NOTE
The network configuration process described in this section is for client hosts. You cannot perform server network configuration, such as Domain Name System (DNS) and DHCP during installation. (See Chapter 23, "Managing DNS," for more information on configuring DNS; see the "DHCP" section later in this chapter for more information on that item.)
Using Graphical Configuration Tools
If you are new to networking or still becoming proficient with the command line, the graphical configuration tool is your best method for configuring new hardware in Fedora. Like most graphical tools, system-config-networkenables you to fill in the blanks; press the proper buttons, and the tool modifies the required files and issues the proper commands. Remember, you must be root to run system-config-network.
You can access system-config-networkby going to the System, Administration menu and selecting Network. You will be asked for the root password because you are able to make systemwide changes using this tool.
After it is started, system-config-networkwill display the screen shown in Figure 14.1.
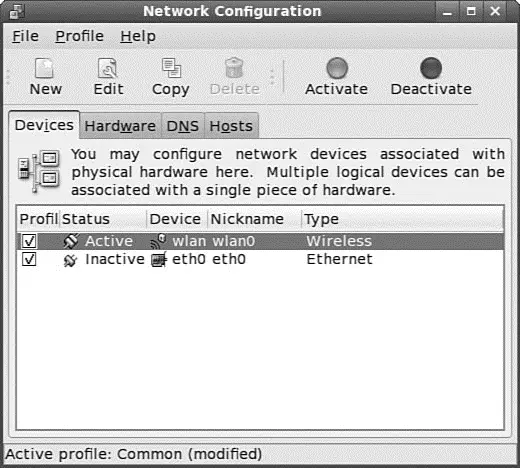
FIGURE 14.1 Use the initial system-config-networknetworking screen to begin configuring your network client host.
Click the DNS tab to configure your system's DNS settings, hostname, or DNS search path. Click the Hosts tab, and then click either the New or Edit button (after selecting a host) to create or edit an entry in your system's /etc/hostsfile — for example, to add the IP addresses, hostnames, and aliases of hosts on your network. See Figure 14.2 for an example of editing a host entry.
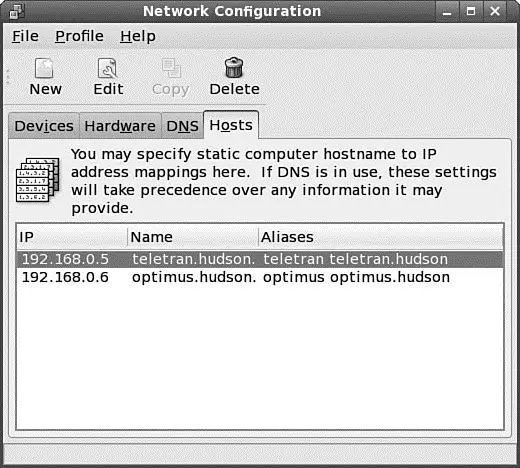
FIGURE 14.2 Highlight an existing entry, and then click the Edit button to change /etc/hostsentries in the Hosts tab of the Network Configuration screen.
Click the Devices tab, and then either click New or select an existing setting and click Edit to automatically or manually set up an ethernet device. Figure 14.3 shows the Ethernet Device dialog box with all necessary information in place for a static, or fixed, IP address assignment. Choose how your card will get its configuration: manually from Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) (see the next section) or from Bootp. Just fill in the blanks as needed.
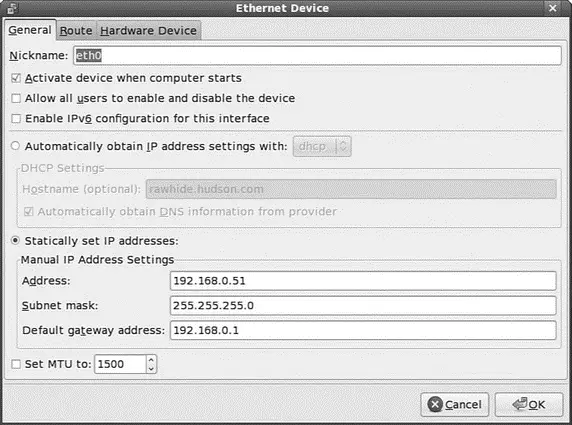
FIGURE 14.3 Configure an ethernet device to use a static IP address by double clicking the device.
NOTE
Bootp is the initial protocol on which DHCP was built, and it has mostly been replaced by DHCP.
When you finish configuring your NIC or editing an IP address or assignment scheme for a NIC, save your changes, using the File menu's Save menu item. Note that you can also use the Profile menu (as shown previously in Figure 14.1) to create different network configurations and IP address assignments for your installed NICs. This is handy if you want to create, for example, a different network setup for home or work on a laptop running Fedora.
Command-Line Network Interface Configuration
You can configure a network interface from the command line, using the basic Linux networking utilities. You configure your network client hosts with the command line by using commands to change your current settings or by editing a number of system files. Two commands, ifconfigand route, are used for network configuration. The netstatcommand displays information about the network connections.
/sbin/ifconfig
ifconfigis used to configure your network interface. You can use it to
► Activate or deactivate your NIC or change your NIC's mode.
► Change your machine's IP address, netmask, or broadcast address.
► Create an IP alias to allow more than one IP address on your NIC.
► Set a destination address for a point-to-point connection.
You can change as many or as few of these options as you'd like with a single command. The basic structure for the command is as follows:
# ifconfig [ network device ] options
Table 14.1 shows a subset of ifconfigoptions and examples of their uses.
TABLE 14.1 ifconfig Options
| Use |
Option |
Example |
| Create alias |
[ network device ] |
ifconfig eth0:0_:[number] |
| Change IP address |
10.10.10.10 |
ifconfig eth0 10.10.10.12 |
| Change the netmask |
netmask [ netmask ] |
ifconfig eth0 netmask 255.255.255.0 |
| Change the broadcast |
broadcast [ address ] |
ifconfig eth0 broadcast 10.10.10.255 |
| Take interface down |
down |
ifconfig eth0 down |
| Bring interface up |
up ( add IP address ) |
ifconfig eth0 up (ifconfig eth0 10.10.10.10) |
| Set NIC promiscuous |
[-]promisc [ifconfig eth0 -promisc] |
ifconfig eth0 promisc mode on [off] |
| Set multicasting mode |
[-]allmulti |
ifconfig eth0_on [off] allmulti [ifconfig eth0 - allmulti] |
| Enable [disable] [ address ] |
[-]pointopoint eth0_pointopoint |
ifconfig_point-to-point address 10.10.10.20 [ifconfig eth0 pointopoint_10.10.10.20] |
The ifconfigman page shows other options that enable your machine to interface with a number of network types such as AppleTalk, Novell, IPv6, and others. Again, read the man page for details on these network types.
NOTE
Promiscuous mode causes the NIC to receive all packets on the network. It is often used to sniff a network. Multicasting mode enables the NIC to receive all multicast traffic on the network.
If no argument is given, ifconfigdisplays the status of active interfaces. For example, the output of ifconfig,without arguments and one active and configured NIC, looks similar to this:
# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:30:1B:0B:07:0D
inet addr:192.168.0.7 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:127948 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:172675 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:7874 txqueuelen:100
RX bytes:19098389 (14.2 Mb) TX bytes:73768657 (70.3 Mb)
Interrupt:11 Base address:0x2000
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:215214 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:215214 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:68739080 (65.5 Mb) TX bytes:68739080 (65.5 Mb)
Читать дальше








![Andrew Radford - Linguistics An Introduction [Second Edition]](/books/397851/andrew-radford-linguistics-an-introduction-second-thumb.webp)






