France’s high command had urged the Poles to concentrate their forces behind the three big rivers in the centre of their country, but the Warsaw government deemed it essential instead to defend its entire nine-hundred-mile frontier with Germany, not least because most Polish industry lay in the west; some divisions thus became responsible for fronts of eighteen miles, when their strengths – around 15,000 men – scarcely sufficed for three or four. The three-pronged German assault, from north, south and west, drove deep into the country in the face of ineffectual resistance, leaving pockets of defenders isolated. Luftwaffe aircraft gave close support to the panzers, and also launched devastating air raids on Warsaw, Łód , D 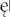 blin and Sandomierz.
blin and Sandomierz.
Polish troops and civilians were strafed and bombed with ruthless impartiality, though some victims took time to recognise the gravity of the threat. After the first wave of attacks Virgilia, American-born wife of Polish nobleman Prince Paul Sapieha, told her household reassuringly: ‘You see: these bombs aren’t so bad. Their bark is worse than their bite.’ When two bombs fell in the park of the Smorczewski family’s stately home at Tarnogóra on the night of 1 September, the young sons of the house, Ralph and Mark, were hastily dragged from their beds by their mother and rushed outside to hide in a wood with other young refugees. ‘After recovering from the initial shock,’ Ralph wrote later, ‘we looked at each other and fell into a fit of unrestrained giggles. What a strange sight we were: a motley collection of youths, some in pyjamas, others with coats thrown over their underwear, standing aimlessly under the trees, playing with gas masks. We decided to go home.’
Soon, however, there was no more giggling: the people of Poland were obliged to recognise the devastating power of the Luftwaffe. ‘I was awakened by the wail of sirens and sound of explosions,’ wrote diplomat Adam Kruczkiewicz in Warsaw. ‘Outside I saw German planes flying at incredibly low level and throwing bombs at their ease. There was some desultory machine-gun fire from the tops of a few buildings, but no Polish fliers…The city was stunned by the almost complete lack of air defence. They felt bitterly disappointed.’ The town of Łuck belied its name: early one morning a dozen German bombs fell on it, killing scores of people, most of them children walking to school. Impotent victims called the cloudless skies of those September days ‘the curse of Poland’. Pilot B.J. Solak wrote: ‘The stench of burning and a brown veil of smoke filled all the air around our town.’ After hiding his unarmed plane beneath some trees, Solak was driving home when he met a peasant on the road, ‘leading a horse whose hip was a blanket of congealed blood. Its head was touching the dust with its nostrils, each step causing it to shudder with pain.’ The young airman asked the peasant where he was taking the stricken animal, victim of a Stuka dive-bomber. ‘To the veterinary clinic in town.’ ‘But that’s four miles more!’ A shrug: ‘I have only one horse.’
A thousand larger tragedies unfolded. As Lt. Piotr Tarczy ski’s artillery battery clattered forward towards the battlefield, Stukas fell on it; every man sprang from his saddle and threw himself to the earth. A few bombs dropped, some men and horses fell. Then the planes were gone, the battery remounted and resumed its march. ‘We saw two women, one middle-aged and one only a girl, carrying a short ladder. On it was stretched a wounded man, still alive and clutching his abdomen. As they passed us, I could see his intestines trailing on the ground.’ Władysław Anders had fought with the Russians in World War I, under the exotically named Tsarist general the Khan of Nakhitchevan. Now, commanding a Polish cavalry brigade, Anders saw a teacher leading a group of her pupils to the shelter of woods. ‘Suddenly, there was the roar of an aeroplane. The pilot circled, descending to a height of fifty metres. As he dropped his bombs and fired his machine-guns, the children scattered like sparrows. The aeroplane disappeared as quickly as it had come, but on the field some crumpled and lifeless bundles of bright clothing remained. The nature of the new war was already clear.’
Thirteen-year-old George 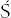 l
l 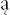 zak was on a train with a party of children travelling home to Łód from summer camp. Suddenly there were explosions, screams, and the train lurched to a stop. The group leader shouted at the boys to get out fast and run for a nearby forest. Shocked and terrified, they lay prostrate for half an hour until the bombing stopped. On emerging, a few hundred yards up the track they saw a blazing troop train which had been the Germans’ target. Some boys burst into tears at the sight of bleeding men; their first attempt to reboard their own train was frustrated by the return of the Luftwaffe, machine-gunning. At last, they resumed their journey in coaches riddled with bullet holes. George reached home to find his mother sobbing by the family radio set: it had reported Germans approaching.
zak was on a train with a party of children travelling home to Łód from summer camp. Suddenly there were explosions, screams, and the train lurched to a stop. The group leader shouted at the boys to get out fast and run for a nearby forest. Shocked and terrified, they lay prostrate for half an hour until the bombing stopped. On emerging, a few hundred yards up the track they saw a blazing troop train which had been the Germans’ target. Some boys burst into tears at the sight of bleeding men; their first attempt to reboard their own train was frustrated by the return of the Luftwaffe, machine-gunning. At last, they resumed their journey in coaches riddled with bullet holes. George reached home to find his mother sobbing by the family radio set: it had reported Germans approaching.
Pilot Franciszek Kornicki went to visit a wounded comrade in a Łód hospital: ‘It was a terrible place, full of wounded and dying men lying everywhere on beds and on the floor, in rooms and corridors, some moaning in agony, others lying silent with their eyes closed or wide open, waiting and hoping.’ Gen. Adrian Carton de Wiart, head of the British military mission in Poland, wrote bitterly: ‘I saw the very face of war change – its glory shorn, no longer the soldier setting forth into battle, but the women and children being buried under it.’
On Sunday, 3 September, Britain and France declared war on Germany, in fulfilment of their guarantees to Poland. Stalin’s alliance with Hitler caused many European communists, compliant with Moscow, to distance themselves from their nations’ stand against the Nazis. Trades unionists’ denunciations of what they branded an ‘imperialist war’ influenced attitudes in many French and British factories, shipyards and coalmines. Street graffiti appeared: ‘Stop the War: The Worker Pays’, ‘No to Capitalist War’. Independent Labour MP Aneurin Bevan, a standard-bearer of the left, hedged his bets by calling for a struggle on two fronts: against Hitler and also against British capitalism.
The secret protocols of the Nazi–Soviet Pact, delineating the parties’ territorial ambitions, were unknown in Western capitals until German archives were captured in 1945. But in September 1939, many citizens of the democracies perceived Russia and Germany alike as their foes. The novelist Evelyn Waugh’s fictional alter ego, Guy Crouchback, adopted a view shared by many European conservatives: Stalin’s deal with Hitler, ‘news that shook the politicians and young poets of a dozen capital cities, brought deep peace to one English heart…The enemy at last was plain in view, huge and hateful, all disguise cast off. It was the Modern Age in arms.’ A few politicians aspired to separate Russia and Germany, to seek the support of Stalin to defeat the greater evil of Hitler. Until June 1941, however, such a prospect seemed remote: the two dictatorships were viewed as common enemies of the democracies.
Читать дальше

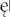 blin and Sandomierz.
blin and Sandomierz.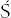 l
l 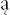 zak was on a train with a party of children travelling home to Łód from summer camp. Suddenly there were explosions, screams, and the train lurched to a stop. The group leader shouted at the boys to get out fast and run for a nearby forest. Shocked and terrified, they lay prostrate for half an hour until the bombing stopped. On emerging, a few hundred yards up the track they saw a blazing troop train which had been the Germans’ target. Some boys burst into tears at the sight of bleeding men; their first attempt to reboard their own train was frustrated by the return of the Luftwaffe, machine-gunning. At last, they resumed their journey in coaches riddled with bullet holes. George reached home to find his mother sobbing by the family radio set: it had reported Germans approaching.
zak was on a train with a party of children travelling home to Łód from summer camp. Suddenly there were explosions, screams, and the train lurched to a stop. The group leader shouted at the boys to get out fast and run for a nearby forest. Shocked and terrified, they lay prostrate for half an hour until the bombing stopped. On emerging, a few hundred yards up the track they saw a blazing troop train which had been the Germans’ target. Some boys burst into tears at the sight of bleeding men; their first attempt to reboard their own train was frustrated by the return of the Luftwaffe, machine-gunning. At last, they resumed their journey in coaches riddled with bullet holes. George reached home to find his mother sobbing by the family radio set: it had reported Germans approaching.










