NOTE
For the broadcom-wl-4.80.53.0.tar.bz2 file, you will need to double-click it because it is a compressed file. When Archive Manager opens, browse to broadcom-wl-4.80.53.0/kmod/ and copy both wl_apsta.o and wl_apsta.mimo.o to your home directory, either by dragging both files onto your Home icon, or by clicking Extract in the toolbar and browsing to your home directory.
Unfortunately it's trial and error from here in, so you will have to try each file in turn to see if it enables your hardware. For the files wl_apsta.oand wl_apsta-3.130.20.0.o, you need to use the command bcm43xx-fwcutter; for the wl_apsta_mimo.ofile, you need to use b43-fwcutter. Either way, the syntax is command file . So, for example, you might enter the following:
$ bcm43xx-fwcutter wl_apsta.o
You then press Enter to extract the firmware. After you have done this, you need to switch to root to move the extracted files to the location that Fedora requires them to be in. You change to root by issuing the command suand entering the root password when requested.
At the root prompt, enter the following command when you have used the bcm43xx-fwcuttercommand:
# mv *.fw /lib/firmware/
Or, if you used the b43-fwcuttercommand earlier, enter this command:
# mv b43 /lib/firmware/
At this point, you must restart your system to ensure that Fedora recognizes the new firmware Go to System, Shutdown, and choose Restart.
When your system comes back up, it's best to open a new terminal window (Applications, System Tools, Terminal) and enter the command dmesg | grep bcmor dmesg | grep b43depending on which tool you used to extract the firmware. You should see something similar to this:
b43-phy0: Broadcom 4306 WLAN found
b43-phy0 debug: Found PHY: Analog 2, Type 2, Revision 2
b43-phy0 debug: Found Radio: Manuf 0x17F, Version 0x2050, Revision 2
b43-phy0 debug: Adding Interface type 2
b43-phy0 debug: Loading firmware version 351.126 (2006-07-29 05:54:02)
b43-phy0 debug: Chip initialized
b43-phy0 debug: 30-bit DMA initialized
b43-phy0 debug: Wireless interface started
This means that Fedora has successfully recognized your Broadcom-based wireless card.
Now all you have to do is start NetworkManager to help you manage your wireless network. To do this, go to System, Administration and choose Services to see the Service Configuration tool shown in Figure 2.8.
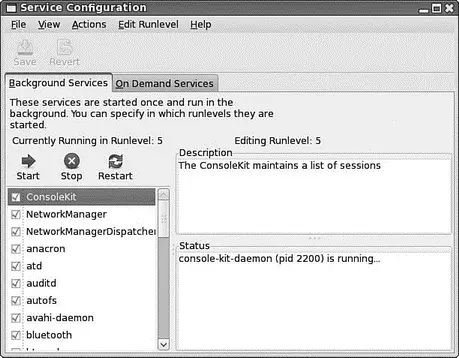
FIGURE 2.8 Control the services that are loaded in Fedora using the Service Configuration tool.
You need to make sure that the check box is marked next to both NetworkManager and NetworkManagerDispatcher; as you check the boxes, click the Start button directly above them to start the services immediately. Finally, click the Save button in the toolbar, and close the Service Configuration tool by going to File, Quit. When you've done this, the NetworkManager icon appears in the notification area of your top panel (see Figure 2.9). This is the applet that handles and monitors network connections.
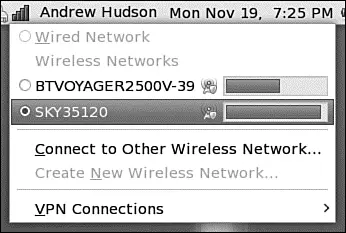
FIGURE 2.9 The NetworkManager notification applet, shown here already connected to a wireless network.
When you are ready, click the NetworkManager icon in the toolbar to connect to a wire less network. If your wireless access point broadcasts its SSID, it should appear in the list under wireless networks (similar to Figure 2.9). Simply click the required network and NetworkManager detects what encryption (if any) is in use and asks you for the passkey. Enter this and NetworkManager starts the wireless connection. The passkey is then stored in the default keyring (essentially a central way of managing security in Fedora); so if you have not yet used the keyring, you are asked to create a password. From now on, when ever you log in to Fedora, you will be asked for the key to unlock the keyring.
If for some reason your wireless network does not appear (you might have your SSID hidden), you have to use the Connect to Other Wireless Network option, which brings up the screen shown in Figure 2.10.
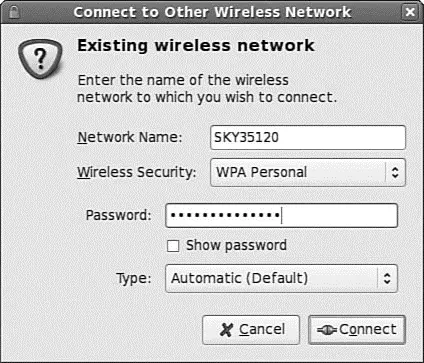
FIGURE 2.10 Use NetworkManager to configure your wireless network connection settings.
NetworkManager can handle WEP and WPA encryption, as well as enterprise variations of WPA. You are advised to use WPA encryption as it is the stronger of the two.
NetworkManager can also connect to Cisco VPN connections. You are able to specify connection settings as appropriate, or if you have access to a predefined configuration (PCF file) you can import it directly into NetworkManager.
CHAPTER 3
Working with GNOME
Imagine a world of black screens with white text, or for those of you who remember, black screens with green text. That used to be the primary interface for users accessing computers. Computing has moved on significantly since then and has adopted the graphical user interface, or GUI, as standard on most desktop and workstation platforms.
Fedora is no different, and its primary window manager is called GNOME (the Gnu Network Object Model Environment) . Based on the ethos of simplicity by design, GNOME offers a rich and full interface that you can use easily to be productive. The principle design objectives include an intuitive system, meaning that it should be easy to pick up and use, as well as good localization/internationalization support and accessibility.
GNOME is founded upon the X Window System, the graphical networking interface found on many Linux distributions, which provides the basis for a wide range of graphical tools and window managers. More commonly known as just X , it can also be referred to as X11R7 and X11 (such as that found on Mac OS X). Coming from the world-renowned Massachusetts Institute of Technology, X has gone through several versions, each of which has extended and enhanced the technology. The open source implementation is managed by the X.Org foundation, the board of which is made up of several key figures from the open source world.
The best way to think about how X works is to see it as a client/server system. The X server provides services to programs that have been developed to make the most of the graphical and networking capabilities that are available under the server and in the supported libraries. X.Org provides versions for many different platforms, including Linux and Mac OS X. Originally implemented as XFree86, X.Org was forked when a disagreement broke out over certain restrictions that were going to be included in the XFree86 license. Taking a snapshot of code that was licensed under the previous version of the license, X.Org drove forward with its own implementation based on the code. Almost in unison, most Linux distributions turned their back on XFree86 and switched their development and efforts to X.Org.
In this chapter, you learn how to work with GNOME and also the version of X that is included with Fedora. We look at the fundamentals of X and how to get X to work with any upgrades that might affect it, such as a new graphics card or that new flat-panel display you just bought. We also take a look at some of the other Window Managers that are included with Fedora, including KDE and Xfce.
Читать дальше








![Andrew Radford - Linguistics An Introduction [Second Edition]](/books/397851/andrew-radford-linguistics-an-introduction-second-thumb.webp)






