Using the ping command to check an address
Before you assign a static IP address, you should make sure that the address isn’t already in use or reserved for use with DHCP. With the ping command, you can check whether an address is in use. Open a command prompt and enter ping, followed by the IP address you want to check.
To test the IPv4 address 10.0.10.12, you would use the following command:
ping 10.0.10.12
To test the IPv6 address FEC0::02BC: FF:BECB: FE4F:961D, you would use the following command:
ping FEC0::02BC: FF:BECB: FE4F:961D
If you receive a successful reply from the ping test, the IP address is in use and you should try another one. If the request times out for all four ping attempts, the IP address isn’t active on the network at this time and probably isn’t in use; however, a firewall could be blocking your ping request. Your company’s network administrator would also be able to confirm whether an IP address is in use.
Configuring a static IPv4 or IPv6 address
One LAN connection is available for each network adapter installed. These connections are created automatically. To configure static IP addresses for a particular connection, follow these steps:
1.In Network And Sharing Center, tap or click Change Adapter Settings. In Network Connections, press and hold or right-click the connection with which you want to work, and then tap or click Properties.
2.Double-tap or double-click Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) or Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) as appropriate for the type of IP address you are configuring.
3.For an IPv6 address, do the following:
■Tap or click Use The Following IPv6 Address, and then enter the IPv6 address in the IPv6 Address text box. The IPv6 address you assign to the computer must not be in use anywhere else on the network.
■The Subnet Prefix Length option ensures that the computer communicates over the network properly. Windows Server 2012 R2 should insert a default value for the subnet prefix into the Subnet Prefix Length text box. If the network doesn’t use variable-length subnetting, the default value should suffice, but if it does use variable-length subnets, you need to change this value as appropriate for your network.
4.For an IPv4 address, do the following:
■Tap or click Use The Following IP Address, and then enter the IPv4 address in the IP Address text box. The IPv4 address you assign to the computer must not be in use anywhere else on the network.
■The Subnet Mask option ensures that the computer communicates over the network properly. Windows Server 2012 R2 should insert a default value for the subnet mask into the Subnet Mask text box. If the network doesn’t use variable-length subnetting, the default value should suffice, but if it does use variable-length subnets, you need to change this value as appropriate for your network.
5.If the computer needs to access other TCP/IP networks, the Internet, or other subnets, you must specify a default gateway. Enter the IP address of the network’s default router in the Default Gateway text box.
6.Domain Name System (DNS) is needed for domain name resolution. Enter a preferred address and an alternate DNS server address in the text boxes provided.
7.When you have finished, tap or click OK twice. Repeat this process for other network adapters and IP protocols you want to configure.
8.With IPv4 addressing, configure WINS as necessary.
Configuring dynamic IP addresses and alternate IP addressing
Although most servers have static IP addresses, you can configure servers to use dynamic addressing, alternate IP addressing, or both. You configure dynamic and alternate addressing by following these steps:
1.In Network And Sharing Center, tap or click Change Adapter Settings. In Network Connections, one LAN connection is shown for each network adapter installed. These connections are created automatically. If you don’t find a LAN connection for an installed adapter, check the driver for the adapter. It might be installed incorrectly. Press and hold or right-click the connection with which you want to work, and then tap or click Properties.
2.Double-tap or double-click Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) or Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) as appropriate for the type of IP address you are configuring.
3.Select Obtain An IPv6 Address Automatically or Obtain An IP Address Automatically as appropriate for the type of IP address you are configuring. You can select Obtain DNS Server Address Automatically, or you can select Use The Following DNS Server Addresses, and then enter a preferred and alternate DNS server address in the text boxes provided.
4.When you use dynamic IPv4 addressing, you can configure an automatic alternate address or manually configure the alternate address. To use an automatic configuration, on the Alternate Configuration tab, select Automatic Private IP Address. Tap or click OK, tap or click Close, and then skip the remaining step.
5.To use a manual configuration, on the Alternate Configuration tab, select User Configured, and then enter the IP address you want to use in the IP Address text box. The IP address you assign to the computer should be a private IP address, as shown earlier in Table 7–1, and it must not be in use anywhere else when the settings are applied. Complete the alternate configuration by entering a subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server, and Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) settings. When you have finished, tap or click OK, and then tap or click Close.
Configuring multiple gateways
To provide fault tolerance in case of a router outage, you can choose to configure Windows Server 2012 R2 computers so that they use multiple default gateways. When you assign multiple gateways, Windows Server 2012 R2 uses the gateway metric to determine which gateway is used and at what time. The gateway metric indicates the routing cost of using a gateway. The gateway with the lowest routing cost, or metric, is used first. If the computer can’t communicate with this gateway, Windows Server 2012 R2 tries to use the gateway with the next lowest metric.
The best way to configure multiple gateways depends on the configuration of your network. If your organization’s computers use DHCP, you probably want to configure the additional gateways through settings on the DHCP server. If computers use static IP addresses or you want to set gateways specifically, assign them by following these steps:
1.In Network And Sharing Center, tap or click Change Adapter Settings. In Network Connections, press and hold or right-click the connection with which you want to work, and then tap or click Properties.
2.Double-tap or double-click Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) or Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) as appropriate for the type of IP address you are configuring.
3.Tap or click Advanced to open the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box, shown in Figure 7–4.
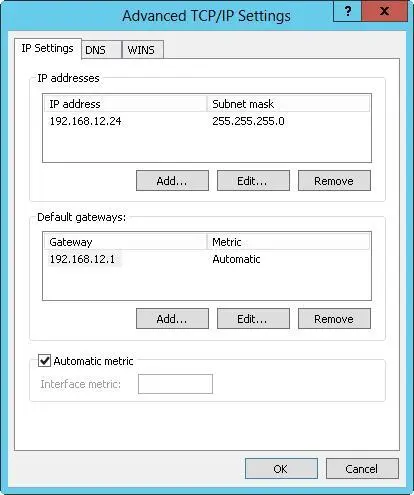
FIGURE 7–4Configure multiple IP addresses and gateways in the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box.
4.The Default Gateways panel shows the current gateways that have been manually configured (if any). You can enter additional default gateways as necessary.
Читать дальше







