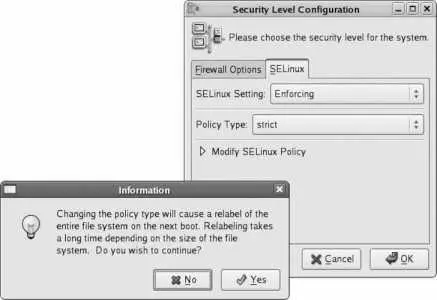
Switch between the installed policies using the graphical configuration tool ( system-config-securitylevel from the command line, or System→Administration→"Security Level and Firewall" from the menu). When more than one policy is installed, a drop-down menu for Policy Type appears on the SELinux tab, as shown in Figure 8-8. When you change the policy, the warning dialog shown at bottom left of Figure 8-8 will appear, informing you that the policy change will cause the filesystem to be relabeled. Click Yes to approve the relabeling, and then click OK in the Security Level Configuration window. Reboot to activate the new policy.
Figure 8-8. Selecting policy using the Security Level Configuration tool
To change the policy from the command prompt, edit /etc/selinux/config and change the SELINUXTYPE value to the policy of your choice ( targeted , strict , or mls ):
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - SELinux is fully disabled.
SELINUX=enforcing
# SELINUXTYPE= type of policy in use. Possible values are:
# targeted - Only targeted network daemons are protected.
# strict - Full SELinux protection.
SELINUXTYPE=mls
# SETLOCALDEFS= Check local definition changes
SETLOCALDEFS=0
Then create the empty file /.autorelabel to ensure that the filesystem will be relabeled when the system is booted:
# touch /.autorelabel
Reboot to activate the change.
Fedora development is focused on the targeted policy. Changing the policy may lead to a number of unexpected system problems!
8.2.3.2. ...booting with SELinux disabled?
If you have SELinux enabled, but your system cannot boot successfully due to an SELinux problem, you may need to temporarily disable it while you investigate.
To boot with SELinux disabled, append selinux=0 to the boot options.
8.2.4. Where Can I Learn More?
The manpages for selinux , getsebool , setsebool , getenforce , setenforce , sestatus , semanage , selinuxenabled , restorecon , getfattr , and audit2why
The manpage for _selinux (for example, the manpage for samba_selinux for details of SELinux protection provided for the Samba server)
The Fedora Wiki SELinux page: http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/SELinux
The setroubleshoot Wiki page: http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/SELinux/setroubleshoot
The NSA SELinux web site: http://www.nsa.gov/selinux/index.cfm
The SELinux project on Sourceforge: http://selinux.sourceforge.net/
The SELinux symposium web site: http://www.selinux-symposium.org/
The NSA SELinux FAQ: http://www.nsa.gov/selinux/info/faq.cfm
The Fedora SELinux FAQ: http://fedora.redhat.com/docs/selinux-faq/
The Unofficial SELinux FAQ: http://www.crypt.gen.nz/selinux/faq.html
The home page of Tresys, a company that has done extensive work on SELinux policy development: http://www.tresys.com/
The Linux Security Modules web site: http://lsm.immunix.org/
8.3. Using Access Control Lists
Unix/Linux permission modes are very simple; they don't cover all security needs. But, because they are simple, they are actually used , which is more than can be said for many other access control technologies.
But sometimes permissions just don't cut it, and a better system of discretionary access control is needed. Access control lists (ACLs) enable you to specify exactly which users and groups can access a file and in what ways.
In order to use ACLs on a filesystem, that filesystem must be mounted with the acl mount option. To check whether this option is active, use the mount command:
$ mount
/dev/mapper/main-root on / type ext3 (rw)
Читать дальше













