Henry Fishwick - A History of Lancashire
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Henry Fishwick - A History of Lancashire» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, foreign_prose, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:A History of Lancashire
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
A History of Lancashire: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «A History of Lancashire»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A History of Lancashire — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «A History of Lancashire», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Clitheroe Castle, though perhaps never a very extensive fortification, is one of the oldest foundations in the county, probably dating back to Saxon times. It stands in a commanding situation on the summit of a rock rising out of the plain, about a mile from Pendle Hill; in Domesday Book it is described as the Castle of Roger (Roger de Lacy). Of the original building nothing is now left but the keep, a square tower of small dimensions. The honour dependent upon this castle extended over a very large area, part only of which is in Lancashire; it included Whalley, Blackburn, Chipping, Ribchester, Tottington (in Salford Hundred), and Rochdale, and consequently the manors of all these places were at one time held of the castle of Clitheroe. Henry de Lacy, second Earl of Lincoln and great–grandson of Roger de Lacy, was born in 1250, and, like his ancestor, he made this castle his Lancashire stronghold and residence, and here each year his tenants and the stewards of the various manors attended his courts to render in their accounts and offer the suit and service required. The town of Clitheroe must, on the occasions when the Earl was at the castle, have put on a festive appearance, as the lord of the honour is said to have assumed an almost regal state. Several of the accounts of the stewards, parkers, and other servants of the Earl have fortunately been preserved, and we are by them enabled to get a glimpse at the social life of the Lancashire people between the years 1295 and 1305. 81We find that, besides the forests of Pendle, Accrington, Rossendale and Trawden, there were parks at Ightenhill and Musbury, well stocked with deer. There were over twenty vaccaries, or breeding farms, all of which added to the Earl’s income. On the estates were iron forges, and iron smelting was practised, and of course coal was dug up from the seams lying near the surface.
The following extracts from these rolls will serve to illustrate the historical value of the details furnished. 82Full allowance must be made by the reader for the difference in value of money between the thirteenth and the nineteenth centuries; 83and it must be remembered that labourers in addition to their wages generally received rations, and were sometimes housed.
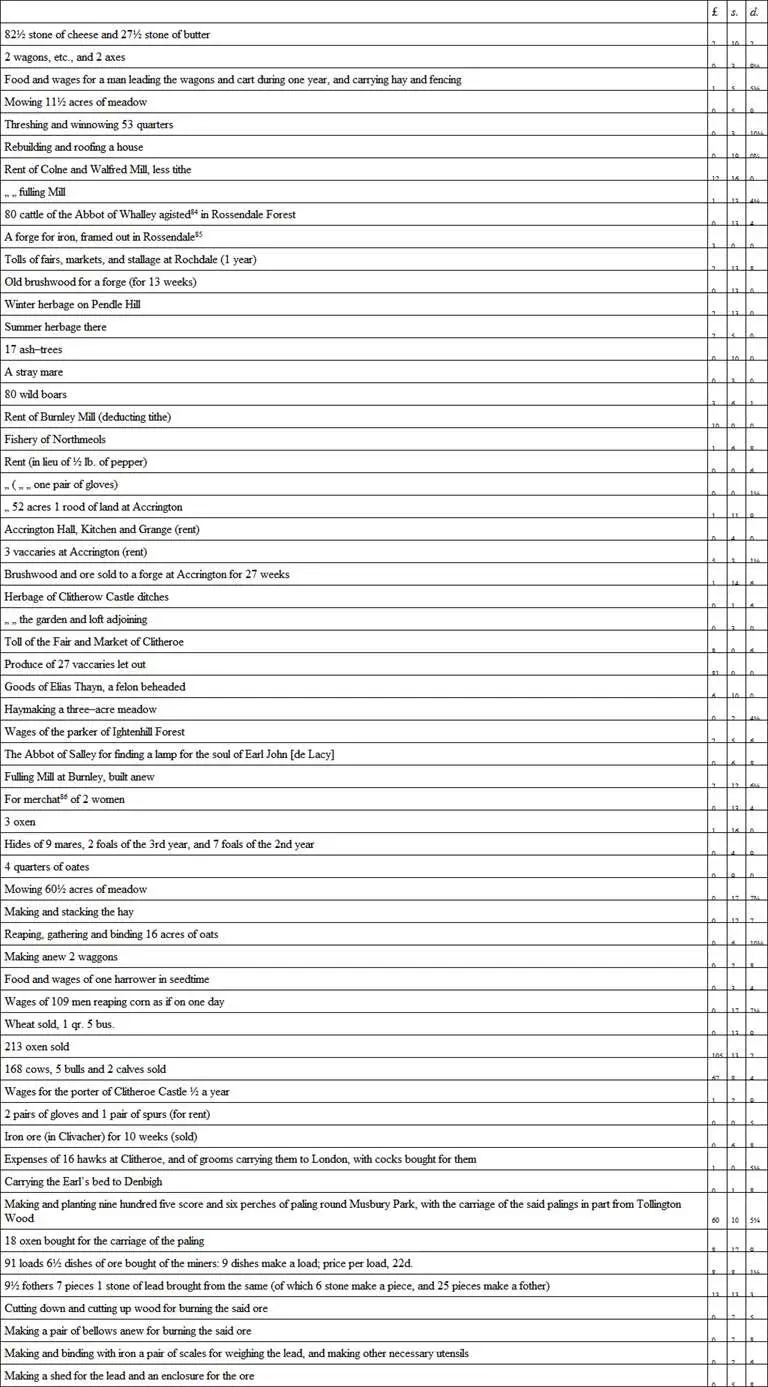
84 Agisted = allowed to graze in the forest.
85 In 1338 the Abbot of Whalley charged certain persons armed “with swords and bows and arrows” with having taken away his goods, and, inter alia , 300 pieces of iron, and from the evidence adduced it appears that near Whitworth (in Rochdale parish), which is adjoining Rossendale, the Abbot and others were accustomed to dig up the ironstone and smelt it. (See Fishwick’s “History of Rochdale,” p. 84.)
86 Merchats = fines paid to the lord for marriage of a daughter. The above sum was the sum returned to the tenant because it was found that the women were not daughters of villeins.
From these references to smelting of lead it is quite clear that the operation was being performed here for the first time – probably as an experiment; but where did the ore come from? A reference is made to carrying ore from Baxenden (near Accrington) to Bradford (in Salford), but there is no evidence that lead was ever worked or discovered there, so probably the ore was imported from some lead–mining district.
Sea–coal ( carbones maris ) is thrice mentioned as being paid for in the Cliviger and Colne district, where it had no doubt been dug up.
The Compotus of the Earl of Lincoln contains many details referring to the various vaccaries in his holding; each of these was looked after by an instaurator , or bailiff, who lived generally at the Grange, whilst his various assistants occupied the humbler “booths.” Accrington vaccary may be accepted as a sample; there were there when the stock was taken on January 26, 1297, 106 cows, 3 bulls, 24 steers, 24 heifers, 31 yearlings, and 46 calves.
In this, as in all the other vaccaries, many cattle died from murrain, and some fell victims to the wolves which infested all the forests.
Toward the end of the year 1349 Lancashire was visited with the pestilence known as the Black Death, which about this time broke out again and again in almost every part of the civilized world. By a fortunate accident a record of the dreadful ravages made by this disease in the Hundred of Amounderness has been preserved.
It appears that the Archdeacon of Richmond (in whose jurisdiction was the whole of Lancashire north of the Ribble) and Adam de Kirkham, Dean of Amounderness, his Proctor, had a dispute relative to the fees for the probate of wills and the administration of the effects of persons dying intestate; the matter was referred to a jury of laymen, whose report furnishes a return of the number of deaths from the plague, and other details which may be accepted as at all events fairly correct, although the district must have been at the time in such a state of panic as to render the collection of statistical facts extremely difficult.
In ten parishes in Amounderness, 13,180 died between September 8, 1349, and January 11, 1349–50, and nine benefices were vacant in consequence. The chapel of the hospital of St. Mary Magdalen at Preston was without a priest for eight weeks, and in that town 3,000 men and women perished; of these, 300 had goods worth £5, and left wills, but 200 others with the like property made no wills. At Poulton–le–Fylde the deaths amounted to 800; at Lancaster 3,000 died, at Garstang 2,000, and at Kirkham 3,000, whilst the other less thickly populated places each lost more or less of its inhabitants. 87How the rest of Lancashire fared under this dreadful visitation is uncertain, but Manchester and a few other places in the south of the county are said to have suffered very heavily.
We have already seen that Edmund Crouchback, the favourite son of the King, had given to him the honour of Lancaster, which was confirmed by Henry III., who granted (in 1267) to him the castle of Kenilworth, the castle and manor of Monmouth, and other territories in various parts of the kingdom. The founder of the house of Lancaster died at Bayonne in May, 1296, and Thomas, his eldest son, succeeded to his vast possessions in Lancashire and elsewhere; and in 1297–98 he passed through the county in company with his royal master on his way to Scotland; in 1310 he married Alice, the sole daughter of Henry de Lacy, Earl of Lincoln, and then got possession of the great estates in the county which had for several generations belonged to the De Lacy family.
In 1316–17 one of the followers of the Earl of Lancaster, in order, it is said, to ingratiate himself with the King, invaded some of the possessions of the Earl, and the result was a pitched battle, which took place near Preston, in which Banastre and his army were completely defeated.
The subsequent quarrel between this celebrated Earl of Lancaster and the King is well known, and need not be repeated here; finding himself unable to meet the royal forces, he retired to his castle at Pontefract, where he was ultimately retained as a prisoner, and near to which town, after suffering great indignities and insults, he was executed as a traitor, March 22, 1321–22. Thomas, Earl of Lancaster, was succeeded by Henry his brother, who, on the reversion of the attainder of the latter, had granted to him, in A.D. 1327, the issues and arrearages of the lands, etc., which had belonged to the earldom of Lancaster and Leicester. On the death of Henry, Earl of Lancaster, the title went to his son Henry (called Grismond), who became Earl of Lancaster, Derby, and Lincoln, and was, as a crowning honour, for his distinguished military services, created in 1353 the first Duke of Lancaster, for his life, having his title confirmed by the prelates and peers assembled in Parliament at Westminster. He was empowered to hold a chancery court for Lancaster, and to issue writs there under his own seal, and to enjoy the same liberties and regalities as belonged to a county palatine, 88in as ample manner as the Earl of Chester had within that county. Henry, who for his deeds of piety was styled “the Good Duke of Lancaster,” obtained a license to go to Syracuse to fight against the infidels there; but being taken prisoner in Germany, he only regained his liberty by the payment of a heavy fine. Towards the close of his life he lived in great state in his palace of Savoy, and became a great patron to several religious houses, one of which was Whalley Abbey (see Chapter IX. Конец ознакомительного фрагмента. Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес». Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес. Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.
). He died March 24, 1360–61, leaving two daughters, one of whom (Blanch) was married to John of Gaunt, Earl of Richmond, fourth son of Edward III.; and to her he bequeathed his Lancashire possessions, and on the death of her sister Maud, the widow of the Duke of Bavaria, in A.D. 1362, without issue, she became entitled to the remainder of the vast estates of her late father.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «A History of Lancashire»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «A History of Lancashire» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «A History of Lancashire» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












