A few weeks after my conversation with David, I met with Emir Kamenica (a professor at the University of Chicago), and Dražen Prelec (a professor at MIT) at a local coffee shop. After discussing a few different research topics, we decided to explore the effect of devaluation on motivation for work. We could have examined Large-M Meaning—that is, we could have measured the value that people who are developing a cure for cancer, helping the poor, building bridges, and otherwise saving the world every day place on their jobs. But instead, and maybe because the three of us are academics, we decided to set up experiments that would examine the effects of small-m meaning—effects that I suspect are more common in everyday life and in the workplace. We wanted to explore how small changes in the work of people like David the banker and Devra the editor affected their desire to work. And so we came up with an idea for an experiment that would test people’s reactions to small reductions in meaning for a task that did not have much meaning to start with.
ONE FALL DAY in Boston, a tall mechanical engineering student named Joe entered the student union at Harvard University. He was all ambition and acne. On a crowded bulletin board boasting flyers about upcoming concerts, lectures, political events, and roommates wanted, he caught sight of a sign reading “Get paid to build Legos!”
As an aspiring engineer, Joe had always loved building things. Drawn to anything that required assembling, Joe had naturally played with Legos throughout his childhood. When he was six years old, he had taken his father’s computer apart, and a year later, he had disassembled the living room stereo system. By the time he was fifteen, his penchant for taking objects apart and putting them back together again had cost his family a small fortune. Fortunately, he had found an outlet for his passion in college, and now he had the opportunity to build with Legos to his heart’s content—and get paid for it.
A few days later, at the agreed-upon time, Joe showed up to take part in our experiment. As luck would have it, he was assigned to the meaningful condition. Sean, the research assistant, greeted Joe as he entered the room, directed him to a chair, and explained the procedure to him. Sean showed Joe a Lego Bionicle—a small fighting robot—and then told Joe that his task would involve constructing this exact type of Bionicle, made up of forty pieces that had to be assembled in a precise way. Next, Sean told Joe the rules for payment. “The basic setup,” he said, “is that you will get paid on a diminishing scale for each Bionicle you assemble. For the first Bionicle, you will receive two dollars. After you finish the first one, I will ask you if you want to build another one, this time for eleven cents less, which is a dollar eighty-nine. If you say that you want to build another one, I will hand you the next one. This same process will continue in the same way, and for each additional Bionicle you build, you will get eleven cents less, until you decide that you don’t want to build any more Bionicles. At that point, you will receive the total amount of money for all the robots you’ve created. There is no time limit, and you can build Bionicles until the benefits you get no longer outweigh the costs.”
Joe nodded, eager to get started. “And one last thing,” Sean warned. “We use the same Bionicles for all of our participants, so at some point before the next participant shows up, I will have to disassemble all the Bionicles you build and place the parts back in their boxes for the next participant. Everything clear?”
Joe quickly opened the first box of plastic parts, scanned the assembly instructions, and began building his first Bionicle. He obviously enjoyed assembling the pieces and seeing the weird robotic form take shape. Once finished, he arranged the robot in a battle position and asked for the next one. Sean reminded him how much he would make for the next Bionicle ($1.89) and handed him the next box of pieces. Once Joe started working on the next Bionicle, Sean took the construction that Joe had just finished and placed it in a box below the desk where it was destined to be disassembled for the next participant.
Like a man on a mission, Joe continued building one Bionicle after another, while Sean continued storing them in the box below the table. After he’d finished assembling ten robots, Joe announced that he’d had his fill and collected his pay of $15.05. Before Joe took off, Sean asked him to answer a few questions about how much he liked Legos in general and how much he had enjoyed the task. Joe responded that he was a Lego fan, that he had really enjoyed the task, and that he would recommend it to his friends.
The next person in line turned out to be a young man named Chad, an exuberant—or perhaps overcaffeinated—premed student. Unlike Joe, Chad was assigned to a procedure that among ourselves we fondly called the “Sisyphean” condition. This was the condition we wanted to focus on.
Sean explained the terms and conditions of the study to Chad in exactly the same way he had to Joe. Chad grabbed the box, opened it, removed the Bionicle’s assembly instruction sheet, and carefully looked it over, planning his strategy. First he separated the pieces into groups, in the order in which they would be needed. Then he began assembling the pieces, moving quickly from one to another. He went about the task cheerily, finished the first Bionicle in a few minutes, and handed it to Sean as instructed. “That’s two dollars,” Sean said. “Would you like to build another one for a dollar eighty-nine?” Chad nodded enthusiastically and started working on his second robot, using the same organized approach.
We used the term “Sisyphean” as a tribute to the mythical king Sisyphus, who was punished by the gods for his avarice and trickery. Besides murdering travelers and guests, seducing his niece, and usurping his brother’s throne, Sisyphus also tricked the gods.
Before he died, Sisyphus, knowing that he was headed to the Underworld, made his wife promise to refrain from offering the expected sacrifice following his death. Once he reached Hades, Sisyphus convinced kindhearted Persephone, the queen of the Underworld, to let him return to the upper world, so that he could ask his wife why she was neglecting her duty. Of course, Persephone had no idea that Sisyphus had intentionally asked his wife not to make the sacrifice, so she agreed, and Sisyphus escaped the Underworld, refusing to return. Eventually Sisyphus was captured and carried back, and the angry gods gave him his punishment: for the rest of eternity, he was forced to push a large rock up a steep hill, in itself a miserable task. Every time he neared the top of the hill, the rock would roll backward and he would have to start over.
Of course, our participants had done nothing deserving of punishment. We simply used the term to describe the condition that the less fortunate among them experienced.
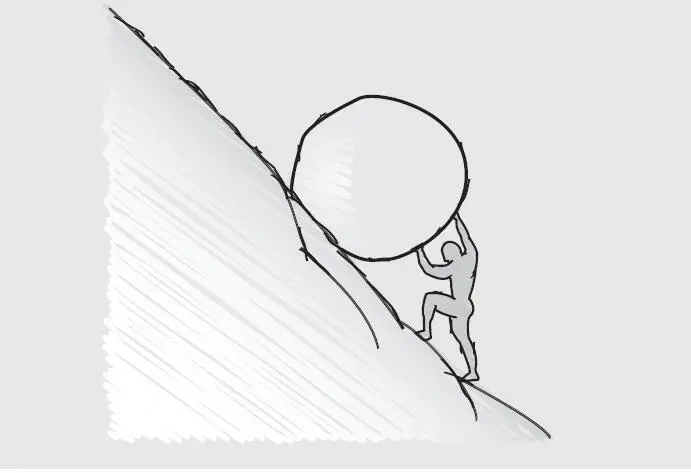
While Chad was putting together the first pieces of his next Bionicle (pay attention, because this is where the two conditions differed), Sean slowly disassembled the first Bionicle, piece by piece, and placed the pieces back into the original box.
“Why are you taking it apart?” Chad asked, looking both puzzled and dismayed.
“This is just the procedure,” Sean explained. “We need to take this one apart in case you want to build another Bionicle.”
Chad returned his attention to the robot he was building, but his energy and excitement about building Bionicles was clearly diminished. When he finished his second construction, he paused. Should he build a third Bionicle or not? After a few seconds, he said he would build another one.
Читать дальше












