Thomas Buick - The Treaty of Waitangi; or, how New Zealand became a British Colony
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Thomas Buick - The Treaty of Waitangi; or, how New Zealand became a British Colony» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, foreign_prose, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The Treaty of Waitangi; or, how New Zealand became a British Colony
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
The Treaty of Waitangi; or, how New Zealand became a British Colony: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The Treaty of Waitangi; or, how New Zealand became a British Colony»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The Treaty of Waitangi; or, how New Zealand became a British Colony — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «The Treaty of Waitangi; or, how New Zealand became a British Colony», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
This state of official negation continued until the tidings of the part played by Captain Stewart and his brig Elizabeth in Te Rauparaha's Akaroa raid reached Sydney. Then Governor Darling and his successor, Sir Richard Bourke, realised that this game of glorified bluff could not go on indefinitely. The strongest possible representations were accordingly made to the Home authorities, and these representations were followed by a pathetic petition from the natives to King William IV., which was transmitted to Sir Richard Bourke through Mr. Yate, one of the principal members of the Church Missionary Society's staff then labouring in the colony.
The leading chiefs of the northern part of the Islands had long ere this realised the ineffectiveness of their tribal system to cope with the altered state of society. The Missionaries on their part watched with anxiety the unhappy trend of affairs, knowing that if some more enlightened course was not given to events, a serious collision would in all probability arise between the two races, which could scarcely terminate otherwise than in the extermination or expulsion of the one or the other.
Being fully persuaded that to maintain the chiefs and their tribes as an independent people was the most effective safeguard against foreign aggression, they saw with deepest regret the intestine warfare which was going on amongst the natives, thinning their ranks, and rendering them every day less able to resist the pretensions of a foreign power. Stung by a sense of failure, and excited by a rumour that the French were at hand, the chiefs placed themselves under Missionary direction and addressed themselves to the King in the following diplomatic terms 7 7 Petition sent to King William through Mr. Yate, per Colonial Secretary of New South Wales, November 16, 1831.
: —
King William – We, the chiefs of New Zealand assembled at this place, called the Kerikeri, write to thee, for we hear that thou art the great Chief of the other side of the water, since the many ships which come to our land are from thee.
We are a people without possessions. We have nothing but timber, flax, pork and potatoes, we sell these things, however, to your people, and then we see the property of Europeans. It is only thy land which is liberal towards us. From thee also come the Missionaries who teach us to believe on Jehovah God, and on Jesus Christ His Son.
We have heard that the tribe of Marian 8 8 The French were called by the natives "the tribe of Marian" after Captain Marian du Fresne, who met his untimely death at their hands in 1772. To show that these fears were not altogether unfounded, it may be mentioned that the French ship La Favourite anchored in the Bay of Islands the day after the petition was signed.
is at hand coming to take away our land, therefore we pray thee to become our friend and guardian of these Islands, lest through the teazing of other tribes should come war to us, and lest strangers should come and take away our land. And if any of thy people should be troublesome or vicious towards us (for some persons are living here who have run away from ships), we pray thee to be angry with them that they may be obedient, lest the anger of the people of this land fall upon them.
This letter is from us the chiefs of the natives of New Zealand:
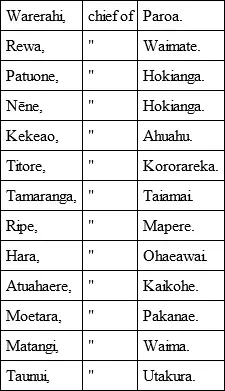
The accumulating reports of increasing disorder, the strenuous recommendations of Governor Bourke, added to the touching appeal of the chiefs, at length moved the Colonial Office to acquiesce in the contention that some one should be sent to New Zealand directly charged with the duty of representing the British Crown. In replying to the Native petition, Lord Goderich, 9 9 He afterwards became Earl of Ripon.
who was then at the Colonial Office, after expressing the gratification the petition had afforded the King, accordingly intimated that it had been decided to appoint as British Resident Mr. James Busby, whose duty it would be to investigate all complaints which might be made to him. "It will also be his endeavour," wrote his Lordship, "to prevent the arrival amongst you of men who have been guilty of crimes in their own country, and who may effect their escape from the place to which they have been banished, as likewise to apprehend such persons of this description who may be found at present at large. In return for the anxious desire which will be manifested by the British Resident to afford his protection to the inhabitants of New Zealand, against any acts of outrage which may be attempted against them by British subjects, it is confidently expected by His Majesty that on your part you will render to the British Resident that assistance and support which are calculated to promote the objects of his appointment, and to extend to your country all the benefits which it is capable of receiving from its friendship and alliance with Great Britain."
Mr. Busby, who had thus been chosen for the responsible task of guarding both British and Native interests, was the son of a successful civil engineer in Australia, but it is doubtful whether he had passed through the administrative experience necessary to fit him in all respects for his arduous post. 10 10 Mr. Busby's father had been appointed in 1823 as a Mineral Surveyor and Civil Engineer for the colony of New South Wales, by Earl Bathurst, and Mr. Busby accompanied him as a settler, taking with him capital to the extent of about £1000. At the time of his appointment Mr. Busby was Collector of Internal Revenue and a Member of the Land Board of New South Wales.
His position was rendered still more difficult by reason of the fact that, much as Ministers might have wished to do so, it had been found impossible to sweep away the constitutional difficulties which faced them on every side. Indeed so hampered was the situation by the circumstance that Britain had not acquired, or claimed Sovereign rights in New Zealand, that when Governor Bourke came to direct Mr. Busby upon the scope of his office, he was compelled to lay greater stress upon the things he could not do, than upon the powers he was at liberty to exercise.
Mr. Busby was instructed to leave Sydney by H.M.S. Imogene , commanded by Captain Blackwood, and on arrival at the Bay of Islands he was to present to the chiefs the King's reply to their petition, "with as much formality as circumstances may permit." This instruction Mr. Busby used his best endeavours to obey, for after a stormy passage across the Tasman Sea he reached the Bay of Islands on Sunday, May 5, 1833. Here he at once made arrangements with the settlers and Missionaries to invest his landing with an importance which was its due; but continued storms made it impossible to perform any kind of open-air ceremony with comfort and dignity until the 17th. On that day, however, the weather had moderated, and at an early hour preparations were afoot for the inevitable feast, a proclivity to which both Maori and European appear equally addicted. At a later hour Mr. Busby, accompanied by the first lieutenant of the Imogene , landed under a salute of seven guns, and no sooner had he set foot on shore than he was claimed by the old chief, Tohitapu, as his Pakeha . A cordial greeting awaited the Resident by the Missionaries, to whose village at Paihia, but a short distance off, the party at once adjourned. Here three hoary-headed chiefs delivered speeches of welcome, a haka was danced, and still more speeches were made in honour of a stranger whose coming was regarded as the event of first importance since the landing of Samuel Marsden seventeen years before. With these evidences of native hospitality at an end, the formal proceedings were commenced in front of the little mission chapel round which the people crowded in motley throng, shouting songs of welcome, and discharging fitful volleys of musketry. By dint of lively exertion order was at length restored, and standing at a table, with Captain Blackwood on his right and Mr. Henry Williams, who interpreted, on his left, Mr. Busby read the King's reply to the people's Petition for protection. The reading of this document was listened to with profound respect by the Europeans, who rose and uncovered their heads, while the natives hung upon the words of Mr. Williams as he explained the professions of the King's good-will, of the sincerity of which Mr. Busby was a living evidence. Then followed Mr. Busby's own address, which was listened to by the wondering crowd with no less rapt attention:
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «The Treaty of Waitangi; or, how New Zealand became a British Colony»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «The Treaty of Waitangi; or, how New Zealand became a British Colony» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «The Treaty of Waitangi; or, how New Zealand became a British Colony» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












