a.Tap or click Add, and then enter the gateway address in the Gateway text box.
b.By default, Windows Server 2012 R2 automatically assigns a metric to the gateway. You can also assign the metric yourself. To do this, clear the Automatic Metric check box, enter a metric in the text box provided, and then tap or click Add.
c.Repeat steps a through b for each gateway you want to add.
5.Tap or click OK, and then tap or click Close.
Configuring networking for Hyper-V
After you install Hyper-V and create an external virtual network, your server uses a virtual network adapter to connect to the physical network. When you work with the Network Connections page, you will find the original network adapter and a new virtual network adapter. The original network adapter will have nothing bound to it except the Microsoft Virtual Network Switch Protocol, and the virtual network adapter will have all the standard protocols and services bound to it. The virtual network adapter that appears under Network Connections will have the same name as the virtual network switch with which it is associated.
NOTE As part of the Hyper-V configuration, you can create an internal virtual network, which enables communications only between the server and hosted virtual machines. This configuration exposes a virtual network adapter to the parent server without the need to have a physical network adapter associated with it and isolates the virtual machine from the Internet and the rest of the LAN. hyper-V binds the virtual network service to a physical network adapter only when an external virtual network is created. An external virtual network is required for communications on the LAN and the Internet.
Following this, when you install Hyper-V on a server and enable external virtual networking, you’ll find that virtual network switching is being used. As shown in Figure 7–5, the server has a network connection with the Hyper-V Extensible Virtual Switch protocol enabled and all other networking components not enabled in the dialog box on the left and an entry for a virtual connection with the key networking components enabled and the Hyper-V Extensible Virtual Switch Protocol disabled in the dialog box on the right. This is the configuration you want to use to ensure proper communications for the server and any hosted virtual machines that use networking. If this configuration is changed, virtual machines won’t be able to connect to the external network.
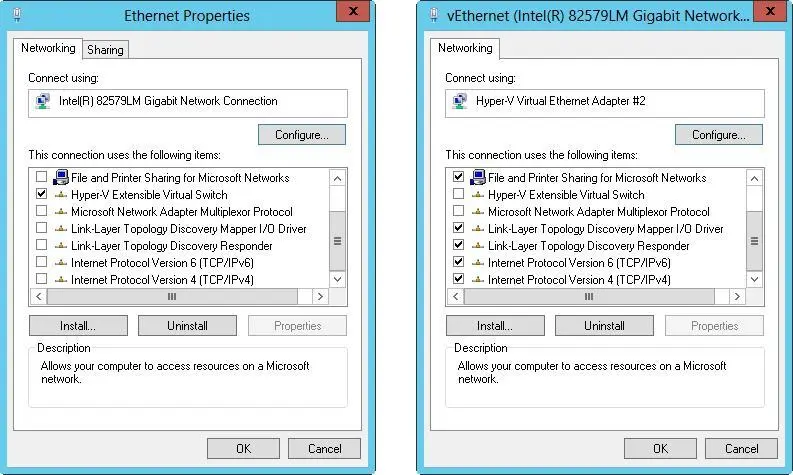 FIGURE 7–5Use switched virtual networking to ensure communications with hosted virtual machines.
FIGURE 7–5Use switched virtual networking to ensure communications with hosted virtual machines.
Managing network connections

Network connections make it possible for computers to access resources on the network and the Internet. One network connection is created automatically for each network adapter installed on a computer. This section examines techniques you can use to manage these connections.
Checking the status, speed, and activity for network connections
To check the status of a network connection, follow these steps:
1.In Network And Sharing Center, tap or click Change Adapter Settings. In Network Connections, press and hold or right-click the connection with which you want to work, and then tap or click Status to display the Status dialog box for the network connection.
2.If the connection is disabled or the media is unplugged, you won’t be able to access the Status dialog box. Enable the connection or connect the network cable to resolve the problem, and then try to display the Status dialog box again.
Enabling and disabling network connections
Network connections are created and connected automatically. If you want to disable a connection so that it cannot be used, follow these steps:
1.In Network And Sharing Center, tap or click Change Adapter Settings. In Network Connections, press and hold or right-click the connection, and then tap or click Disable to deactivate the connection and disable it.
2.If you want to enable the connection later, press and hold or right-click the connection in Network Connections, and then tap or click Enable.
If you want to disconnect from a network, follow these steps:
1.In Network And Sharing Center, tap or click Change Adapter Settings. In Network Connections, press and hold or right-click the connection and then tap or click Disconnect. Typically, only remote access connections have a Disconnect option.
2.If you want to activate the connection later, press and hold or right-click the connection in Network Connections, and then tap or click Connect.
Renaming network connections
Windows Server 2012 R2 initially assigns default names to network connections. In Network Connections, you can rename a connection at any time by pressing and holding or right-clicking the connection, tapping or clicking Rename, and then entering a new name. If a computer has multiple network connections, a descriptive name can help you and others better understand the uses of a particular connection.

CHAPTER 8: Running DHCP clients and servers
■Understanding DHCP
■Installing a DHCP server
■Configuring DHCP servers
■Managing DHCP scopes
■Managing the address pool, leases, and reservations
■Backing up and restoring the DHCP database
You can use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to simplify administration of Active Directory domains, and in this chapter you’ll learn how to do that. You use DHCP to dynamically assign TCP/IP configuration information to network clients. This not only saves time during system configuration, but also provides a centralized mechanism for updating the configuration. To enable DHCP on the network, you need to install and configure a DHCP server. This server is responsible for assigning the necessary network information.

DHCP gives you centralized control over IP addressing and more. After DHCP is installed, you rely on the DHCP server to supply the basic information necessary for TCP/IP networking. This basic information can include the following: IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway; primary and secondary Domain Name System (DNS) servers; primary and secondary Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) servers; and the DNS domain name. DHCP servers can assign a dynamic IP version 4 (IPv4) address, a dynamic IP version 6 (IPv6) address, or both addresses to any of the network interface cards (NICs) on a computer.
Using dynamic IPv4 addressing and configuration
A computer that uses dynamic IPv4 addressing and configuration is called a DHCPv4 client . When you start a DHCPv4 client, a 32-bit IPv4 address can be retrieved from a pool of IPv4 addresses defined for the network’s DHCP server.
The address is assigned to the client for a specified time period known as a lease . When the lease is approximately 50 percent expired, the client tries to renew it. If the client can’t renew the lease at that time, it tries again before the lease expires. If this attempt fails, the client tries to contact an alternate DHCP server. IPv4 addresses that aren’t renewed are returned to the address pool. If the client is able to contact the DHCP server but the current IP address can’t be reassigned, the DHCP server assigns a new IPv4 address to the client.
Читать дальше

 FIGURE 7–5Use switched virtual networking to ensure communications with hosted virtual machines.
FIGURE 7–5Use switched virtual networking to ensure communications with hosted virtual machines.






