John Ruskin - Lectures on Architecture and Painting, Delivered at Edinburgh in November 1853
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «John Ruskin - Lectures on Architecture and Painting, Delivered at Edinburgh in November 1853» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, foreign_home, architecture_book, literature_19, visual_arts, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Lectures on Architecture and Painting, Delivered at Edinburgh in November 1853
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Lectures on Architecture and Painting, Delivered at Edinburgh in November 1853: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Lectures on Architecture and Painting, Delivered at Edinburgh in November 1853»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Lectures on Architecture and Painting, Delivered at Edinburgh in November 1853 — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Lectures on Architecture and Painting, Delivered at Edinburgh in November 1853», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
20. Such being the state of the case with respect to tower-building in general, let me follow for a few minutes the changes which occur in the towers of northern and southern architects.
Many of us are familiar with the ordinary form of the Italian bell-tower or campanile. From the eighth century to the thirteenth there was little change in that form: 8four-square, rising high and without tapering into the air, story above story, they stood like giants in the quiet fields beside the piles of the basilica or the Lombardic church, in this form ( fig. 9), tiled at the top in a flat gable, with open arches below, and fewer and fewer arches on each inferior story, down to the bottom. It is worth while noting the difference in form between these and the towers built for military service. The latter were built as in fig. 10, projecting vigorously at the top over a series of brackets or machicolations, with very small windows, and no decoration below. Such towers as these were attached to every important palace in the cities of Italy, and stood in great circles—troops of towers—around their external walls: their ruins still frown along the crests of every promontory of the Apennines, and are seen from far away in the great Lombardic plain, from distances of half-a-day's journey, dark against the amber sky of the horizon. These are of course now built no more, the changed methods of modern warfare having cast them into entire disuse; but the belfry or campanile has had a very different influence on European architecture. Its form in the plains of Italy and South France being that just shown you, the moment we enter the valleys of the Alps, where there is snow to be sustained, we find its form of roof altered by the substitution of a steep gable for a flat one. 9There are probably few in the room who have not been in some parts of South Switzerland, and who do not remember the beautiful effect of the gray mountain churches, many of them hardly changed since the tenth and eleventh centuries, whose pointed towers stand up through the green level of the vines, or crown the jutting rocks that border the valley.
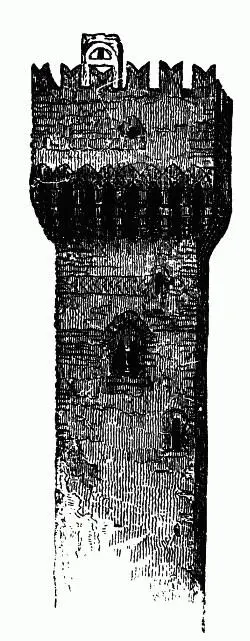
Fig. 10.
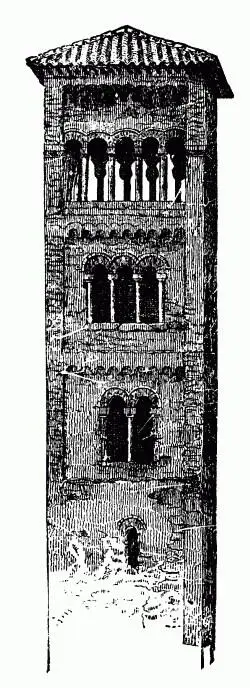
Fig. 9.
PLATE VI.
21. From this form to the true spire the change is slight, and consists in little more than various decoration; generally in putting small pinnacles at the angles, and piercing the central pyramid with traceried windows; sometimes, as at Fribourg and Burgos, throwing it into tracery altogether: but to do this is invariably the sign of a vicious style, as it takes away from the spire its character of a true roof, and turns it nearly into an ornamental excrescence. At Antwerp and Brussels, the celebrated towers (one, observe, ecclesiastical, being the tower of the cathedral, and the other secular), are formed by successions of diminishing towers, set one above the other, and each supported by buttresses thrown to the angles of the one beneath. At the English cathedrals of Lichfield and Salisbury, the spire is seen in great purity, only decorated by sculpture; but I am aware of no example so striking in its entire simplicity as that of the towers of the cathedral of Coutances in Normandy. There is a dispute between French and English antiquaries as to the date of the building, the English being unwilling to admit its complete priority to all their own Gothic. I have no doubt of this priority myself; and I hope that the time will soon come when men will cease to confound vanity with patriotism, and will think the honor of their nation more advanced by their own sincerity and courtesy, than by claims, however learnedly contested, to the invention of pinnacles and arches. I believe the French nation was, in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries, the greatest in the world; and that the French not only invented Gothic architecture, but carried it to a perfection which no other nation has approached, then or since: but, however this may be, there can be no doubt that the towers of Coutances, if not the earliest, are among the very earliest, examples of the fully developed spire. I have drawn one of them carefully for you ( fig. 11), and you will see immediately that they are literally domestic roofs, with garret windows, executed on a large scale, and in stone. Their only ornament is a kind of scaly mail, which is nothing more than the copying in stone of the common wooden shingles of the house-roof; and their security is provided for by strong gabled dormer windows, of massy masonry, which, though supported on detached shafts, have weight enough completely to balance the lateral thrusts of the spires. Nothing can surpass the boldness or the simplicity of the plan; and yet, in spite of this simplicity, the clear detaching of the shafts from the slope of the spire, and their great height, strengthened by rude cross-bars of stone, carried back to the wall behind, occasion so great a complexity and play of cast shadows, that I remember no architectural composition of which the aspect is so completely varied at different hours of the day. 10But the main thing I wish you to observe is, the complete domesticity of the work; the evident treatment of the church spire merely as a magnified house-roof; and the proof herein of the great truth of which I have been endeavoring to persuade you, that all good architecture rises out of good and simple domestic work; and that, therefore, before you attempt to build great churches and palaces, you must build good house doors and garret windows.
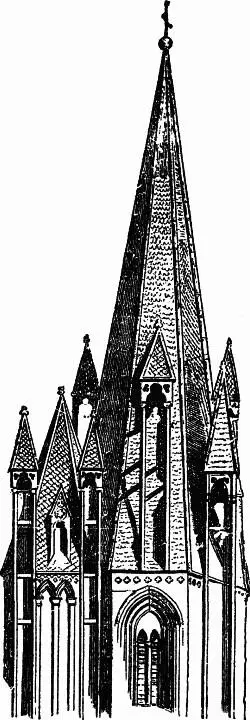
Fig. 11.
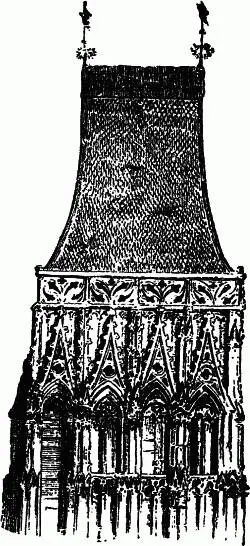
Fig. 12.
PLATE VII.
22. Nor is the spire the only ecclesiastical form deducible from domestic architecture. The spires of France and Germany are associated with other towers, even simpler and more straightforward in confession of their nature, in which, though the walls of the tower are covered with sculpture, there is an ordinary ridged gable roof on the top. The finest example I know of this kind of tower, is that on the north-west angle of Rouen Cathedral ( fig. 12); but they occur in multitudes in the older towns of Germany; and the backgrounds of Albert Dürer are full of them, and owe to them a great part of their interest: all these great and magnificent masses of architecture being repeated on a smaller scale by the little turret roofs and pinnacles of every house in the town; and the whole system of them being expressive, not by any means of religious feeling, 11but merely of joyfulness and exhilaration of spirit in the inhabitants of such cities, leading them to throw their roofs high into the sky, and therefore giving to the style of architecture with which these grotesque roofs are associated, a certain charm like that of cheerfulness in a human face; besides a power of interesting the beholder which is testified, not only by the artist in his constant search after such forms as the elements of his landscape, but by every phrase of our language and literature bearing on such topics. Have not these words, Pinnacle, Turret, Belfry, Spire, Tower, a pleasant sound in all your ears? I do not speak of your scenery, I do not ask you how much you feel that it owes to the gray battlements that frown through the woods of Craigmillar, to the pointed turrets that flank the front of Holyrood, or to the massy keeps of your Crichtoun and Borthwick and other border towers. But look merely through your poetry and romances; take away out of your border ballads the word tower wherever it occurs, and the ideas connected with it, and what will become of the ballads? See how Sir Walter Scott cannot even get through a description of Highland scenery without help from the idea:—
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Lectures on Architecture and Painting, Delivered at Edinburgh in November 1853»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Lectures on Architecture and Painting, Delivered at Edinburgh in November 1853» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Lectures on Architecture and Painting, Delivered at Edinburgh in November 1853» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












![John Bruce - The Lettsomian Lectures on Diseases and Disorders of the Heart and Arteries in Middle and Advanced Life [1900-1901]](/books/749387/john-bruce-the-lettsomian-lectures-on-diseases-and-disorders-of-the-heart-and-arteries-in-middle-and-advanced-life-1900-1901-thumb.webp)