Alfred Thayer Mahan - The Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Alfred Thayer Mahan - The Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_prose, История, foreign_edu, foreign_antique, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
The Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «The Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Charleston Harbour opens between two of the sea-islands which fringe the coasts of South Carolina and Georgia. On the north is Sullivan's Island, on the south James Island. The bar of the main entrance was not abreast the mouth of the port, but some distance south of it. Inside the bar, the channel turned to the northward, and thence led near Sullivan's Island, the southern end of which was therefore chosen as the site of the rude fort hastily thrown up to meet this attack, and afterwards called Fort Moultrie, from the name of the commander. From these conditions, a southerly wind was needed to bring ships into action. After sounding and buoying the bar, the transports and frigates crossed on the 7th and anchored inside; but as it was necessary to remove some of the Bristol's guns, she could not follow until the 10th. On the 9th Clinton had landed in person with five hundred men, and by the 15th all the troops had disembarked upon Long Island, next north of Sullivan's. It was understood that the inlet between the two was fordable, allowing the troops to coöperate with the naval attack, by diversion or otherwise; but this proved to be a mistake. The passage was seven feet deep at low water, and there were no means for crossing; consequently a small American detachment in the scrub wood of the island sufficed to check any movement in that quarter. The fighting therefore was confined to the cannonading of the fort by the ships.
Circumstances not fully explained caused the attack to be fixed for the 23d; an inopportune delay, during which Americans were strengthening their still very imperfect defences. On the 23d the wind was unfavourable. On the 25th the Experiment , 50, arrived, crossed the bar, and, after taking in her guns again, was ready to join in the assault. On the 27th, at 10 A.M., the ships got under way with a south-east breeze, but this shifted soon afterwards to north-west, and they had to anchor again, about a mile nearer to Sullivan's Island. On the following day the wind served, and the attack was made.
In plan, Fort Moultrie was square, with a bastion at each angle. In construction, the sides were palmetto logs, dovetailed and bolted together, laid in parallel rows, sixteen feet apart; the interspace being filled with sand. At the time of the engagement, the south and west fronts were finished; the other fronts were only seven feet high, but surmounted by thick planks, to be tenable against escalade. Thirty-one guns were in place, 18 and 9-pounders, of which twenty-one were on the south face, commanding the channel. Within was a traverse running east and west, protecting the gunners from shots from the rear; but there was no such cover against enfilading fire, in case an enemy's ship passed the fort and anchored above it. "The general opinion before the action," Moultrie says, "and especially among sailors, was that two frigates would be sufficient to knock the town about our ears, notwithstanding our batteries." Parker may have shared this impression, and it may account for his leisureliness. When the action began, the garrison had but twenty-eight rounds for each of twenty-six cannon, but this deficiency was unknown to the British.
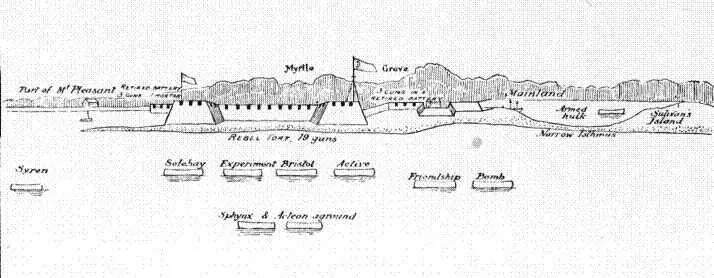
Attack on Fort Moultrie in 1776
Parker's plan was that the two 50's, Bristol and Experiment , and two 28-gun frigates, the Active and the Solebay , should engage the main front; while two frigates of the same class, the Actæon and the Syren , with a 20-gun corvette, the Sphinx , should pass the fort, anchoring to the westward, up-channel, to protect the heavy vessels against fire-ships, as well as to enfilade the principal American battery. The main attack was to be further supported by a bomb-vessel, the Thunder , accompanied by the armed transport Friendship , which were to take station to the southeast of the east bastion of the engaged front of the fort. The order to weigh was given at 10.30 A.M., when the flood-tide had fairly made; and at 11.15 the Active , Bristol , Experiment , and Solebay , anchored in line ahead, in the order named, the Active to the eastward. These ships seem to have taken their places skilfully without confusion, and their fire, which opened at once, was rapid, well-sustained, and well-directed; but their position suffered under the radical defect that, whether from actual lack of water, or only from fear of grounding, they were too far from the works to use grape effectively. The sides of ships being much weaker than those of shore works, while their guns were much more numerous, the secret of success was to get near enough to beat down the hostile fire by a multitude of projectiles. The bomb-vessel Thunder anchored in the situation assigned her; but her shells, though well aimed, were ineffective. "Most of them fell within the fort," Moultrie reported, "but we had a morass in the middle, which swallowed them instantly, and those that fell in the sand were immediately buried." During the action the mortar bed broke, disabling the piece.
Owing to the scarcity of ammunition in the fort, the garrison had positive orders not to engage at ranges exceeding four hundred yards. Four or five shots were thrown at the Active , while still under sail, but with this exception the fort kept silence until the ships anchored, at a distance estimated by the Americans to be three hundred and fifty yards. The word was then passed along the platform, "Mind the Commodore; mind the two 50-gun ships,"—an order which was strictly obeyed, as the losses show. The protection of the work proved to be almost perfect,—a fact which doubtless contributed to the coolness and precision of fire vitally essential with such deficient resources. The texture of the palmetto wood suffered the balls to sink smoothly into it without splintering, so that the facing of the work held well. At times, when three or four broadsides struck together, the merlons shook so that Moultrie feared they would come bodily in; but they withstood, and the small loss inflicted was chiefly through the embrasures. The flagstaff being shot away, falling outside into the ditch, a young sergeant, named Jasper, distinguished himself by jumping after it, fetching back and rehoisting the colours under a heavy fire.
In the squadron an equal gallantry was shown under circumstances which made severe demands upon endurance. Whatever Parker's estimate of the worth of the defences, no trace of vain-confidence appears in his dispositions, which were thorough and careful, as the execution of the main attack was skilful and vigorous; but the ships' companies, expecting an easy victory, had found themselves confronted with a resistance and a punishment as severe as were endured by the leading ships at Trafalgar, and far more prolonged. Such conditions impose upon men's tenacity the additional test of surprise and discomfiture. The Experiment , though very small for a ship of the line, lost 23 killed and 56 wounded, out of a total probably not much exceeding 300; while the Bristol , having the spring shot away, swung with her head to the southward and her stern to the fort, undergoing for a long time a raking fire to which she could make little reply. Three several attempts to replace the spring were made by Mr. James Saumarez,—afterwards the distinguished admiral, Lord de Saumarez, then a midshipman,—before the ship was relieved from this grave disadvantage. Her loss was 40 killed and 71 wounded; not a man escaping of those stationed on the quarter-deck at the beginning of the action. Among the injured was the Commodore himself, whose cool heroism must have been singularly conspicuous, from the notice it attracted in a service where such bearing was not rare. At one time when the quarter-deck was cleared and he stood alone upon the poop-ladder, Saumarez suggested to him to come down; but he replied, smiling, "You want to get rid of me, do you?" and refused to move. The captain of the ship, John Morris, was mortally wounded. With commendable modesty Parker only reported himself as slightly bruised; but deserters stated that for some days he needed the assistance of two men to walk, and that his trousers had been torn off him by shot or splinters. The loss in the other ships was only one killed, 14 wounded. The Americans had 37 killed and wounded.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «The Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «The Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «The Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












