Nicolas Besson - Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Nicolas Besson - Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit» весь текст электронной книги совершенно бесплатно (целиком полную версию без сокращений). В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Город: Redmond, Год выпуска: 2008, Издательство: Microsoft, Жанр: Руководства, ОС и Сети, Программы, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit
- Автор:
- Издательство:Microsoft
- Жанр:
- Год:2008
- Город:Redmond
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit — читать онлайн бесплатно полную книгу (весь текст) целиком
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Regardless of the shell, you can implement power management functions in your device drivers and applications to control energy usage. The default Power Manager implementation covers the typical needs, but OEMs with special requirements add custom logic. The Power Manager source code is included with Windows Embedded CE. The power management framework is flexible and supports any number of custom system power states that can map device power states by means of registry settings.
Key Terms
Do you know what these key terms mean? You can check your answers by looking up the terms in the glossary at the end of the book.
■ ILTiming
■ Kiosk Mode
■ Synchronization Objects
■ Power Manager
■ RequestDeviceNotifications
Suggested Practices
Complete the following tasks to help you successfully master the exam objectives presented in this chapter:
Use the ILTiming and OSBench Tools
Use Iltiming and OSBench on the emulator device to examine the emulated ARMV4 processor's performance.
Implement a Custom Shell
Customize the look and feel of the target device by using Task Manager, included in Windows Embedded CE with source code, to replace the shell.
Experiment with Multithreaded Applications and Critical Sections
Use critical section objects in a multithreaded application to protect access to a global variable. Complete the following tasks:
1. Create two threads in the main code of the applications and in the thread functions wait two seconds (Sleep(2000)) and three seconds (Sleep(3000)) in an infinite loop. The primary thread of the application should wait until both threads exit by using the WaitForMultipleObjects function.
2. Create a global variable and access it from both threads. One thread should write to the variable and the other thread should read the variable. By accessing the variable before and after the first Sleep and displaying the values, you should be able visualize concurrent access.
3. Protect access to the variable by using a CriticalSection object shared between both threads. Grab the critical section at the beginnings of the loops and release it at the ends of the loops. Compare the results with the previous output.
Chapter 4
Debugging and Testing the System
Debugging and system testing are vital tasks during the software-development cycle, with the ultimate goal to identify and solve software-related and hardware-related defects on a target device. Debugging generally refers to the process of stepping through the code and analyzing debug messages during code execution in order to diagnose root causes of errors. It can also be an efficient tool to study the implementation of system components and applications in general. System testing, on the other hand, is a quality-assurance activity to validate the system in its final configuration in terms of typical usage scenarios, performance, reliability, security, and any other relevant aspects. The overall purpose of system testing is to discover product defects and faults, such as memory leaks, deadlocks, or hardware conflicts, whereas debugging is a means to get to the bottom of these problems and eliminate them. For many developers of small-footprint and consumer devices, locating and eliminating system defects is the hardest part of software development, with a measurable impact on productivity. This chapter covers the debugging and testing tools available in Microsoft® Visual Studio® 2005 with Platform Builder for Microsoft Windows® Embedded CE 6.0 R2 and in the Windows Embedded CE Test Kit (CETK) to help you automate and accelerate these processes so that you can release your systems faster and with fewer bugs. The better you master these tools, the more time you can spend writing code instead of fixing code.
Exam objectives in this chapter:
■ Identifying requirements for debugging a run-time image
■ Using debugger features to analyze code execution
■ Understanding debug zones to manage the output of debug messages
■ Utilizing the CETK tool to run default and user-defined tests
■ Debugging the boot loader and operating system (OS)
To complete the lessons in this chapter, you must have the following:
■ At least some basic knowledge about Windows Embedded CE software development and debugging concepts.
■ A basic understanding of the driver architectures supported in Windows Embedded CE.
■ Familiarity with OS design and system configuration concepts.
■ A development computer with Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 Service Pack 1 and Platform Builder for Windows Embedded CE 6.0 R2 installed.
Lesson 1: Detecting Software-Related Errors
Software-related errors range from simple typos, uninitialized variables, and infinite loops to more complex and profound issues, such as critical race conditions and other thread synchronization problems. Fortunately, the vast majority of errors are easy to fix once they are located. The most cost-effective way to find these errors is through code analysis. You can use a variety of tools on Windows Embedded CE devices to debug the operating system and step through drivers and applications. A good understanding of these debugging tools will help you accelerate your code analysis so that you can fix software errors as efficiently as possible.
After this lesson, you will be able to:
■ Identify important debugging tools for Windows Embedded CE.
■ Control debug messages through debug zones in drivers and applications.
■ Use the target control shell to identify memory issues.
Estimated lesson time: 90 minutes.
Debugging and Target Device Control
The primary tool to debug and control a Windows Embedded CE target device is by using Platform Builder on the development workstation, as illustrated in Figure 4-1. The Platform Builder integrated development environment (IDE) includes a variety of tools for this purpose, such as a system debugger, CE target control shell (CESH), and debug message (DbgMsg) feature, that you can use to step through code after reaching a breakpoint or to display information on memory, variables, and processes. Moreover, the Platform Builder IDE includes a collection of remote tools, such as Heap Walker, Process Viewer, and Kernel Tracker, to analyze the state of the target device at run time.
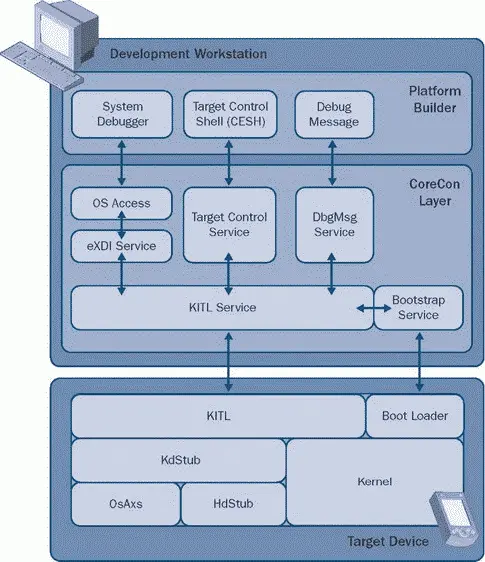
Figure 4-1CE debugging and target control architecture
In order to communicate with the target device, Platform Builder relies on the Core Connectivity (CoreCon) infrastructure and debugging components deployed on the target device as part of the run-time image. The CoreCon infrastructure provides OS Access (OsAxS), target control, and DbgMsg services to Platform Builder on one side, and interfaces with the target device through the Kernel Independent Transport Layer (KITL) and the bootstrap service on the other side. On the target device itself, the debugging and target control architecture relies on KITL and the boot loader for communication purposes. If the run-time image includes debugging components, such as the kernel debugger stub (KdStub), hardware debugger stub (HdStub), and the OsAxS library, you can use Platform Builder to obtain kernel run-time information and perform just-in-time (JIT) debugging. Platform Builder also supports hardware- assisted debugging through Extended Debugging Interface (eXDI), so that you can debug target device routines prior to loading the kernel.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Microsoft Windows Embedded CE 6.0 Exam Preparation Kit» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.








